Supervised Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview with Applications to Banking
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2020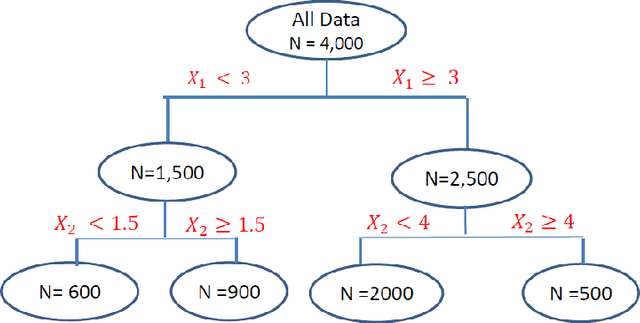
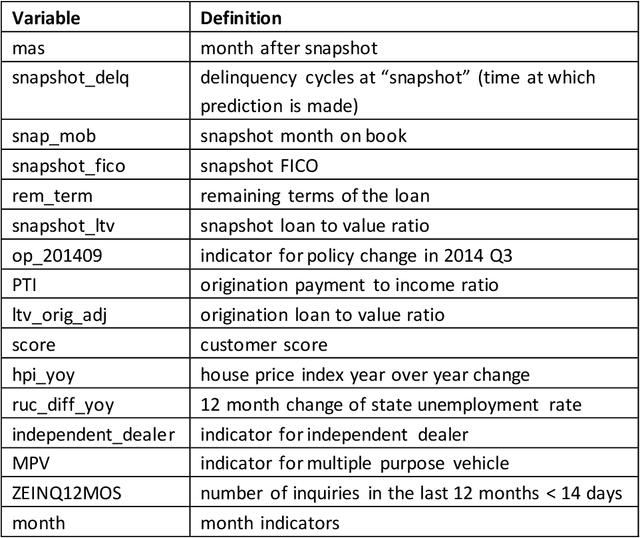
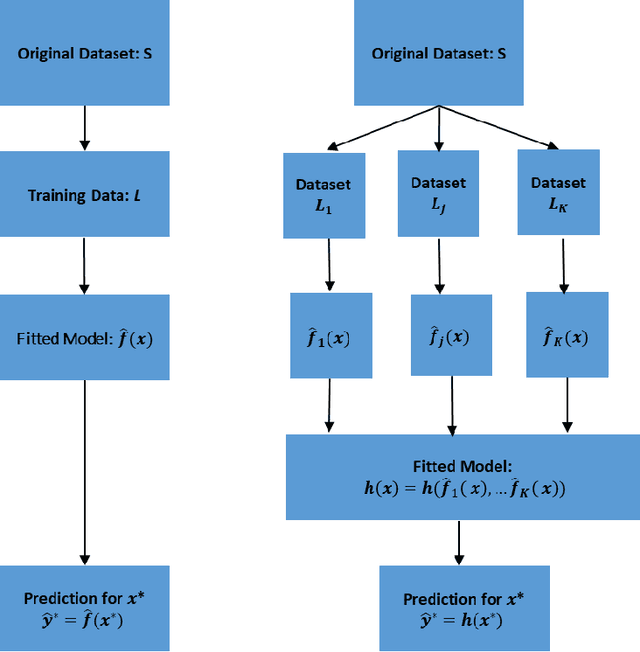
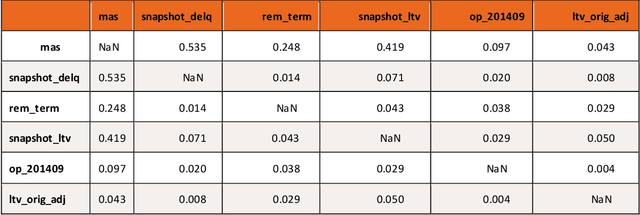
This article provides an overview of Supervised Machine Learning (SML) with a focus on applications to banking. The SML techniques covered include Bagging (Random Forest or RF), Boosting (Gradient Boosting Machine or GBM) and Neural Networks (NNs). We begin with an introduction to ML tasks and techniques. This is followed by a description of: i) tree-based ensemble algorithms including Bagging with RF and Boosting with GBMs, ii) Feedforward NNs, iii) a discussion of hyper-parameter optimization techniques, and iv) machine learning interpretability. The paper concludes with a comparison of the features of different ML algorithms. Examples taken from credit risk modeling in banking are used throughout the paper to illustrate the techniques and interpret the results of the algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge