Low-Rank Covariance Completion for Graph Quilting with Applications to Functional Connectivity
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2022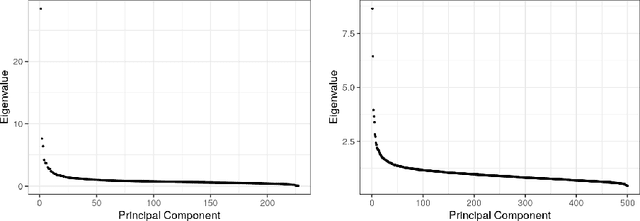
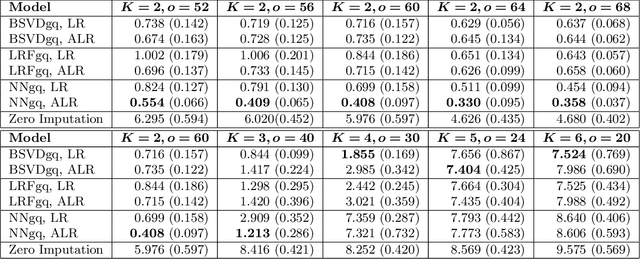
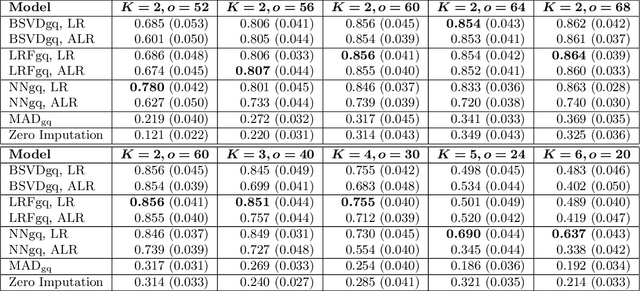
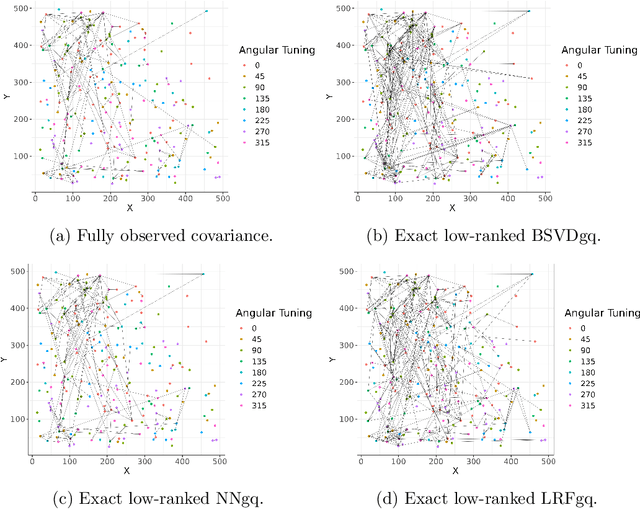
As a tool for estimating networks in high dimensions, graphical models are commonly applied to calcium imaging data to estimate functional neuronal connectivity, i.e. relationships between the activities of neurons. However, in many calcium imaging data sets, the full population of neurons is not recorded simultaneously, but instead in partially overlapping blocks. This leads to the Graph Quilting problem, as first introduced by (Vinci et.al. 2019), in which the goal is to infer the structure of the full graph when only subsets of features are jointly observed. In this paper, we study a novel two-step approach to Graph Quilting, which first imputes the complete covariance matrix using low-rank covariance completion techniques before estimating the graph structure. We introduce three approaches to solve this problem: block singular value decomposition, nuclear norm penalization, and non-convex low-rank factorization. While prior works have studied low-rank matrix completion, we address the challenges brought by the block-wise missingness and are the first to investigate the problem in the context of graph learning. We discuss theoretical properties of the two-step procedure, showing graph selection consistency of one proposed approach by proving novel L infinity-norm error bounds for matrix completion with block-missingness. We then investigate the empirical performance of the proposed methods on simulations and on real-world data examples, through which we show the efficacy of these methods for estimating functional connectivity from calcium imaging data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge