Lili Zheng
iLOCO: Distribution-Free Inference for Feature Interactions
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Feature importance measures are widely studied and are essential for understanding model behavior, guiding feature selection, and enhancing interpretability. However, many machine learning fitted models involve complex, higher-order interactions between features. Existing feature importance metrics fail to capture these higher-order effects while existing interaction metrics often suffer from limited applicability or excessive computation; no methods exist to conduct statistical inference for feature interactions. To bridge this gap, we first propose a new model-agnostic metric, interaction Leave-One-Covariate-Out iLOCO, for measuring the importance of higher-order feature interactions. Next, we leverage recent advances in LOCO inference to develop distribution-free and assumption-light confidence intervals for our iLOCO metric. To address computational challenges, we also introduce an ensemble learning method for calculating the iLOCO metric and confidence intervals that we show is both computationally and statistically efficient. We validate our iLOCO metric and our confidence intervals on both synthetic and real data sets, showing that our approach outperforms existing methods and provides the first inferential approach to detecting feature interactions.
Cluster Quilting: Spectral Clustering for Patchwork Learning
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Patchwork learning arises as a new and challenging data collection paradigm where both samples and features are observed in fragmented subsets. Due to technological limits, measurement expense, or multimodal data integration, such patchwork data structures are frequently seen in neuroscience, healthcare, and genomics, among others. Instead of analyzing each data patch separately, it is highly desirable to extract comprehensive knowledge from the whole data set. In this work, we focus on the clustering problem in patchwork learning, aiming at discovering clusters amongst all samples even when some are never jointly observed for any feature. We propose a novel spectral clustering method called Cluster Quilting, consisting of (i) patch ordering that exploits the overlapping structure amongst all patches, (ii) patchwise SVD, (iii) sequential linear mapping of top singular vectors for patch overlaps, followed by (iv) k-means on the combined and weighted singular vectors. Under a sub-Gaussian mixture model, we establish theoretical guarantees via a non-asymptotic misclustering rate bound that reflects both properties of the patch-wise observation regime as well as the clustering signal and noise dependencies. We also validate our Cluster Quilting algorithm through extensive empirical studies on both simulated and real data sets in neuroscience and genomics, where it discovers more accurate and scientifically more plausible clusters than other approaches.
Interpretable Machine Learning for Discovery: Statistical Challenges \& Opportunities
Aug 02, 2023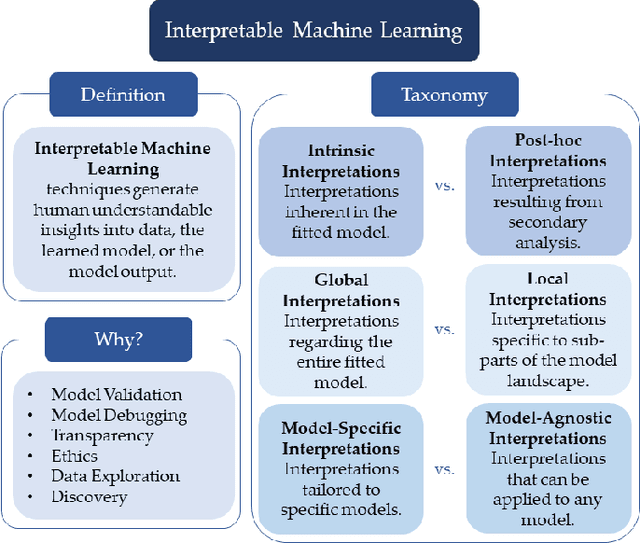
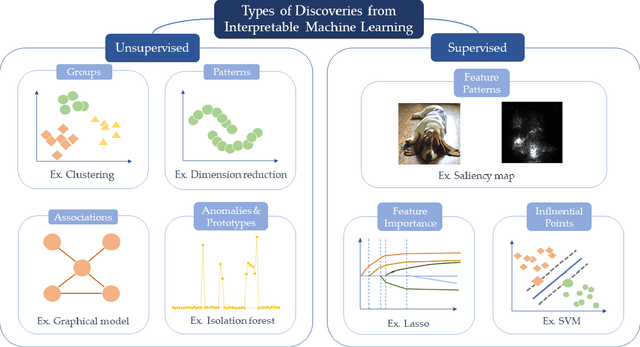
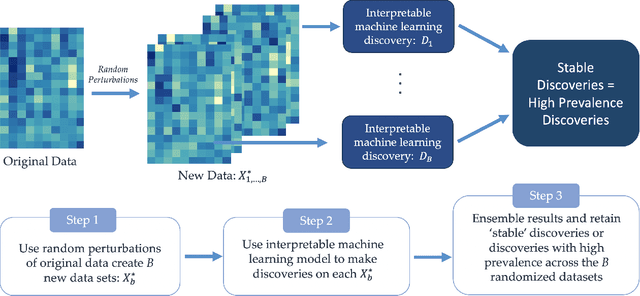
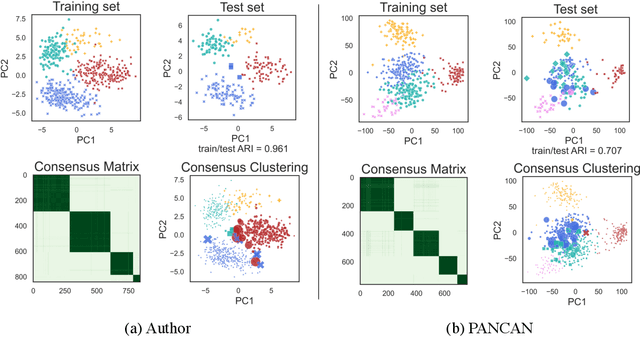
Abstract:New technologies have led to vast troves of large and complex datasets across many scientific domains and industries. People routinely use machine learning techniques to not only process, visualize, and make predictions from this big data, but also to make data-driven discoveries. These discoveries are often made using Interpretable Machine Learning, or machine learning models and techniques that yield human understandable insights. In this paper, we discuss and review the field of interpretable machine learning, focusing especially on the techniques as they are often employed to generate new knowledge or make discoveries from large data sets. We outline the types of discoveries that can be made using Interpretable Machine Learning in both supervised and unsupervised settings. Additionally, we focus on the grand challenge of how to validate these discoveries in a data-driven manner, which promotes trust in machine learning systems and reproducibility in science. We discuss validation from both a practical perspective, reviewing approaches based on data-splitting and stability, as well as from a theoretical perspective, reviewing statistical results on model selection consistency and uncertainty quantification via statistical inference. Finally, we conclude by highlighting open challenges in using interpretable machine learning techniques to make discoveries, including gaps between theory and practice for validating data-driven-discoveries.
Nonparanormal Graph Quilting with Applications to Calcium Imaging
May 22, 2023Abstract:Probabilistic graphical models have become an important unsupervised learning tool for detecting network structures for a variety of problems, including the estimation of functional neuronal connectivity from two-photon calcium imaging data. However, in the context of calcium imaging, technological limitations only allow for partially overlapping layers of neurons in a brain region of interest to be jointly recorded. In this case, graph estimation for the full data requires inference for edge selection when many pairs of neurons have no simultaneous observations. This leads to the Graph Quilting problem, which seeks to estimate a graph in the presence of block-missingness in the empirical covariance matrix. Solutions for the Graph Quilting problem have previously been studied for Gaussian graphical models; however, neural activity data from calcium imaging are often non-Gaussian, thereby requiring a more flexible modeling approach. Thus, in our work, we study two approaches for nonparanormal Graph Quilting based on the Gaussian copula graphical model, namely a maximum likelihood procedure and a low-rank based framework. We provide theoretical guarantees on edge recovery for the former approach under similar conditions to those previously developed for the Gaussian setting, and we investigate the empirical performance of both methods using simulations as well as real data calcium imaging data. Our approaches yield more scientifically meaningful functional connectivity estimates compared to existing Gaussian graph quilting methods for this calcium imaging data set.
DASECount: Domain-Agnostic Sample-Efficient Wireless Indoor Crowd Counting via Few-shot Learning
Nov 18, 2022



Abstract:Accurate indoor crowd counting (ICC) is a key enabler to many smart home/office applications. In this paper, we propose a Domain-Agnostic and Sample-Efficient wireless indoor crowd Counting (DASECount) framework that suffices to attain robust cross-domain detection accuracy given very limited data samples in new domains. DASECount leverages the wisdom of few-shot learning (FSL) paradigm consisting of two major stages: source domain meta training and target domain meta testing. Specifically, in the meta-training stage, we design and train two separate convolutional neural network (CNN) modules on the source domain dataset to fully capture the implicit amplitude and phase features of CSI measurements related to human activities. A subsequent knowledge distillation procedure is designed to iteratively update the CNN parameters for better generalization performance. In the meta-testing stage, we use the partial CNN modules to extract low-dimension features out of the high-dimension input target domain CSI data. With the obtained low-dimension CSI features, we can even use very few shots of target domain data samples (e.g., 5-shot samples) to train a lightweight logistic regression (LR) classifier, and attain very high cross-domain ICC accuracy. Experiment results show that the proposed DASECount method achieves over 92.68\%, and on average 96.37\% detection accuracy in a 0-8 people counting task under various domain setups, which significantly outperforms the other representative benchmark methods considered.
Low-Rank Covariance Completion for Graph Quilting with Applications to Functional Connectivity
Sep 17, 2022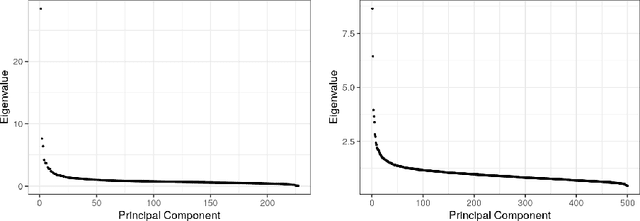
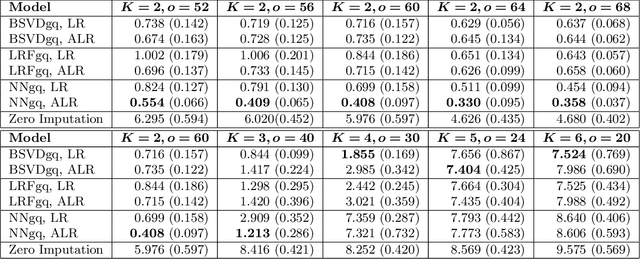
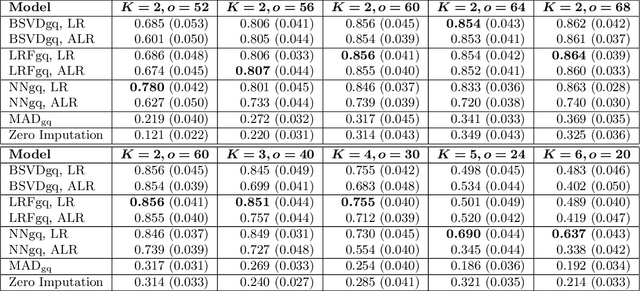
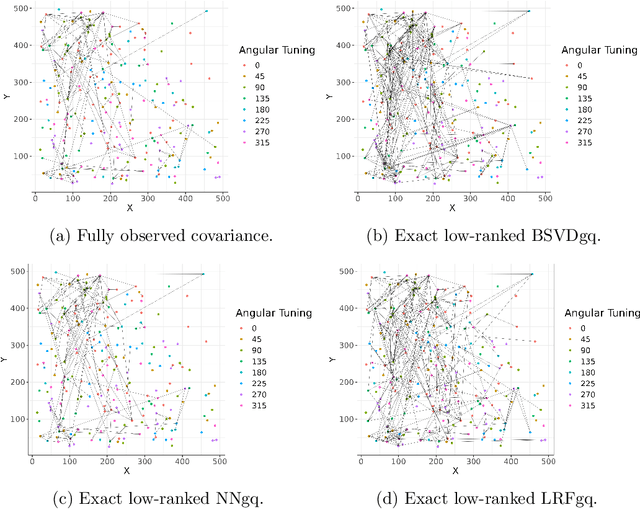
Abstract:As a tool for estimating networks in high dimensions, graphical models are commonly applied to calcium imaging data to estimate functional neuronal connectivity, i.e. relationships between the activities of neurons. However, in many calcium imaging data sets, the full population of neurons is not recorded simultaneously, but instead in partially overlapping blocks. This leads to the Graph Quilting problem, as first introduced by (Vinci et.al. 2019), in which the goal is to infer the structure of the full graph when only subsets of features are jointly observed. In this paper, we study a novel two-step approach to Graph Quilting, which first imputes the complete covariance matrix using low-rank covariance completion techniques before estimating the graph structure. We introduce three approaches to solve this problem: block singular value decomposition, nuclear norm penalization, and non-convex low-rank factorization. While prior works have studied low-rank matrix completion, we address the challenges brought by the block-wise missingness and are the first to investigate the problem in the context of graph learning. We discuss theoretical properties of the two-step procedure, showing graph selection consistency of one proposed approach by proving novel L infinity-norm error bounds for matrix completion with block-missingness. We then investigate the empirical performance of the proposed methods on simulations and on real-world data examples, through which we show the efficacy of these methods for estimating functional connectivity from calcium imaging data.
Inference for Interpretable Machine Learning: Fast, Model-Agnostic Confidence Intervals for Feature Importance
Jun 05, 2022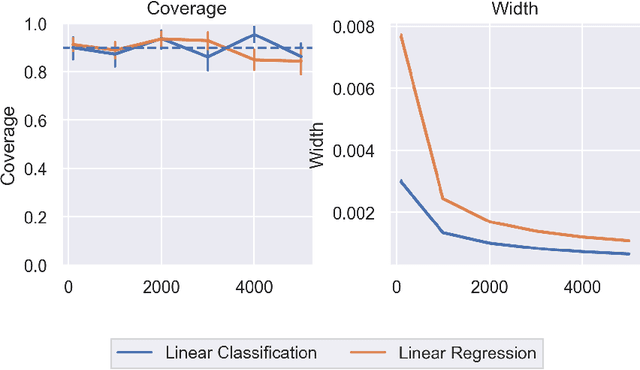
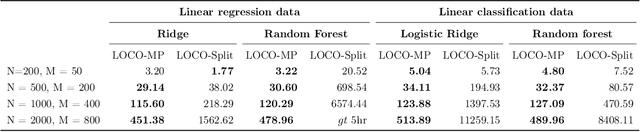
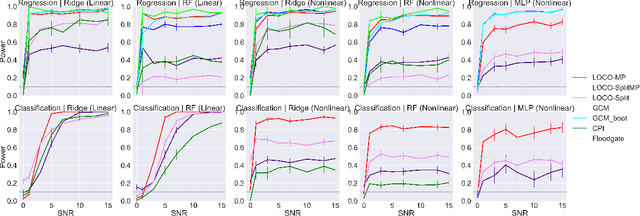
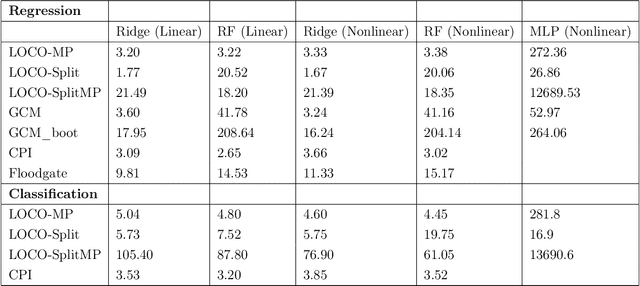
Abstract:In order to trust machine learning for high-stakes problems, we need models to be both reliable and interpretable. Recently, there has been a growing body of work on interpretable machine learning which generates human understandable insights into data, models, or predictions. At the same time, there has been increased interest in quantifying the reliability and uncertainty of machine learning predictions, often in the form of confidence intervals for predictions using conformal inference. Yet, there has been relatively little attention given to the reliability and uncertainty of machine learning interpretations, which is the focus of this paper. Our goal is to develop confidence intervals for a widely-used form of machine learning interpretation: feature importance. We specifically seek to develop universal model-agnostic and assumption-light confidence intervals for feature importance that will be valid for any machine learning model and for any regression or classification task. We do so by leveraging a form of random observation and feature subsampling called minipatch ensembles and show that our approach provides assumption-light asymptotic coverage for the feature importance score of any model. Further, our approach is fast as computations needed for inference come nearly for free as part of the ensemble learning process. Finally, we also show that our same procedure can be leveraged to provide valid confidence intervals for predictions, hence providing fast, simultaneous quantification of the uncertainty of both model predictions and interpretations. We validate our intervals on a series of synthetic and real data examples, showing that our approach detects the correct important features and exhibits many computational and statistical advantages over existing methods.
Gaussian Process Inference Using Mini-batch Stochastic Gradient Descent: Convergence Guarantees and Empirical Benefits
Nov 19, 2021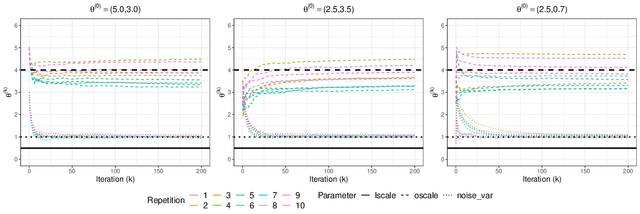
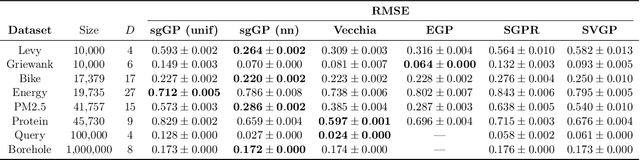
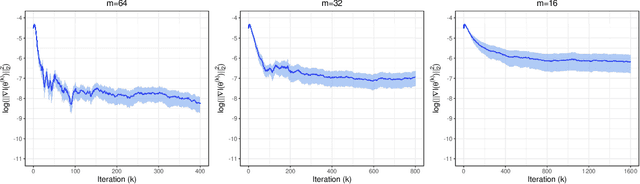
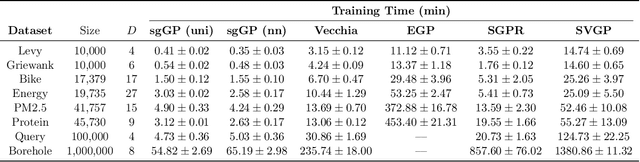
Abstract:Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and its variants have established themselves as the go-to algorithms for large-scale machine learning problems with independent samples due to their generalization performance and intrinsic computational advantage. However, the fact that the stochastic gradient is a biased estimator of the full gradient with correlated samples has led to the lack of theoretical understanding of how SGD behaves under correlated settings and hindered its use in such cases. In this paper, we focus on hyperparameter estimation for the Gaussian process (GP) and take a step forward towards breaking the barrier by proving minibatch SGD converges to a critical point of the full log-likelihood loss function, and recovers model hyperparameters with rate $O(\frac{1}{K})$ for $K$ iterations, up to a statistical error term depending on the minibatch size. Our theoretical guarantees hold provided that the kernel functions exhibit exponential or polynomial eigendecay which is satisfied by a wide range of kernels commonly used in GPs. Numerical studies on both simulated and real datasets demonstrate that minibatch SGD has better generalization over state-of-the-art GP methods while reducing the computational burden and opening a new, previously unexplored, data size regime for GPs.
Optimal High-order Tensor SVD via Tensor-Train Orthogonal Iteration
Oct 06, 2020



Abstract:This paper studies a general framework for high-order tensor SVD. We propose a new computationally efficient algorithm, tensor-train orthogonal iteration (TTOI), that aims to estimate the low tensor-train rank structure from the noisy high-order tensor observation. The proposed TTOI consists of initialization via TT-SVD (Oseledets, 2011) and new iterative backward/forward updates. We develop the general upper bound on estimation error for TTOI with the support of several new representation lemmas on tensor matricizations. By developing a matching information-theoretic lower bound, we also prove that TTOI achieves the minimax optimality under the spiked tensor model. The merits of the proposed TTOI are illustrated through applications to estimation and dimension reduction of high-order Markov processes, numerical studies, and a real data example on New York City taxi travel records. The software of the proposed algorithm is available online.
Context-dependent self-exciting point processes: models, methods, and risk bounds in high dimensions
Mar 16, 2020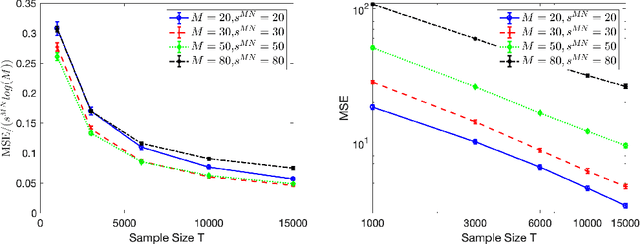
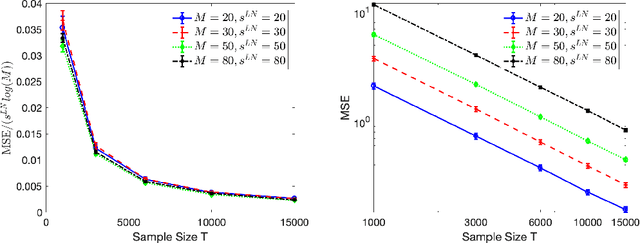
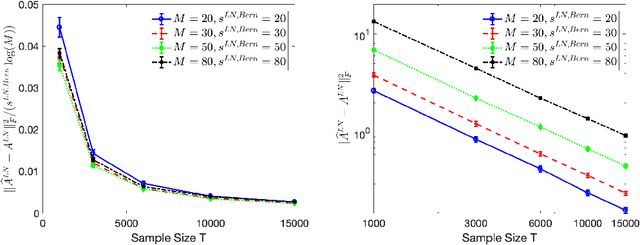
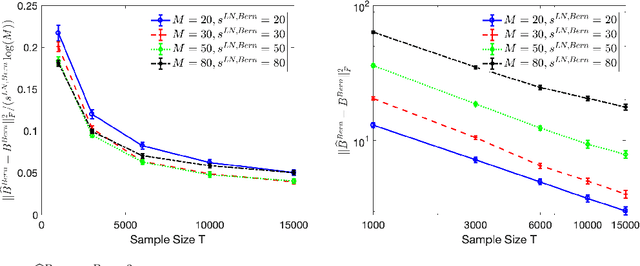
Abstract:High-dimensional autoregressive point processes model how current events trigger or inhibit future events, such as activity by one member of a social network can affect the future activity of his or her neighbors. While past work has focused on estimating the underlying network structure based solely on the times at which events occur on each node of the network, this paper examines the more nuanced problem of estimating context-dependent networks that reflect how features associated with an event (such as the content of a social media post) modulate the strength of influences among nodes. Specifically, we leverage ideas from compositional time series and regularization methods in machine learning to conduct network estimation for high-dimensional marked point processes. Two models and corresponding estimators are considered in detail: an autoregressive multinomial model suited to categorical marks and a logistic-normal model suited to marks with mixed membership in different categories. Importantly, the logistic-normal model leads to a convex negative log-likelihood objective and captures dependence across categories. We provide theoretical guarantees for both estimators, which we validate by simulations and a synthetic data-generating model. We further validate our methods through two real data examples and demonstrate the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge