Laurent Caraffa
Dissipative Learning: A Framework for Viable Adaptive Systems
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:We propose a perspective in which learning is an intrinsically dissipative process. Forgetting and regularization are not heuristic add-ons but structural requirements for adaptive systems. Drawing on information theory, thermodynamics, and information geometry, we introduce the BEDS (Bayesian Emergent Dissipative Structures) framework, modeling learning as the evolution of compressed belief states under dissipation constraints. A central contribution is the Conditional Optimality Theorem, showing that Fisher-Rao regularization measuring change via information divergence rather than Euclidean distance is the unique thermodynamically optimal regularization strategy, achieving minimal dissipation. Euclidean regularization is shown to be structurally suboptimal. The framework unifies existing methods (Ridge, SIGReg, EMA, SAC) as special cases of a single governing equation. Within this view, overfitting corresponds to over-crystallization, while catastrophic forgetting reflects insufficient dissipation control. The framework distinguishes BEDS-crystallizable problems, where beliefs converge to stable equilibria, from BEDS-maintainable problems, which require continual adaptation. It extends naturally to continual and multi-agent systems, where viability, stability under adaptation and finite resources replaces asymptotic optimality as the primary criterion. Overall, this work reframes learning as maintaining viable belief states under dissipation constraints, providing a principled lens on forgetting, regularization, and stability.
Thermodynamically Optimal Regularization under Information-Geometric Constraints
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Modern machine learning relies on a collection of empirically successful but theoretically heterogeneous regularization techniques, such as weight decay, dropout, and exponential moving averages. At the same time, the rapidly increasing energetic cost of training large models raises the question of whether learning algorithms approach any fundamental efficiency bound. In this work, we propose a unifying theoretical framework connecting thermodynamic optimality, information geometry, and regularization. Under three explicit assumptions -- (A1) that optimality requires an intrinsic, parametrization-invariant measure of information, (A2) that belief states are modeled by maximum-entropy distributions under known constraints, and (A3) that optimal processes are quasi-static -- we prove a conditional optimality theorem. Specifically, the Fisher--Rao metric is the unique admissible geometry on belief space, and thermodynamically optimal regularization corresponds to minimizing squared Fisher--Rao distance to a reference state. We derive the induced geometries for Gaussian and circular belief models, yielding hyperbolic and von Mises manifolds, respectively, and show that classical regularization schemes are structurally incapable of guaranteeing thermodynamic optimality. We introduce a notion of thermodynamic efficiency of learning and propose experimentally testable predictions. This work provides a principled geometric and thermodynamic foundation for regularization in machine learning.
BEDS : Bayesian Emergent Dissipative Structures : A Formal Framework for Continuous Inference Under Energy Constraints
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We introduce BEDS (Bayesian Emergent Dissipative Structures), a formal framework for analyzing inference systems that must maintain beliefs continuously under energy constraints. Unlike classical computational models that assume perfect memory and focus on one-shot computation, BEDS explicitly incorporates dissipation (information loss over time) as a fundamental constraint. We prove a central result linking energy, precision, and dissipation: maintaining a belief with precision $τ$ against dissipation rate $γ$ requires power $P \geq γk_{\rm B} T / 2$, with scaling $P \propto γ\cdot τ$. This establishes a fundamental thermodynamic cost for continuous inference. We define three classes of problems -- BEDS-attainable, BEDS-maintainable, and BEDS-crystallizable -- and show these are distinct from classical decidability. We propose the Gödel-Landauer-Prigogine conjecture, suggesting that closure pathologies across formal systems, computation, and thermodynamics share a common structure.
Pointmap-Conditioned Diffusion for Consistent Novel View Synthesis
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we present PointmapDiffusion, a novel framework for single-image novel view synthesis (NVS) that utilizes pre-trained 2D diffusion models. Our method is the first to leverage pointmaps (i.e. rasterized 3D scene coordinates) as a conditioning signal, capturing geometric prior from the reference images to guide the diffusion process. By embedding reference attention blocks and a ControlNet for pointmap features, our model balances between generative capability and geometric consistency, enabling accurate view synthesis across varying viewpoints. Extensive experiments on diverse real-world datasets demonstrate that PointmapDiffusion achieves high-quality, multi-view consistent results with significantly fewer trainable parameters compared to other baselines for single-image NVS tasks.
Scaled Inverse Graphics: Efficiently Learning Large Sets of 3D Scenes
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:While the field of inverse graphics has been witnessing continuous growth, techniques devised thus far predominantly focus on learning individual scene representations. In contrast, learning large sets of scenes has been a considerable bottleneck in NeRF developments, as repeatedly applying inverse graphics on a sequence of scenes, though essential for various applications, remains largely prohibitive in terms of resource costs. We introduce a framework termed "scaled inverse graphics", aimed at efficiently learning large sets of scene representations, and propose a novel method to this end. It operates in two stages: (i) training a compression model on a subset of scenes, then (ii) training NeRF models on the resulting smaller representations, thereby reducing the optimization space per new scene. In practice, we compact the representation of scenes by learning NeRFs in a latent space to reduce the image resolution, and sharing information across scenes to reduce NeRF representation complexity. We experimentally show that our method presents both the lowest training time and memory footprint in scaled inverse graphics compared to other methods applied independently on each scene. Our codebase is publicly available as open-source. Our project page can be found at https://scaled-ig.github.io .
Bringing NeRFs to the Latent Space: Inverse Graphics Autoencoder
Oct 30, 2024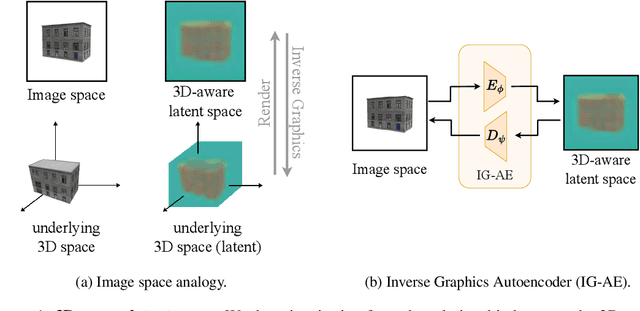
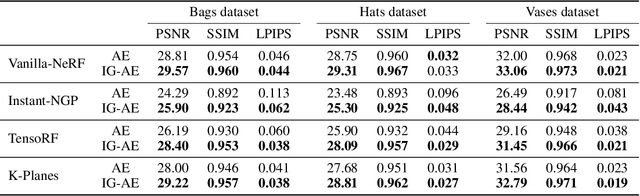
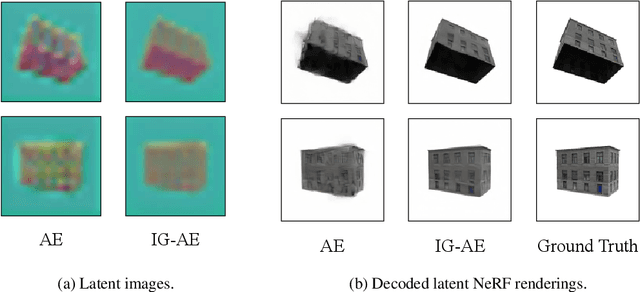

Abstract:While pre-trained image autoencoders are increasingly utilized in computer vision, the application of inverse graphics in 2D latent spaces has been under-explored. Yet, besides reducing the training and rendering complexity, applying inverse graphics in the latent space enables a valuable interoperability with other latent-based 2D methods. The major challenge is that inverse graphics cannot be directly applied to such image latent spaces because they lack an underlying 3D geometry. In this paper, we propose an Inverse Graphics Autoencoder (IG-AE) that specifically addresses this issue. To this end, we regularize an image autoencoder with 3D-geometry by aligning its latent space with jointly trained latent 3D scenes. We utilize the trained IG-AE to bring NeRFs to the latent space with a latent NeRF training pipeline, which we implement in an open-source extension of the Nerfstudio framework, thereby unlocking latent scene learning for its supported methods. We experimentally confirm that Latent NeRFs trained with IG-AE present an improved quality compared to a standard autoencoder, all while exhibiting training and rendering accelerations with respect to NeRFs trained in the image space. Our project page can be found at https://ig-ae.github.io .
Exploring 3D-aware Latent Spaces for Efficiently Learning Numerous Scenes
Mar 18, 2024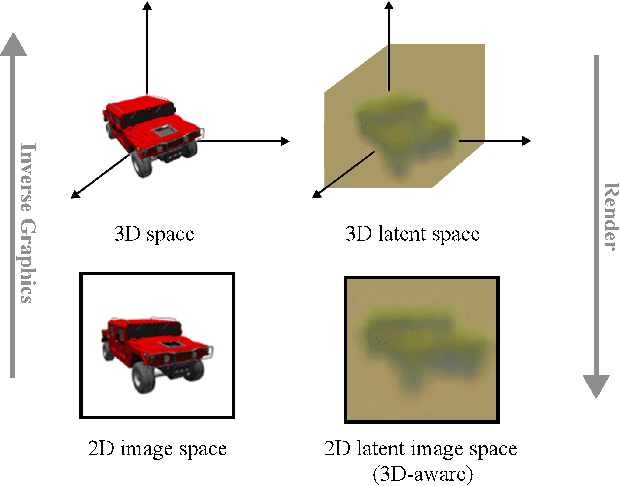
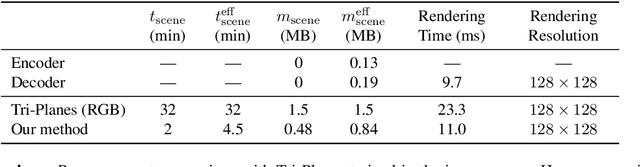
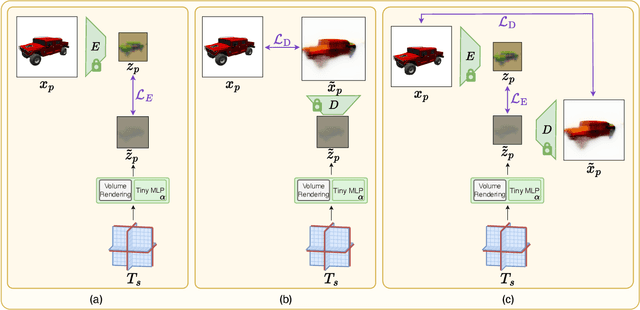
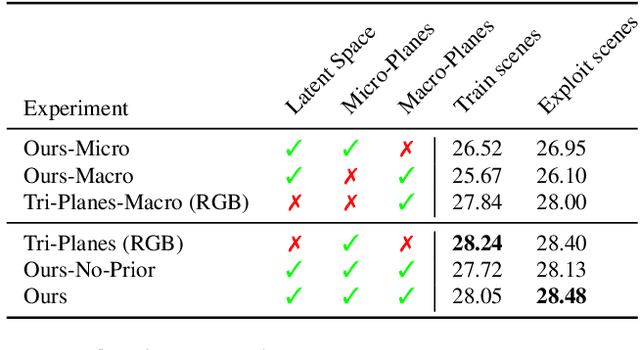
Abstract:We present a method enabling the scaling of NeRFs to learn a large number of semantically-similar scenes. We combine two techniques to improve the required training time and memory cost per scene. First, we learn a 3D-aware latent space in which we train Tri-Plane scene representations, hence reducing the resolution at which scenes are learned. Moreover, we present a way to share common information across scenes, hence allowing for a reduction of model complexity to learn a particular scene. Our method reduces effective per-scene memory costs by 44% and per-scene time costs by 86% when training 1000 scenes. Our project page can be found at https://3da-ae.github.io .
EvE: Exploiting Generative Priors for Radiance Field Enrichment
Dec 01, 2023



Abstract:Modeling large-scale scenes from unconstrained image collections in-the-wild has proven to be a major challenge in computer vision. Existing methods tackling in-the-wild neural rendering operate in a closed-world setting, where knowledge is limited to a scene's captured images within a training set. We propose EvE, which is, to the best of our knowledge, the first method leveraging generative priors to improve in-the-wild scene modeling. We employ pre-trained generative networks to enrich K-Planes representations with extrinsic knowledge. To this end, we define an alternating training procedure to conduct optimization guidance of K-Planes trained on the training set. We carry out extensive experiments and verify the merit of our method on synthetic data as well as real tourism photo collections. EvE enhances rendered scenes with richer details and outperforms the state of the art on the task of novel view synthesis in-the-wild. Our project page can be found at https://eve-nvs.github.io .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge