Lee Xiong
LLaTTE: Scaling Laws for Multi-Stage Sequence Modeling in Large-Scale Ads Recommendation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present LLaTTE (LLM-Style Latent Transformers for Temporal Events), a scalable transformer architecture for production ads recommendation. Through systematic experiments, we demonstrate that sequence modeling in recommendation systems follows predictable power-law scaling similar to LLMs. Crucially, we find that semantic features bend the scaling curve: they are a prerequisite for scaling, enabling the model to effectively utilize the capacity of deeper and longer architectures. To realize the benefits of continued scaling under strict latency constraints, we introduce a two-stage architecture that offloads the heavy computation of large, long-context models to an asynchronous upstream user model. We demonstrate that upstream improvements transfer predictably to downstream ranking tasks. Deployed as the largest user model at Meta, this multi-stage framework drives a 4.3\% conversion uplift on Facebook Feed and Reels with minimal serving overhead, establishing a practical blueprint for harnessing scaling laws in industrial recommender systems.
RakutenAI-7B: Extending Large Language Models for Japanese
Mar 21, 2024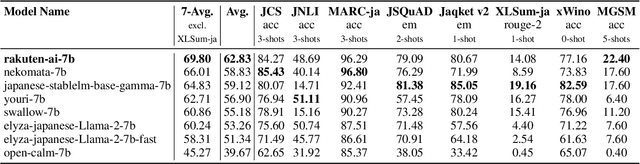
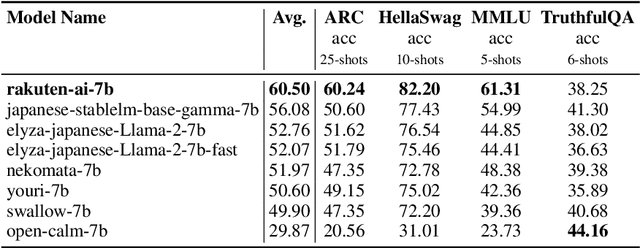
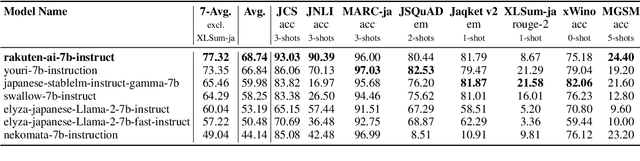
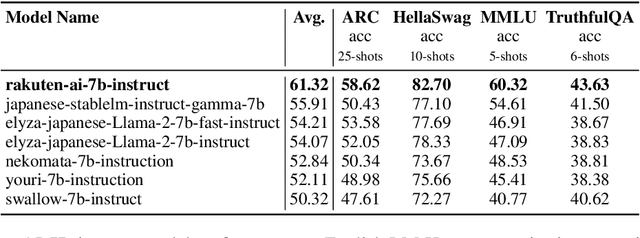
Abstract:We introduce RakutenAI-7B, a suite of Japanese-oriented large language models that achieve the best performance on the Japanese LM Harness benchmarks among the open 7B models. Along with the foundation model, we release instruction- and chat-tuned models, RakutenAI-7B-instruct and RakutenAI-7B-chat respectively, under the Apache 2.0 license.
Approximate Nearest Neighbor Negative Contrastive Learning for Dense Text Retrieval
Jul 01, 2020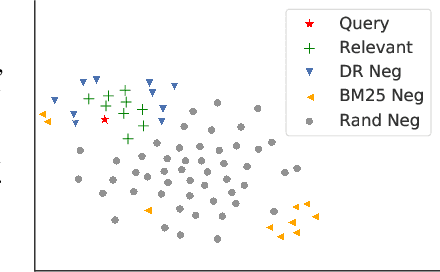
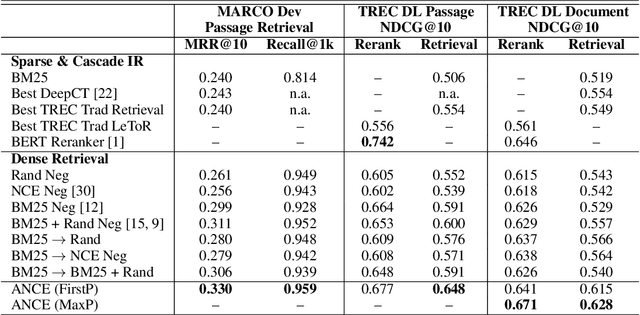
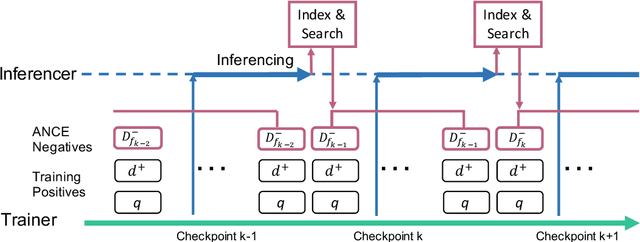
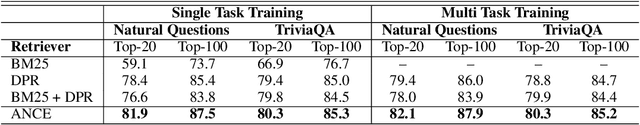
Abstract:Conducting text retrieval in a dense learned representation space has many intriguing advantages over sparse retrieval. Yet the effectiveness of dense retrieval (DR) often requires combination with sparse retrieval. In this paper, we identify that the main bottleneck is in the training mechanisms, where the negative instances used in training are not representative of the irrelevant documents in testing. This paper presents Approximate nearest neighbor Negative Contrastive Estimation (ANCE), a training mechanism that constructs negatives from an Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) index of the corpus, which is parallelly updated with the learning process to select more realistic negative training instances. This fundamentally resolves the discrepancy between the data distribution used in the training and testing of DR. In our experiments, ANCE boosts the BERT-Siamese DR model to outperform all competitive dense and sparse retrieval baselines. It nearly matches the accuracy of sparse-retrieval-and-BERT-reranking using dot-product in the ANCE-learned representation space and provides almost 100x speed-up.
Open Domain Web Keyphrase Extraction Beyond Language Modeling
Nov 06, 2019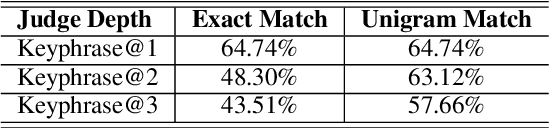
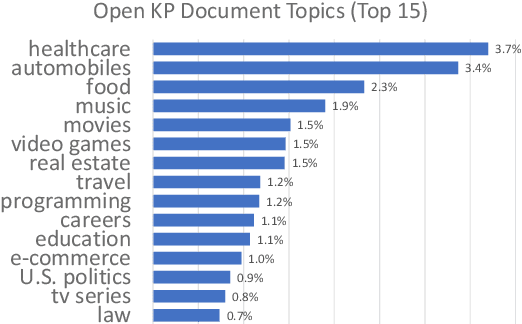
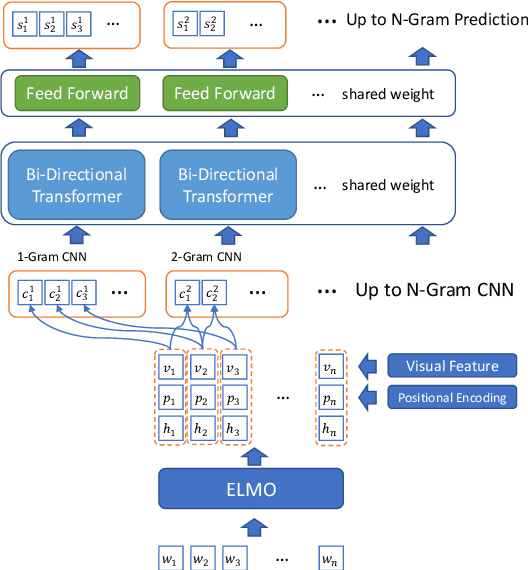
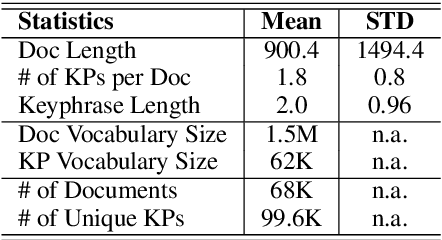
Abstract:This paper studies keyphrase extraction in real-world scenarios where documents are from diverse domains and have variant content quality. We curate and release OpenKP, a large scale open domain keyphrase extraction dataset with near one hundred thousand web documents and expert keyphrase annotations. To handle the variations of domain and content quality, we develop BLING-KPE, a neural keyphrase extraction model that goes beyond language understanding using visual presentations of documents and weak supervision from search queries. Experimental results on OpenKP confirm the effectiveness of BLING-KPE and the contributions of its neural architecture, visual features, and search log weak supervision. Zero-shot evaluations on DUC-2001 demonstrate the improved generalization ability of learning from the open domain data compared to a specific domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge