Lambert Deng
Differentiable Cluster Graph Neural Network
May 25, 2024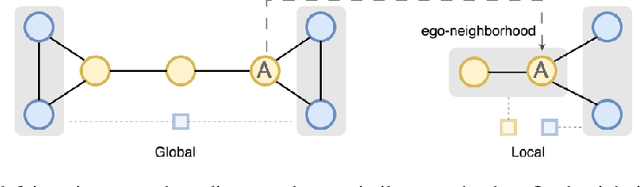

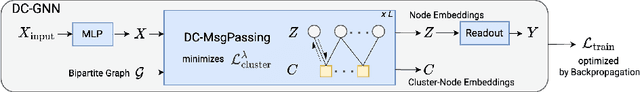

Abstract:Graph Neural Networks often struggle with long-range information propagation and in the presence of heterophilous neighborhoods. We address both challenges with a unified framework that incorporates a clustering inductive bias into the message passing mechanism, using additional cluster-nodes. Central to our approach is the formulation of an optimal transport based implicit clustering objective function. However, the algorithm for solving the implicit objective function needs to be differentiable to enable end-to-end learning of the GNN. To facilitate this, we adopt an entropy regularized objective function and propose an iterative optimization process, alternating between solving for the cluster assignments and updating the node/cluster-node embeddings. Notably, our derived closed-form optimization steps are themselves simple yet elegant message passing steps operating seamlessly on a bipartite graph of nodes and cluster-nodes. Our clustering-based approach can effectively capture both local and global information, demonstrated by extensive experiments on both heterophilous and homophilous datasets.
Lightweight Spatial Modeling for Combinatorial Information Extraction From Documents
May 08, 2024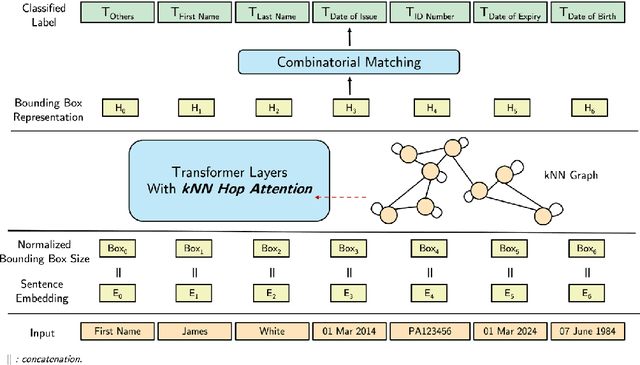



Abstract:Documents that consist of diverse templates and exhibit complex spatial structures pose a challenge for document entity classification. We propose KNN-former, which incorporates a new kind of spatial bias in attention calculation based on the K-nearest-neighbor (KNN) graph of document entities. We limit entities' attention only to their local radius defined by the KNN graph. We also use combinatorial matching to address the one-to-one mapping property that exists in many documents, where one field has only one corresponding entity. Moreover, our method is highly parameter-efficient compared to existing approaches in terms of the number of trainable parameters. Despite this, experiments across various datasets show our method outperforms baselines in most entity types. Many real-world documents exhibit combinatorial properties which can be leveraged as inductive biases to improve extraction accuracy, but existing datasets do not cover these documents. To facilitate future research into these types of documents, we release a new ID document dataset that covers diverse templates and languages. We also release enhanced annotations for an existing dataset.
Enabling Roll-up and Drill-down Operations in News Exploration with Knowledge Graphs for Due Diligence and Risk Management
May 08, 2024

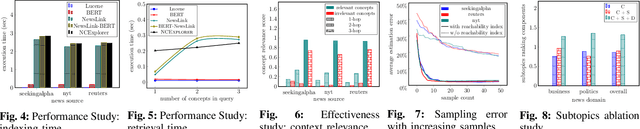

Abstract:Efficient news exploration is crucial in real-world applications, particularly within the financial sector, where numerous control and risk assessment tasks rely on the analysis of public news reports. The current processes in this domain predominantly rely on manual efforts, often involving keywordbased searches and the compilation of extensive keyword lists. In this paper, we introduce NCEXPLORER, a framework designed with OLAP-like operations to enhance the news exploration experience. NCEXPLORER empowers users to use roll-up operations for a broader content overview and drill-down operations for detailed insights. These operations are achieved through integration with external knowledge graphs (KGs), encompassing both fact-based and ontology-based structures. This integration significantly augments exploration capabilities, offering a more comprehensive and efficient approach to unveiling the underlying structures and nuances embedded in news content. Extensive empirical studies through master-qualified evaluators on Amazon Mechanical Turk demonstrate NCEXPLORER's superiority over existing state-of-the-art news search methodologies across an array of topic domains, using real-world news datasets.
Web News Timeline Generation with Extended Task Prompting
Nov 20, 2023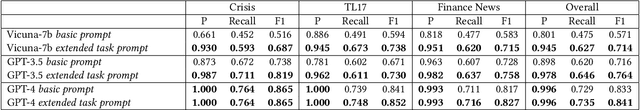


Abstract:The creation of news timeline is essential for a comprehensive and contextual understanding of events as they unfold over time. This approach aids in discerning patterns and trends that might be obscured when news is viewed in isolation. By organizing news in a chronological sequence, it becomes easier to track the development of stories, understand the interrelation of events, and grasp the broader implications of news items. This is particularly helpful in sectors like finance and insurance, where timely understanding of the event development-ranging from extreme weather to political upheavals and health crises-is indispensable for effective risk management. While traditional natural language processing (NLP) techniques have had some success, they often fail to capture the news with nuanced relevance that are readily apparent to domain experts, hindering broader industry integration. The advance of Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a renewed opportunity to tackle this challenge. However, direct prompting LLMs for this task is often ineffective. Our study investigates the application of an extended task prompting technique to assess past news relevance. We demonstrate that enhancing conventional prompts with additional tasks boosts their effectiveness on various news dataset, rendering news timeline generation practical for professional use. This work has been deployed as a publicly accessible browser extension which is adopted within our network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge