Lianglun Cheng
IMAN: An Adaptive Network for Robust NPC Mortality Prediction with Missing Modalities
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Accurate prediction of mortality in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), a complex malignancy particularly challenging in advanced stages, is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes. However, this predictive process is often compromised by the high-dimensional and heterogeneous nature of NPC-related data, coupled with the pervasive issue of incomplete multi-modal data, manifesting as missing radiological images or incomplete diagnostic reports. Traditional machine learning approaches suffer significant performance degradation when faced with such incomplete data, as they fail to effectively handle the high-dimensionality and intricate correlations across modalities. Even advanced multi-modal learning techniques like Transformers struggle to maintain robust performance in the presence of missing modalities, as they lack specialized mechanisms to adaptively integrate and align the diverse data types, while also capturing nuanced patterns and contextual relationships within the complex NPC data. To address these problem, we introduce IMAN: an adaptive network for robust NPC mortality prediction with missing modalities.
Composited-Nested-Learning with Data Augmentation for Nested Named Entity Recognition
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Nested Named Entity Recognition (NNER) focuses on addressing overlapped entity recognition. Compared to Flat Named Entity Recognition (FNER), annotated resources are scarce in the corpus for NNER. Data augmentation is an effective approach to address the insufficient annotated corpus. However, there is a significant lack of exploration in data augmentation methods for NNER. Due to the presence of nested entities in NNER, existing data augmentation methods cannot be directly applied to NNER tasks. Therefore, in this work, we focus on data augmentation for NNER and resort to more expressive structures, Composited-Nested-Label Classification (CNLC) in which constituents are combined by nested-word and nested-label, to model nested entities. The dataset is augmented using the Composited-Nested-Learning (CNL). In addition, we propose the Confidence Filtering Mechanism (CFM) for a more efficient selection of generated data. Experimental results demonstrate that this approach results in improvements in ACE2004 and ACE2005 and alleviates the impact of sample imbalance.
Rotate to Scan: UNet-like Mamba with Triplet SSM Module for Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 01, 2024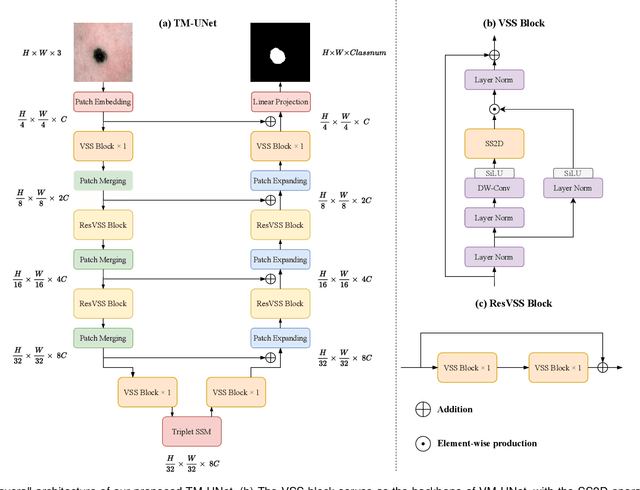
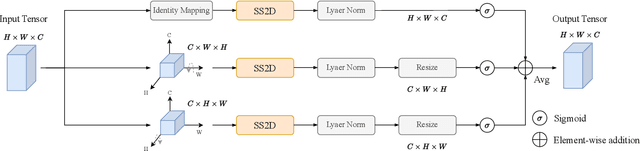
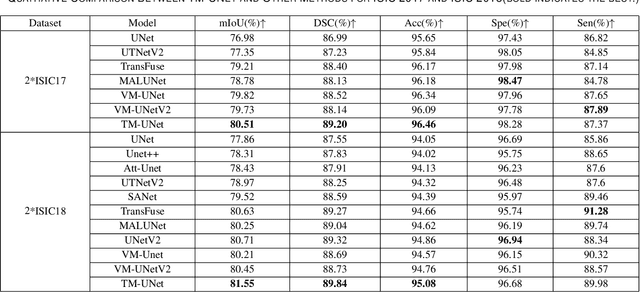
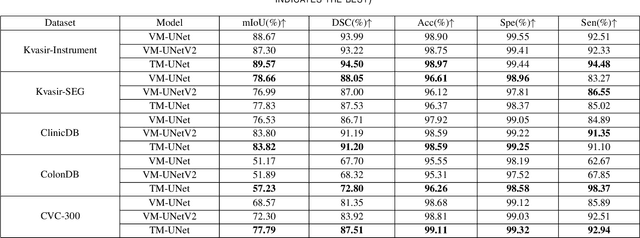
Abstract:Image segmentation holds a vital position in the realms of diagnosis and treatment within the medical domain. Traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformer models have made significant advancements in this realm, but they still encounter challenges because of limited receptive field or high computing complexity. Recently, State Space Models (SSMs), particularly Mamba and its variants, have demonstrated notable performance in the field of vision. However, their feature extraction methods may not be sufficiently effective and retain some redundant structures, leaving room for parameter reduction. Motivated by previous spatial and channel attention methods, we propose Triplet Mamba-UNet. The method leverages residual VSS Blocks to extract intensive contextual features, while Triplet SSM is employed to fuse features across spatial and channel dimensions. We conducted experiments on ISIC17, ISIC18, CVC-300, CVC-ClinicDB, Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ColonDB, and Kvasir-Instrument datasets, demonstrating the superior segmentation performance of our proposed TM-UNet. Additionally, compared to the previous VM-UNet, our model achieves a one-third reduction in parameters.
Self-attention-based BiGRU and capsule network for named entity recognition
Jan 30, 2020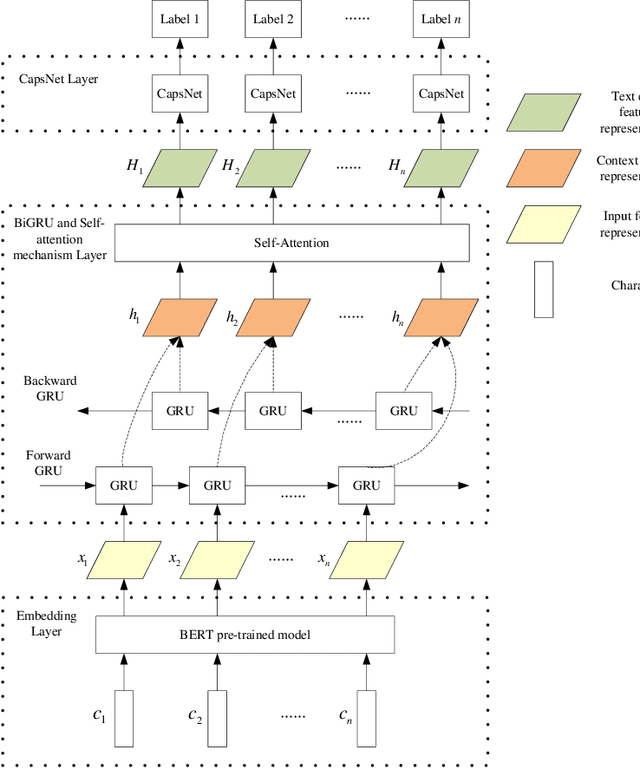
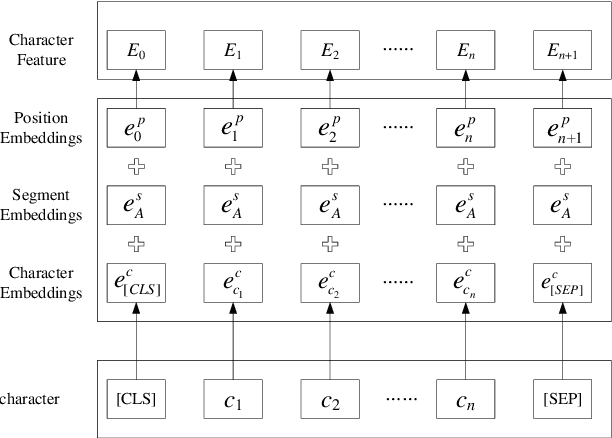
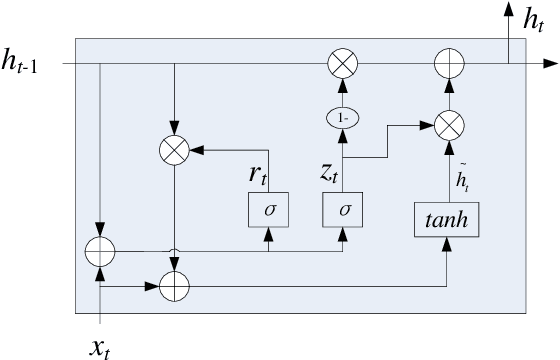
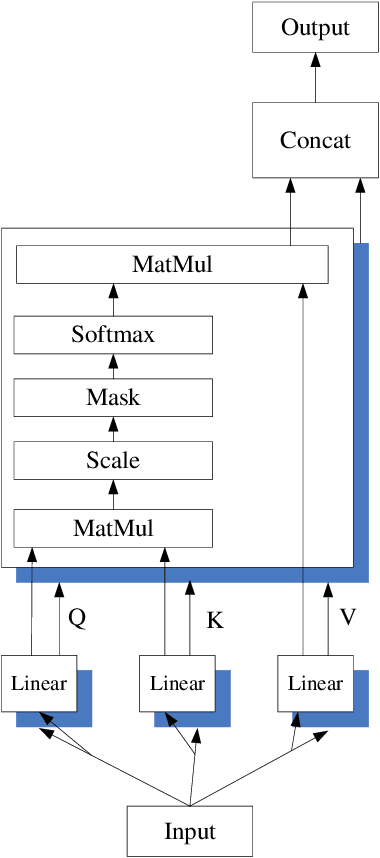
Abstract:Named entity recognition(NER) is one of the tasks of natural language processing(NLP). In view of the problem that the traditional character representation ability is weak and the neural network method is unable to capture the important sequence information. An self-attention-based bidirectional gated recurrent unit(BiGRU) and capsule network(CapsNet) for NER is proposed. This model generates character vectors through bidirectional encoder representation of transformers(BERT) pre-trained model. BiGRU is used to capture sequence context features, and self-attention mechanism is proposed to give different focus on the information captured by hidden layer of BiGRU. Finally, we propose to use CapsNet for entity recognition. We evaluated the recognition performance of the model on two datasets. Experimental results show that the model has better performance without relying on external dictionary information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge