Liangliang Chen
EDU-CIRCUIT-HW: Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models on Real-World University-Level STEM Student Handwritten Solutions
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) hold significant promise for revolutionizing traditional education and reducing teachers' workload. However, accurately interpreting unconstrained STEM student handwritten solutions with intertwined mathematical formulas, diagrams, and textual reasoning poses a significant challenge due to the lack of authentic and domain-specific benchmarks. Additionally, current evaluation paradigms predominantly rely on the outcomes of downstream tasks (e.g., auto-grading), which often probe only a subset of the recognized content, thereby failing to capture the MLLMs' understanding of complex handwritten logic as a whole. To bridge this gap, we release EDU-CIRCUIT-HW, a dataset consisting of 1,300+ authentic student handwritten solutions from a university-level STEM course. Utilizing the expert-verified verbatim transcriptions and grading reports of student solutions, we simultaneously evaluate various MLLMs' upstream recognition fidelity and downstream auto-grading performance. Our evaluation uncovers an astonishing scale of latent failures within MLLM-recognized student handwritten content, highlighting the models' insufficient reliability for auto-grading and other understanding-oriented applications in high-stakes educational settings. In solution, we present a case study demonstrating that leveraging identified error patterns to preemptively detect and rectify recognition errors, with only minimal human intervention (approximately 4% of the total solutions), can significantly enhance the robustness of the deployed AI-enabled grading system on unseen student solutions.
PsychēChat: An Empathic Framework Focused on Emotion Shift Tracking and Safety Risk Analysis in Psychological Counseling
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated notable advancements in psychological counseling. However, existing models generally do not explicitly model seekers' emotion shifts across counseling sessions, a core focus in classical psychological schools. Moreover, how to align counselor models' responses with these emotion shifts while proactively mitigating safety risks remains underexplored. To bridge these gaps, we propose PsychēChat, which explicitly integrates emotion shift tracking and safety risk analysis for psychological counseling. Specifically, we employ interactive role-playing to synthesize counselor--seeker dialogues, incorporating two modules: Emotion Management Module, to capture seekers' current emotions and emotion shifts; and Risk Control Module, to anticipate seekers' subsequent reactions and identify potential risks. Furthermore, we introduce two modeling paradigms. The Agent Mode structures emotion management, risk control, and counselor responses into a collaborative multi-agent pipeline. The LLM Mode integrates these stages into a unified chain-of-thought for end-to-end inference, balancing efficiency and performance. Extensive experiments, including interactive scoring, dialogue-level evaluation, and human assessment, demonstrate that PsychēChat outperforms existing methods for emotional insight and safety control.
Enhancing Large Language Models for End-to-End Circuit Analysis Problem Solving
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown strong performance in data-rich domains such as programming, but their reliability in engineering tasks remains limited. Circuit analysis -- requiring multimodal understanding and precise mathematical reasoning -- highlights these challenges. Although Gemini 2.5 Pro improves diagram interpretation and analog-circuit reasoning, it still struggles to consistently produce correct solutions when given both text and circuit diagrams. At the same time, engineering education needs scalable AI tools capable of generating accurate solutions for tasks such as automated homework feedback and question-answering. This paper presents an enhanced, end-to-end circuit problem solver built on Gemini 2.5 Pro. We first benchmark Gemini on a representative set of undergraduate circuit problems and identify two major failure modes: 1) circuit-recognition hallucinations, particularly incorrect source polarity detection, and 2) reasoning-process hallucinations, such as incorrect current directions. To address recognition errors, we integrate a fine-tuned YOLO detector and OpenCV processing to isolate voltage and current sources, enabling Gemini to re-identify source polarities from cropped images with near-perfect accuracy. To reduce reasoning errors, we introduce an ngspice-based verification loop in which Gemini generates a .cir file, ngspice simulates the circuit, and discrepancies trigger iterative regeneration with optional human-in-the-loop review. Across 83 problems, the proposed pipeline achieves a 97.59% success rate (81 correct solutions), substantially outperforming Gemini 2.5 Pro's original 79.52% accuracy. This system extends LLM capabilities for multimodal engineering problem-solving and supports the creation of high-quality educational datasets and AI-powered instructional tools.
WIP: Large Language Model-Enhanced Smart Tutor for Undergraduate Circuit Analysis
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:This research-to-practice work-in-progress (WIP) paper presents an AI-enabled smart tutor designed to provide homework assessment and feedback for students in an undergraduate circuit analysis course. We detail the tutor's design philosophy and core components, including open-ended question answering and homework feedback generation. The prompts are carefully crafted to optimize responses across different problems. The smart tutor was deployed on the Microsoft Azure platform and is currently in use in an undergraduate circuit analysis course at the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering in a large, public, research-intensive institution in the Southeastern United States. Beyond offering personalized instruction and feedback, the tutor collects student interaction data, which is summarized and shared with the course instructor. To evaluate its effectiveness, we collected student feedback, with 90.9% of responses indicating satisfaction with the tutor. Additionally, we analyze a subset of collected data on preliminary circuit analysis topics to assess tutor usage frequency for each problem and identify frequently asked questions. These insights help instructors gain real-time awareness of student difficulties, enabling more targeted classroom instruction. In future work, we will release a full analysis once the complete dataset is available after the Spring 2025 semester. We also explore the potential applications of this smart tutor across a broader range of engineering disciplines by developing improved prompts, diagram-recognition methods, and database management strategies, which remain ongoing areas of research.
ExACT: An End-to-End Autonomous Excavator System Using Action Chunking With Transformers
May 09, 2024Abstract:Excavators are crucial for diverse tasks such as construction and mining, while autonomous excavator systems enhance safety and efficiency, address labor shortages, and improve human working conditions. Different from the existing modularized approaches, this paper introduces ExACT, an end-to-end autonomous excavator system that processes raw LiDAR, camera data, and joint positions to control excavator valves directly. Utilizing the Action Chunking with Transformers (ACT) architecture, ExACT employs imitation learning to take observations from multi-modal sensors as inputs and generate actionable sequences. In our experiment, we build a simulator based on the captured real-world data to model the relations between excavator valve states and joint velocities. With a few human-operated demonstration data trajectories, ExACT demonstrates the capability of completing different excavation tasks, including reaching, digging and dumping through imitation learning in validations with the simulator. To the best of our knowledge, ExACT represents the first instance towards building an end-to-end autonomous excavator system via imitation learning methods with a minimal set of human demonstrations. The video about this work can be accessed at https://youtu.be/NmzR_Rf-aEk.
RLingua: Improving Reinforcement Learning Sample Efficiency in Robotic Manipulations With Large Language Models
Mar 19, 2024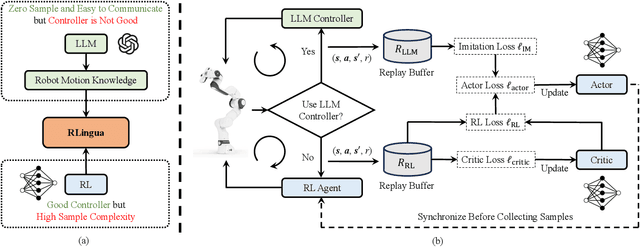
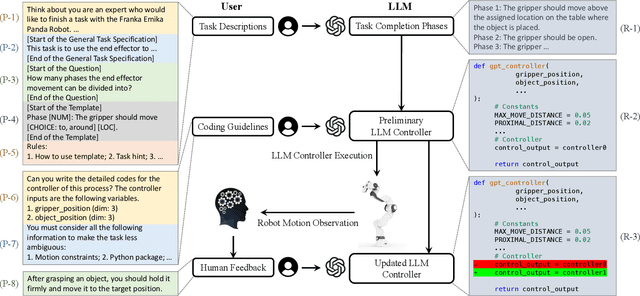
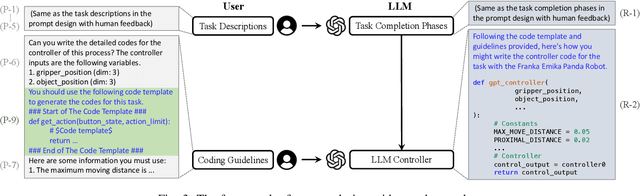
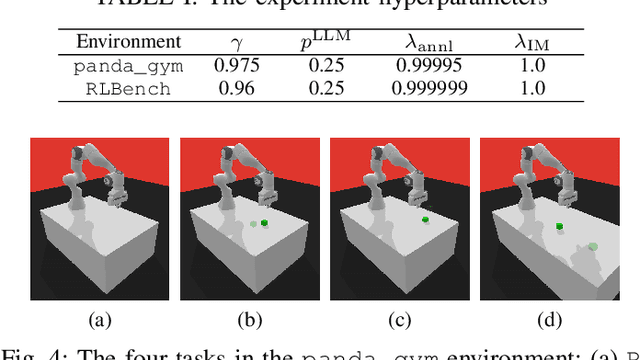
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated its capability in solving various tasks but is notorious for its low sample efficiency. In this paper, we propose RLingua, a framework that can leverage the internal knowledge of large language models (LLMs) to reduce the sample complexity of RL in robotic manipulations. To this end, we first present a method for extracting the prior knowledge of LLMs by prompt engineering so that a preliminary rule-based robot controller for a specific task can be generated in a user-friendly manner. Despite being imperfect, the LLM-generated robot controller is utilized to produce action samples during rollouts with a decaying probability, thereby improving RL's sample efficiency. We employ TD3, the widely-used RL baseline method, and modify the actor loss to regularize the policy learning towards the LLM-generated controller. RLingua also provides a novel method of improving the imperfect LLM-generated robot controllers by RL. We demonstrate that RLingua can significantly reduce the sample complexity of TD3 in four robot tasks of panda_gym and achieve high success rates in 12 sampled sparsely rewarded robot tasks in RLBench, where the standard TD3 fails. Additionally, We validated RLingua's effectiveness in real-world robot experiments through Sim2Real, demonstrating that the learned policies are effectively transferable to real robot tasks. Further details about our work are available at our project website https://rlingua.github.io.
Dual-Scale Interest Extraction Framework with Self-Supervision for Sequential Recommendation
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:In the sequential recommendation task, the recommender generally learns multiple embeddings from a user's historical behaviors, to catch the diverse interests of the user. Nevertheless, the existing approaches just extract each interest independently for the corresponding sub-sequence while ignoring the global correlation of the entire interaction sequence, which may fail to capture the user's inherent preference for the potential interests generalization and unavoidably make the recommended items homogeneous with the historical behaviors. In this paper, we propose a novel Dual-Scale Interest Extraction framework (DSIE) to precisely estimate the user's current interests. Specifically, DSIE explicitly models the user's inherent preference with contrastive learning by attending over his/her entire interaction sequence at the global scale and catches the user's diverse interests in a fine granularity at the local scale. Moreover, we develop a novel interest aggregation module to integrate the multi-interests according to the inherent preference to generate the user's current interests for the next-item prediction. Experiments conducted on three real-world benchmark datasets demonstrate that DSIE outperforms the state-of-the-art models in terms of recommendation preciseness and novelty.
NR-RRT: Neural Risk-Aware Near-Optimal Path Planning in Uncertain Nonconvex Environments
May 14, 2022



Abstract:Balancing the trade-off between safety and efficiency is of significant importance for path planning under uncertainty. Many risk-aware path planners have been developed to explicitly limit the probability of collision to an acceptable bound in uncertain environments. However, convex obstacles or Gaussian uncertainties are usually assumed to make the problem tractable in the existing method. These assumptions limit the generalization and application of path planners in real-world implementations. In this article, we propose to apply deep learning methods to the sampling-based planner, developing a novel risk bounded near-optimal path planning algorithm named neural risk-aware RRT (NR-RRT). Specifically, a deterministic risk contours map is maintained by perceiving the probabilistic nonconvex obstacles, and a neural network sampler is proposed to predict the next most-promising safe state. Furthermore, the recursive divide-and-conquer planning and bidirectional search strategies are used to accelerate the convergence to a near-optimal solution with guaranteed bounded risk. Worst-case theoretical guarantees can also be proven owing to a standby safety guaranteed planner utilizing a uniform sampling distribution. Simulation experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art remarkably for finding risk bounded low-cost paths in seen and unseen environments with uncertainty and nonconvex constraints.
Detect Rumors in Microblog Posts for Low-Resource Domains via Adversarial Contrastive Learning
Apr 19, 2022
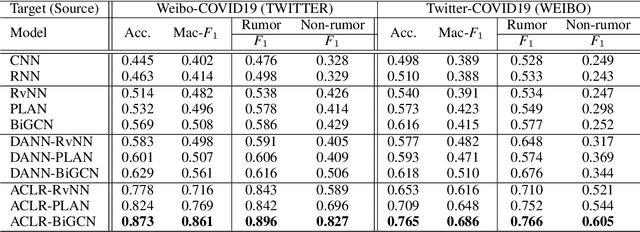
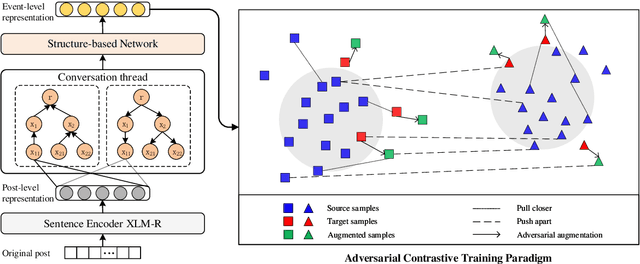
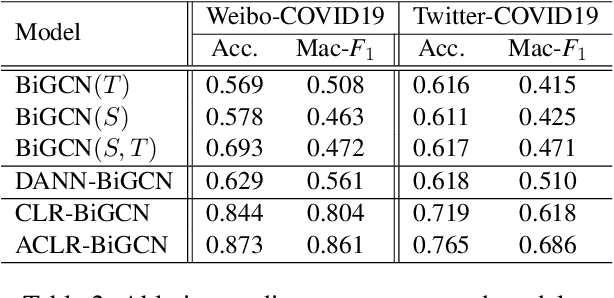
Abstract:Massive false rumors emerging along with breaking news or trending topics severely hinder the truth. Existing rumor detection approaches achieve promising performance on the yesterday's news, since there is enough corpus collected from the same domain for model training. However, they are poor at detecting rumors about unforeseen events especially those propagated in different languages due to the lack of training data and prior knowledge (i.e., low-resource regimes). In this paper, we propose an adversarial contrastive learning framework to detect rumors by adapting the features learned from well-resourced rumor data to that of the low-resourced. Our model explicitly overcomes the restriction of domain and/or language usage via language alignment and a novel supervised contrastive training paradigm. Moreover, we develop an adversarial augmentation mechanism to further enhance the robustness of low-resource rumor representation. Extensive experiments conducted on two low-resource datasets collected from real-world microblog platforms demonstrate that our framework achieves much better performance than state-of-the-art methods and exhibits a superior capacity for detecting rumors at early stages.
* The first study for the low-resource rumor detection on social media in cross-domain and cross-lingual settings
Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks
Oct 09, 2021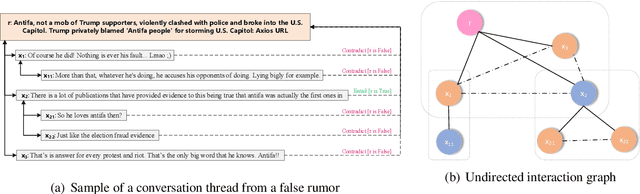

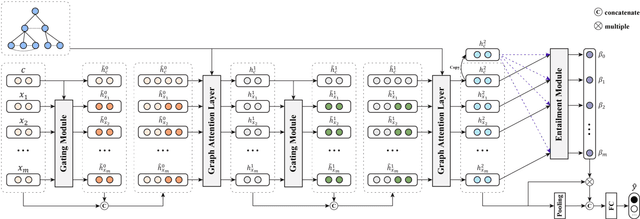

Abstract:Rumors are rampant in the era of social media. Conversation structures provide valuable clues to differentiate between real and fake claims. However, existing rumor detection methods are either limited to the strict relation of user responses or oversimplify the conversation structure. In this study, to substantially reinforces the interaction of user opinions while alleviating the negative impact imposed by irrelevant posts, we first represent the conversation thread as an undirected interaction graph. We then present a Claim-guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Network for rumor classification, which enhances the representation learning for responsive posts considering the entire social contexts and attends over the posts that can semantically infer the target claim. Extensive experiments on three Twitter datasets demonstrate that our rumor detection method achieves much better performance than state-of-the-art methods and exhibits a superior capacity for detecting rumors at early stages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge