Lingyu Gao
Harnessing the Intrinsic Knowledge of Pretrained Language Models for Challenging Text Classification Settings
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:Text classification is crucial for applications such as sentiment analysis and toxic text filtering, but it still faces challenges due to the complexity and ambiguity of natural language. Recent advancements in deep learning, particularly transformer architectures and large-scale pretraining, have achieved inspiring success in NLP fields. Building on these advancements, this thesis explores three challenging settings in text classification by leveraging the intrinsic knowledge of pretrained language models (PLMs). Firstly, to address the challenge of selecting misleading yet incorrect distractors for cloze questions, we develop models that utilize features based on contextualized word representations from PLMs, achieving performance that rivals or surpasses human accuracy. Secondly, to enhance model generalization to unseen labels, we create small finetuning datasets with domain-independent task label descriptions, improving model performance and robustness. Lastly, we tackle the sensitivity of large language models to in-context learning prompts by selecting effective demonstrations, focusing on misclassified examples and resolving model ambiguity regarding test example labels.
Ambiguity-Aware In-Context Learning with Large Language Models
Sep 14, 2023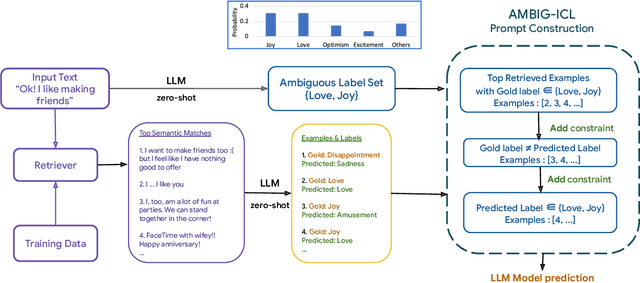
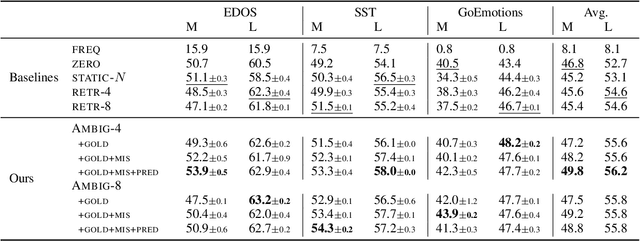
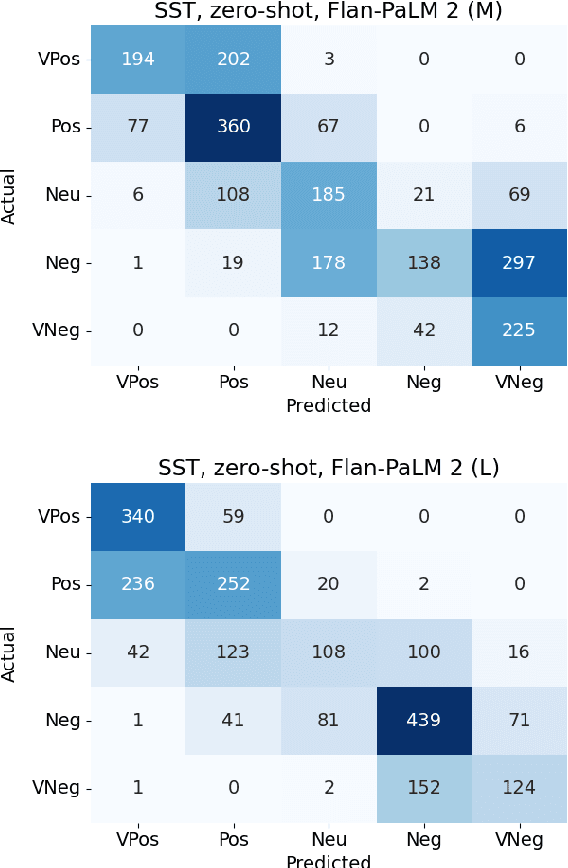
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) i.e. showing LLMs only a few task-specific demonstrations has led to downstream gains with no task-specific fine-tuning required. However, LLMs are sensitive to the choice of prompts, and therefore a crucial research question is how to select good demonstrations for ICL. One effective strategy is leveraging semantic similarity between the ICL demonstrations and test inputs by using a text retriever, which however is sub-optimal as that does not consider the LLM's existing knowledge about that task. From prior work (Min et al., 2022), we already know that labels paired with the demonstrations bias the model predictions. This leads us to our hypothesis whether considering LLM's existing knowledge about the task, especially with respect to the output label space can help in a better demonstration selection strategy. Through extensive experimentation on three text classification tasks, we find that it is beneficial to not only choose semantically similar ICL demonstrations but also to choose those demonstrations that help resolve the inherent label ambiguity surrounding the test example. Interestingly, we find that including demonstrations that the LLM previously mis-classified and also fall on the test example's decision boundary, brings the most performance gain.
ToMChallenges: A Principle-Guided Dataset and Diverse Evaluation Tasks for Exploring Theory of Mind
May 24, 2023



Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM), the capacity to comprehend the mental states of distinct individuals, is essential for numerous practical applications. With the development of large language models, there is a heated debate about whether they are able to perform ToM tasks. Previous studies have used different tasks and prompts to test the ToM on large language models and the results are inconsistent: some studies asserted these models are capable of exhibiting ToM, while others suggest the opposite. In this study, We present ToMChallenges, a dataset for comprehensively evaluating Theory of Mind based on Sally-Anne and Smarties tests. We created 30 variations of each test (e.g., changing the person's name, location, and items). For each variation, we test the model's understanding of different aspects: reality, belief, 1st order belief, and 2nd order belief. We adapt our data for various tasks by creating unique prompts tailored for each task category: Fill-in-the-Blank, Multiple Choice, True/False, Chain-of-Thought True/False, Question Answering, and Text Completion. If the model has a robust ToM, it should be able to achieve good performance for different prompts across different tests. We evaluated two GPT-3.5 models, text-davinci-003 and gpt-3.5-turbo-0301, with our datasets. Our results indicate that consistent performance in ToM tasks remains a challenge.
The Benefits of Label-Description Training for Zero-Shot Text Classification
May 03, 2023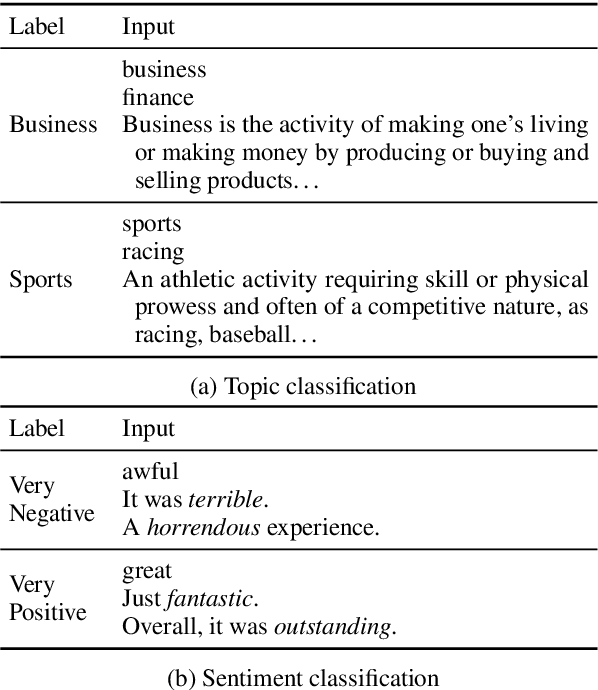
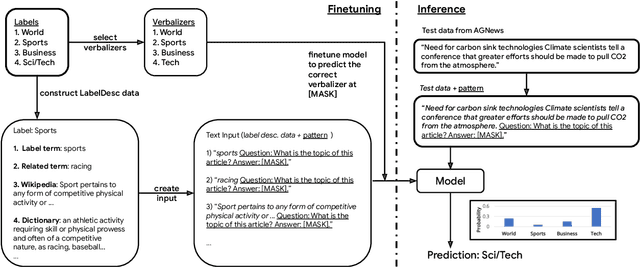
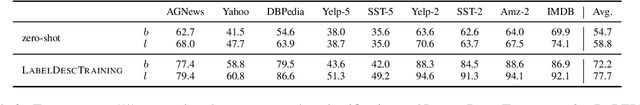
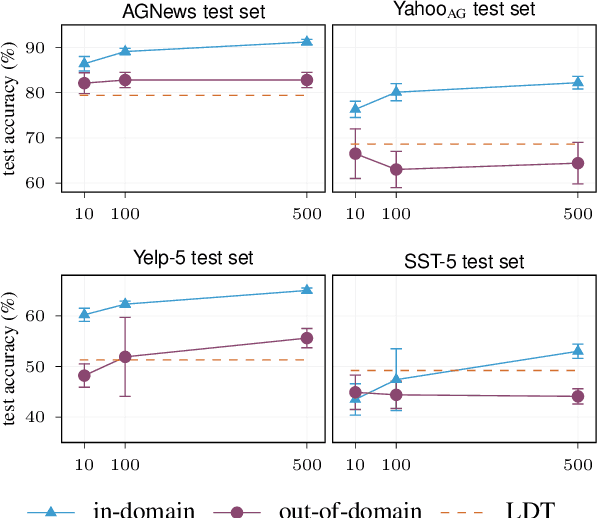
Abstract:Large language models have improved zero-shot text classification by allowing the transfer of semantic knowledge from the training data in order to classify among specific label sets in downstream tasks. We propose a simple way to further improve zero-shot accuracies with minimal effort. We curate small finetuning datasets intended to describe the labels for a task. Unlike typical finetuning data, which has texts annotated with labels, our data simply describes the labels in language, e.g., using a few related terms, dictionary/encyclopedia entries, and short templates. Across a range of topic and sentiment datasets, our method is more accurate than zero-shot by 15-17% absolute. It is also more robust to choices required for zero-shot classification, such as patterns for prompting the model to classify and mappings from labels to tokens in the model's vocabulary. Furthermore, since our data merely describes the labels but does not use input texts, finetuning on it yields a model that performs strongly on multiple text domains for a given label set, even improving over few-shot out-of-domain classification in multiple settings.
Evaluating Transformer Models and Human Behaviors on Chinese Character Naming
Mar 22, 2023Abstract:Neural network models have been proposed to explain the grapheme-phoneme mapping process in humans for many alphabet languages. These models not only successfully learned the correspondence of the letter strings and their pronunciation, but also captured human behavior in nonce word naming tasks. How would the neural models perform for a non-alphabet language (e.g., Chinese) unknown character task? How well would the model capture human behavior? In this study, we evaluate a set of transformer models and compare their performances with human behaviors on an unknown Chinese character naming task. We found that the models and humans behaved very similarly, that they had similar accuracy distribution for each character, and had a substantial overlap in answers. In addition, the models' answers are highly correlated with humans' answers. These results suggested that the transformer models can well capture human's character naming behavior.
How do we get there? Evaluating transformer neural networks as cognitive models for English past tense inflection
Oct 17, 2022



Abstract:There is an ongoing debate on whether neural networks can grasp the quasi-regularities in languages like humans. In a typical quasi-regularity task, English past tense inflections, the neural network model has long been criticized that it learns only to generalize the most frequent pattern, but not the regular pattern, thus can not learn the abstract categories of regular and irregular and is dissimilar to human performance. In this work, we train a set of transformer models with different settings to examine their behavior on this task. The models achieved high accuracy on unseen regular verbs and some accuracy on unseen irregular verbs. The models' performance on the regulars is heavily affected by type frequency and ratio but not token frequency and ratio, and vice versa for the irregulars. The different behaviors on the regulars and irregulars suggest that the models have some degree of symbolic learning on the regularity of the verbs. In addition, the models are weakly correlated with human behavior on nonce verbs. Although the transformer model exhibits some level of learning on the abstract category of verb regularity, its performance does not fit human data well, suggesting that it might not be a good cognitive model.
"What makes a question inquisitive?" A Study on Type-Controlled Inquisitive Question Generation
May 19, 2022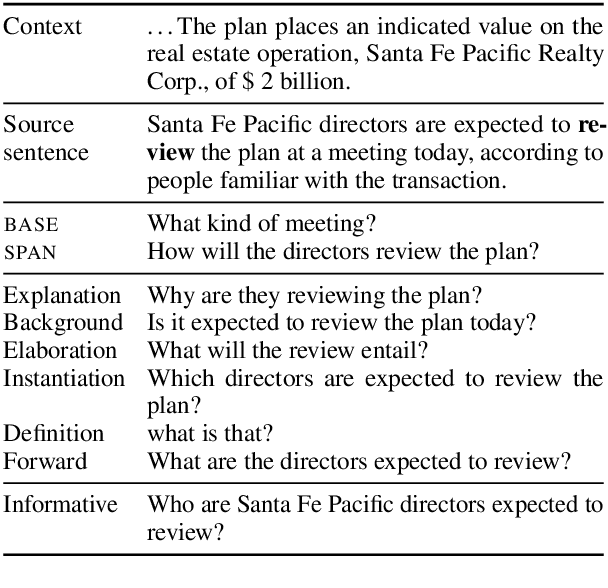
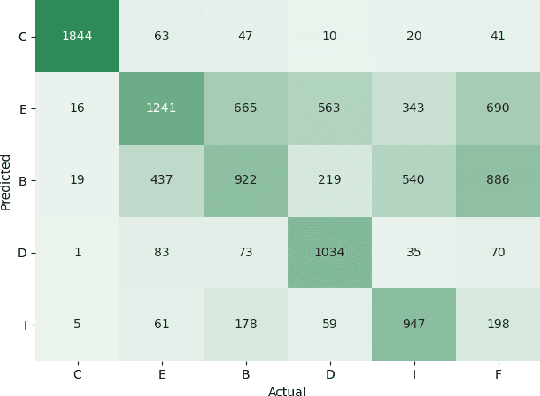
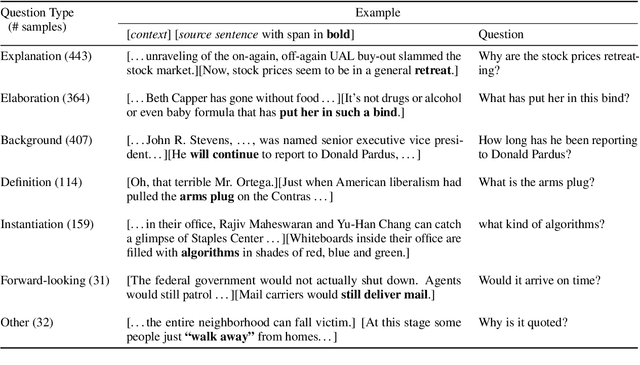

Abstract:We propose a type-controlled framework for inquisitive question generation. We annotate an inquisitive question dataset with question types, train question type classifiers, and finetune models for type-controlled question generation. Empirical results demonstrate that we can generate a variety of questions that adhere to specific types while drawing from the source texts. We also investigate strategies for selecting a single question from a generated set, considering both an informative vs.~inquisitive question classifier and a pairwise ranker trained from a small set of expert annotations. Question selection using the pairwise ranker yields strong results in automatic and manual evaluation. Our human evaluation assesses multiple aspects of the generated questions, finding that the ranker chooses questions with the best syntax (4.59), semantics (4.37), and inquisitiveness (3.92) on a scale of 1-5, even rivaling the performance of human-written questions.
A Cross-Task Analysis of Text Span Representations
Jun 06, 2020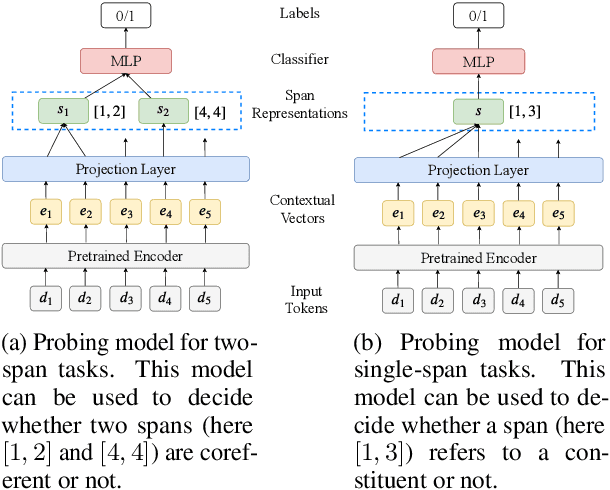
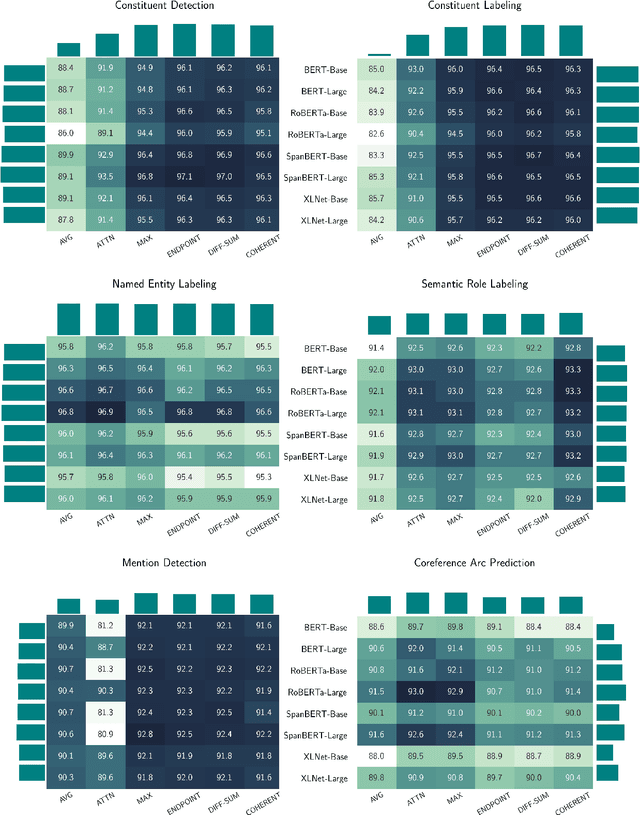
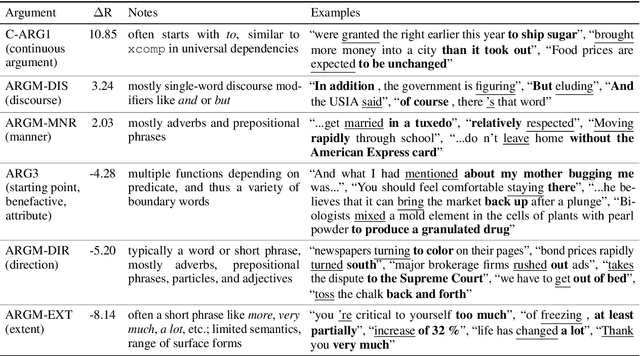
Abstract:Many natural language processing (NLP) tasks involve reasoning with textual spans, including question answering, entity recognition, and coreference resolution. While extensive research has focused on functional architectures for representing words and sentences, there is less work on representing arbitrary spans of text within sentences. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive empirical evaluation of six span representation methods using eight pretrained language representation models across six tasks, including two tasks that we introduce. We find that, although some simple span representations are fairly reliable across tasks, in general the optimal span representation varies by task, and can also vary within different facets of individual tasks. We also find that the choice of span representation has a bigger impact with a fixed pretrained encoder than with a fine-tuned encoder.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge