Lingchuan Meng
Restructurable Activation Networks
Aug 17, 2022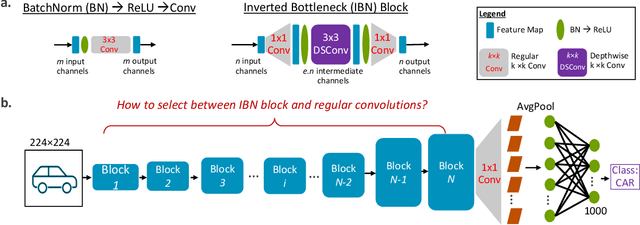
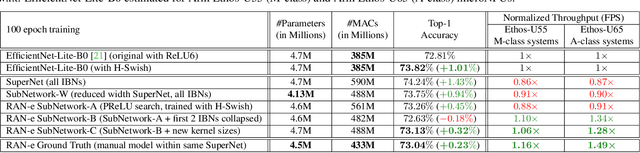
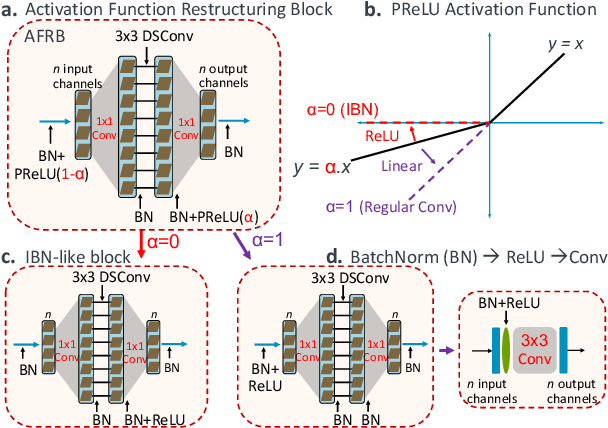
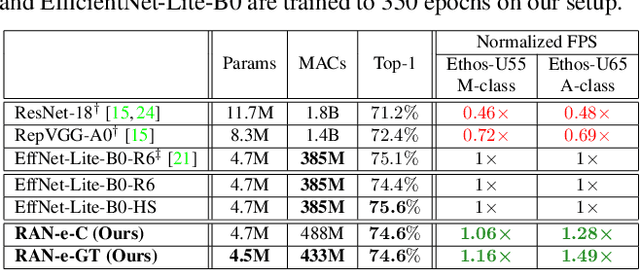
Abstract:Is it possible to restructure the non-linear activation functions in a deep network to create hardware-efficient models? To address this question, we propose a new paradigm called Restructurable Activation Networks (RANs) that manipulate the amount of non-linearity in models to improve their hardware-awareness and efficiency. First, we propose RAN-explicit (RAN-e) -- a new hardware-aware search space and a semi-automatic search algorithm -- to replace inefficient blocks with hardware-aware blocks. Next, we propose a training-free model scaling method called RAN-implicit (RAN-i) where we theoretically prove the link between network topology and its expressivity in terms of number of non-linear units. We demonstrate that our networks achieve state-of-the-art results on ImageNet at different scales and for several types of hardware. For example, compared to EfficientNet-Lite-B0, RAN-e achieves a similar accuracy while improving Frames-Per-Second (FPS) by 1.5x on Arm micro-NPUs. On the other hand, RAN-i demonstrates up to 2x reduction in #MACs over ConvNexts with a similar or better accuracy. We also show that RAN-i achieves nearly 40% higher FPS than ConvNext on Arm-based datacenter CPUs. Finally, RAN-i based object detection networks achieve a similar or higher mAP and up to 33% higher FPS on datacenter CPUs compared to ConvNext based models.
Armour: Generalizable Compact Self-Attention for Vision Transformers
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:Attention-based transformer networks have demonstrated promising potential as their applications extend from natural language processing to vision. However, despite the recent improvements, such as sub-quadratic attention approximation and various training enhancements, the compact vision transformers to date using the regular attention still fall short in comparison with its convnet counterparts, in terms of \textit{accuracy,} \textit{model size}, \textit{and} \textit{throughput}. This paper introduces a compact self-attention mechanism that is fundamental and highly generalizable. The proposed method reduces redundancy and improves efficiency on top of the existing attention optimizations. We show its drop-in applicability for both the regular attention mechanism and some most recent variants in vision transformers. As a result, we produced smaller and faster models with the same or better accuracies.
Collapsible Linear Blocks for Super-Efficient Super Resolution
Mar 17, 2021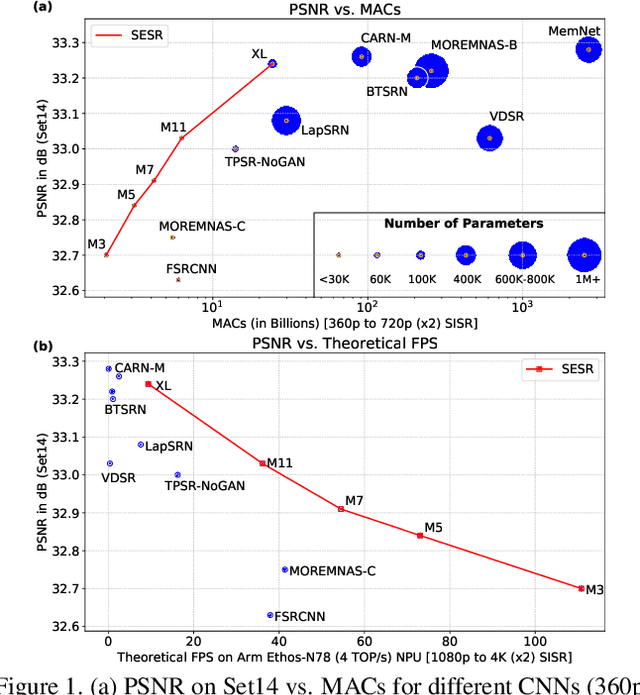
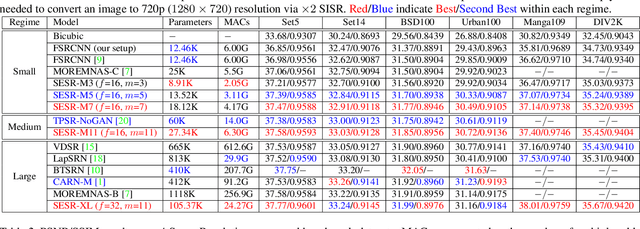
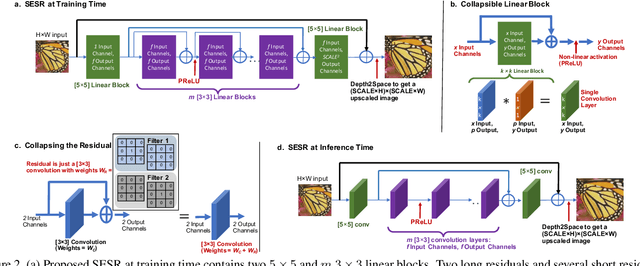
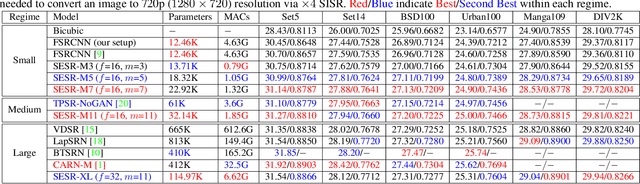
Abstract:With the advent of smart devices that support 4K and 8K resolution, Single Image Super Resolution (SISR) has become an important computer vision problem. However, most super resolution deep networks are computationally very expensive. In this paper, we propose SESR, a new class of Super-Efficient Super Resolution networks that significantly improve image quality and reduce computational complexity. Detailed experiments across six benchmark datasets demonstrate that SESR achieves similar or better image quality than state-of-the-art models while requiring 2x to 330x fewer Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations. As a result, SESR can be used on constrained hardware to perform x2 (1080p to 4K) and x4 SISR (1080p to 8K). Towards this, we simulate hardware performance numbers for a commercial mobile Neural Processing Unit (NPU) for 1080p to 4K (x2) and 1080p to 8K (x4) SISR. Our results highlight the challenges faced by super resolution on AI accelerators and demonstrate that SESR is significantly faster than existing models. Overall, SESR establishes a new Pareto frontier on the quality (PSNR)-computation relationship for the super resolution task.
Efficient Winograd Convolution via Integer Arithmetic
Jan 07, 2019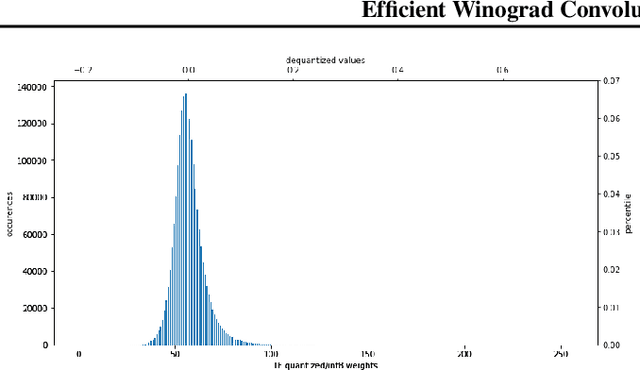
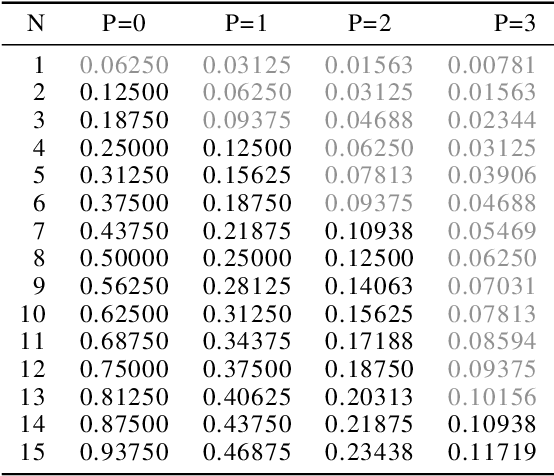
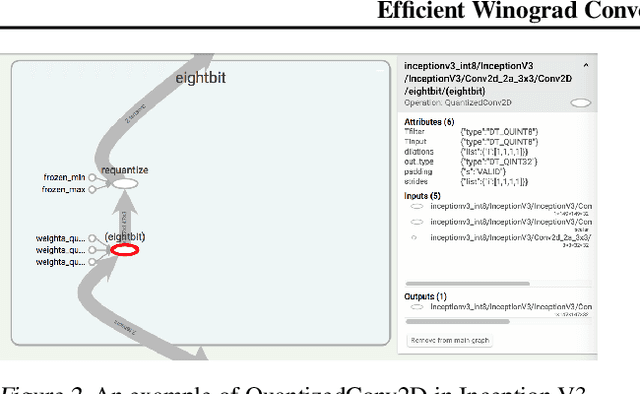
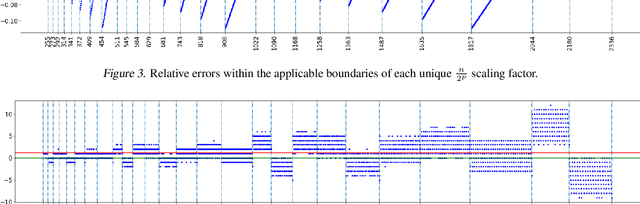
Abstract:Convolution is the core operation for many deep neural networks. The Winograd convolution algorithms have been shown to accelerate the widely-used small convolution sizes. Quantized neural networks can effectively reduce model sizes and improve inference speed, which leads to a wide variety of kernels and hardware accelerators that work with integer data. The state-of-the-art Winograd algorithms pose challenges for efficient implementation and execution by the integer kernels and accelerators. We introduce a new class of Winograd algorithms by extending the construction to the field of complex and propose optimizations that reduce the number of general multiplications. The new algorithm achieves an arithmetic complexity reduction of $3.13$x over the direct method and an efficiency gain up to $17.37\%$ over the rational algorithms. Furthermore, we design and implement an integer-based filter scaling scheme to effectively reduce the filter bit width by $30.77\%$ without any significant accuracy loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge