Kyunghyun Sung
Cross-Slice Attention and Evidential Critical Loss for Uncertainty-Aware Prostate Cancer Detection
Jul 01, 2024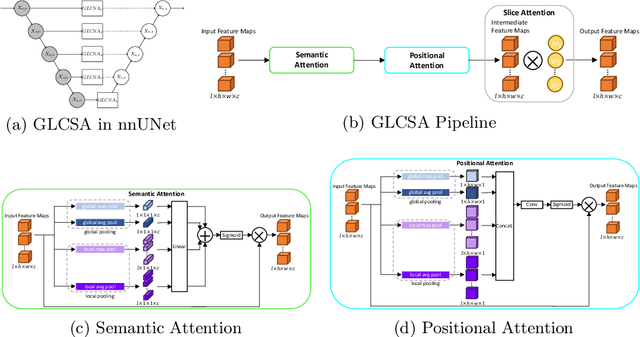

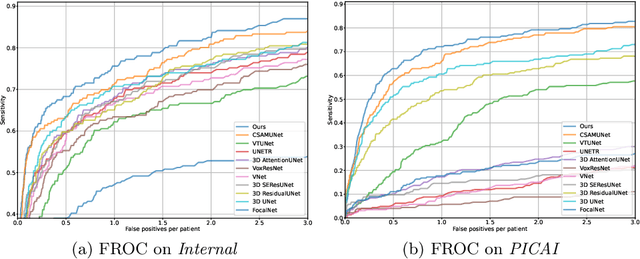
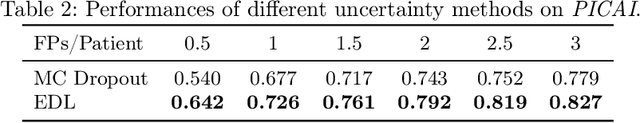
Abstract:Current deep learning-based models typically analyze medical images in either 2D or 3D albeit disregarding volumetric information or suffering sub-optimal performance due to the anisotropic resolution of MR data. Furthermore, providing an accurate uncertainty estimation is beneficial to clinicians, as it indicates how confident a model is about its prediction. We propose a novel 2.5D cross-slice attention model that utilizes both global and local information, along with an evidential critical loss, to perform evidential deep learning for the detection in MR images of prostate cancer, one of the most common cancers and a leading cause of cancer-related death in men. We perform extensive experiments with our model on two different datasets and achieve state-of-the-art performance in prostate cancer detection along with improved epistemic uncertainty estimation. The implementation of the model is available at https://github.com/aL3x-O-o-Hung/GLCSA_ECLoss.
CSAM: A 2.5D Cross-Slice Attention Module for Anisotropic Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 08, 2023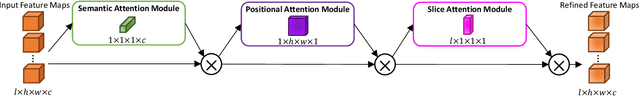
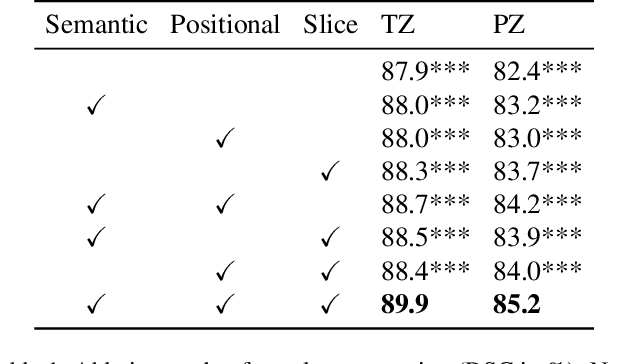
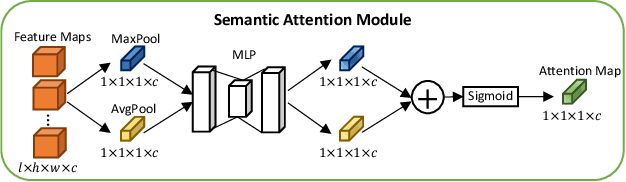
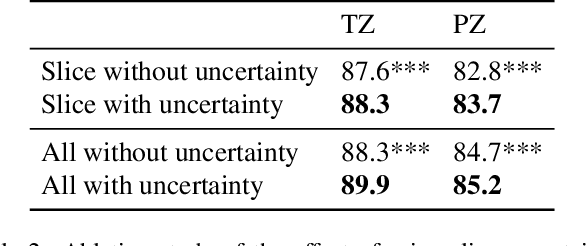
Abstract:A large portion of volumetric medical data, especially magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, is anisotropic, as the through-plane resolution is typically much lower than the in-plane resolution. Both 3D and purely 2D deep learning-based segmentation methods are deficient in dealing with such volumetric data since the performance of 3D methods suffers when confronting anisotropic data, and 2D methods disregard crucial volumetric information. Insufficient work has been done on 2.5D methods, in which 2D convolution is mainly used in concert with volumetric information. These models focus on learning the relationship across slices, but typically have many parameters to train. We offer a Cross-Slice Attention Module (CSAM) with minimal trainable parameters, which captures information across all the slices in the volume by applying semantic, positional, and slice attention on deep feature maps at different scales. Our extensive experiments using different network architectures and tasks demonstrate the usefulness and generalizability of CSAM. Associated code is available at https://github.com/aL3x-O-o-Hung/CSAM.
PartDiff: Image Super-resolution with Partial Diffusion Models
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) have achieved impressive performance on various image generation tasks, including image super-resolution. By learning to reverse the process of gradually diffusing the data distribution into Gaussian noise, DDPMs generate new data by iteratively denoising from random noise. Despite their impressive performance, diffusion-based generative models suffer from high computational costs due to the large number of denoising steps.In this paper, we first observed that the intermediate latent states gradually converge and become indistinguishable when diffusing a pair of low- and high-resolution images. This observation inspired us to propose the Partial Diffusion Model (PartDiff), which diffuses the image to an intermediate latent state instead of pure random noise, where the intermediate latent state is approximated by the latent of diffusing the low-resolution image. During generation, Partial Diffusion Models start denoising from the intermediate distribution and perform only a part of the denoising steps. Additionally, to mitigate the error caused by the approximation, we introduce "latent alignment", which aligns the latent between low- and high-resolution images during training. Experiments on both magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and natural images show that, compared to plain diffusion-based super-resolution methods, Partial Diffusion Models significantly reduce the number of denoising steps without sacrificing the quality of generation.
CAT-Net: A Cross-Slice Attention Transformer Model for Prostate Zonal Segmentation in MRI
Mar 29, 2022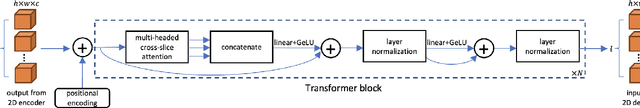
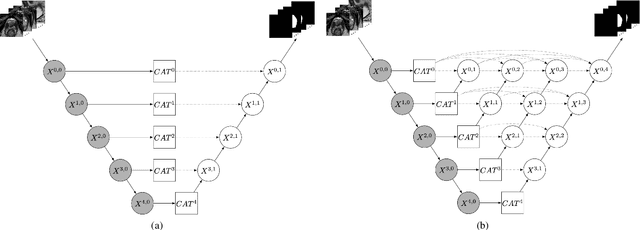
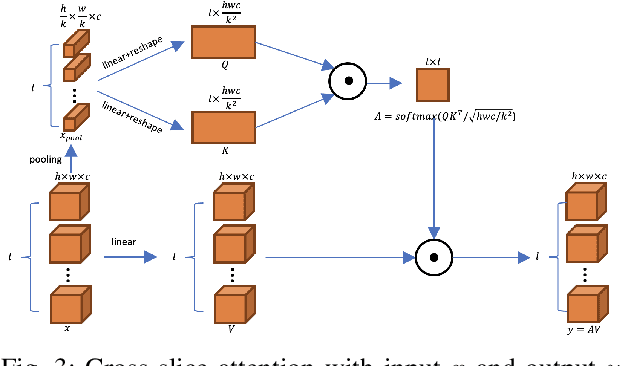
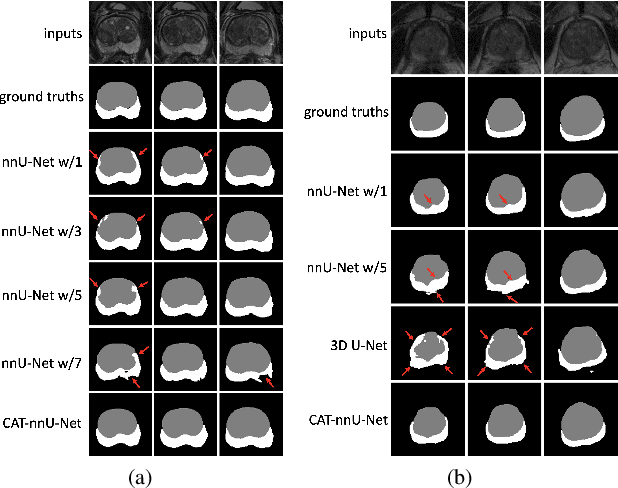
Abstract:Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death among men in the United States. The diagnosis of prostate MRI often relies on the accurate prostate zonal segmentation. However, state-of-the-art automatic segmentation methods often fail to produce well-contained volumetric segmentation of the prostate zones since certain slices of prostate MRI, such as base and apex slices, are harder to segment than other slices. This difficulty can be overcome by accounting for the cross-slice relationship of adjacent slices, but current methods do not fully learn and exploit such relationships. In this paper, we propose a novel cross-slice attention mechanism, which we use in a Transformer module to systematically learn the cross-slice relationship at different scales. The module can be utilized in any existing learning-based segmentation framework with skip connections. Experiments show that our cross-slice attention is able to capture the cross-slice information in prostate zonal segmentation and improve the performance of current state-of-the-art methods. Our method significantly improves segmentation accuracy in the peripheral zone, such that the segmentation results are consistent across all the prostate slices (apex, mid-gland, and base).
Automatic Prostate Zonal Segmentation Using Fully Convolutional Network with Feature Pyramid Attention
Oct 31, 2019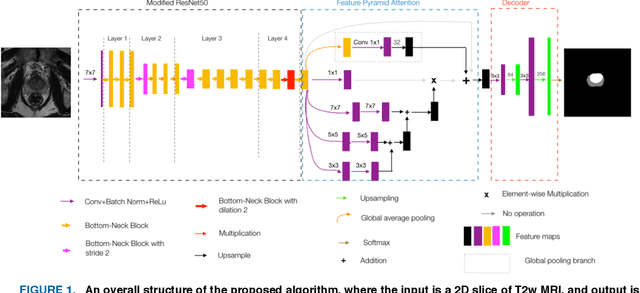
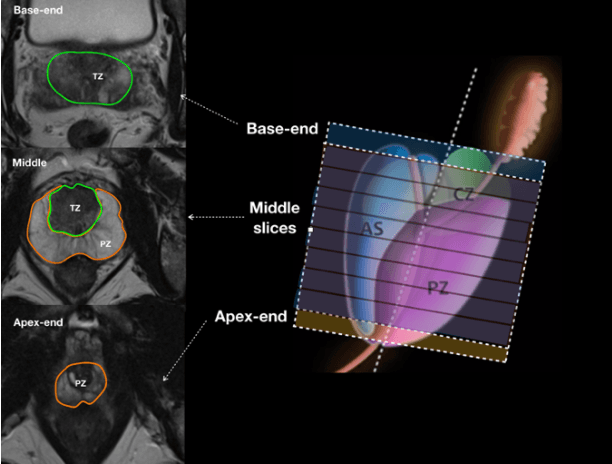
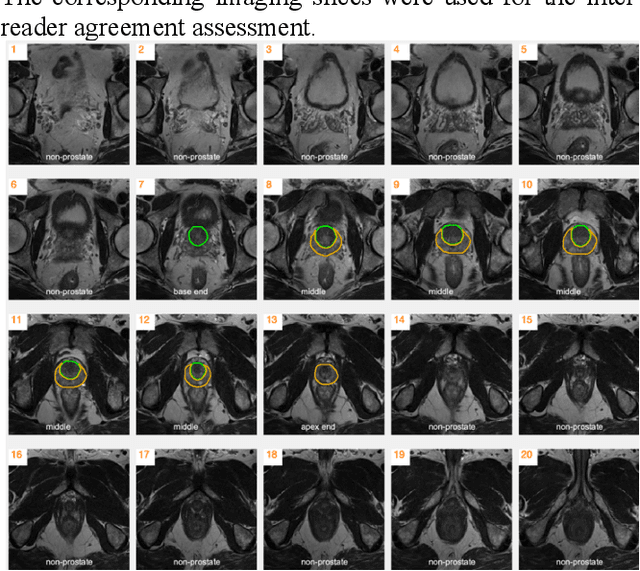
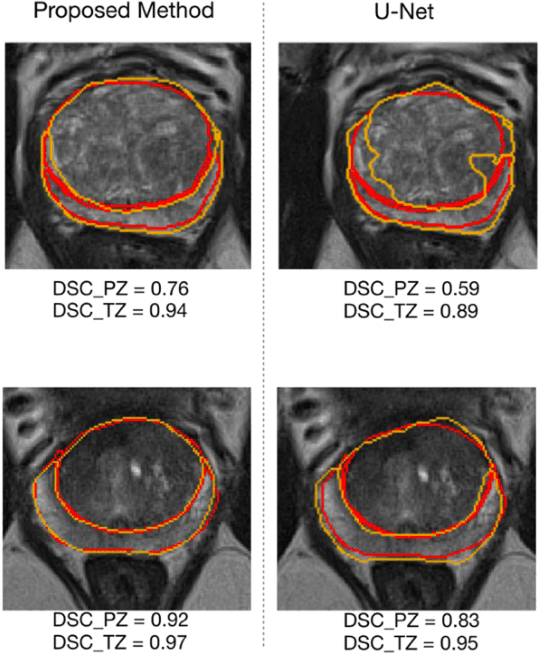
Abstract:Our main objective is to develop a novel deep learning-based algorithm for automatic segmentation of prostate zone and to evaluate the proposed algorithm on an additional independent testing data in comparison with inter-reader consistency between two experts. With IRB approval and HIPAA compliance, we designed a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) for automatic segmentation of the prostatic transition zone (TZ) and peripheral zone (PZ) on T2-weighted (T2w) MRI. The total study cohort included 359 patients from two sources; 313 from a deidentified publicly available dataset (SPIE-AAPM-NCI PROSTATEX challenge) and 46 from a large U.S. tertiary referral center with 3T MRI (external testing dataset (ETD)). The TZ and PZ contours were manually annotated by research fellows, supervised by genitourinary (GU) radiologists. The model was developed using 250 patients and tested internally using the remaining 63 patients from the PROSTATEX (internal testing dataset (ITD)) and tested again (n=46) externally using the ETD. The Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) was used to evaluate the segmentation performance. DSCs for PZ and TZ were 0.74 and 0.86 in the ITD respectively. In the ETD, DSCs for PZ and TZ were 0.74 and 0.792, respectively. The inter-reader consistency (Expert 2 vs. Expert 1) were 0.71 (PZ) and 0.75 (TZ). This novel DL algorithm enabled automatic segmentation of PZ and TZ with high accuracy on both ITD and ETD without a performance difference for PZ and less than 10% TZ difference. In the ETD, the proposed method can be comparable to experts in the segmentation of prostate zones.
Deep Learning-based Radiomic Features for Improving Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Response Prediction in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Sep 09, 2019
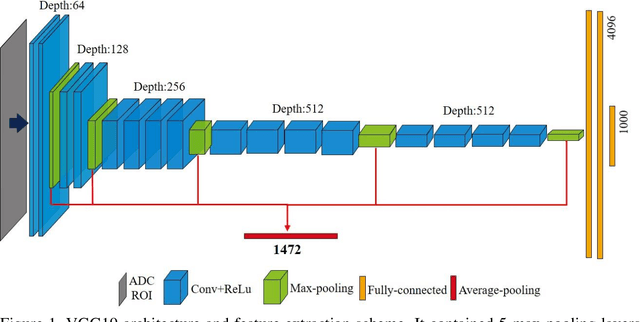
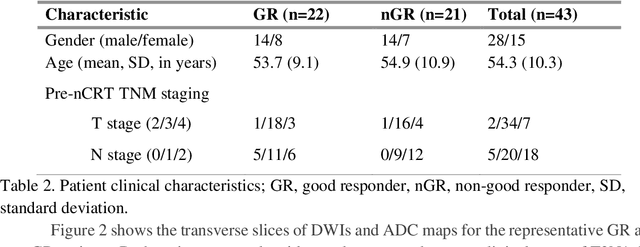
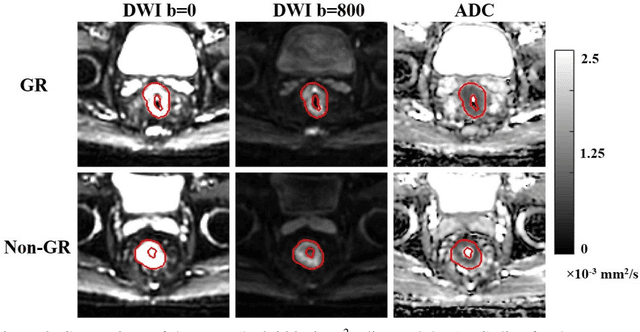
Abstract:Radiomic features achieve promising results in cancer diagnosis, treatment response prediction, and survival prediction. Our goal is to compare the handcrafted (explicitly designed) and deep learning (DL)-based radiomic features extracted from pre-treatment diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images (DWIs) for predicting neoadjuvant chemoradiation treatment (nCRT) response in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). 43 patients receiving nCRT were included. All patients underwent DWIs before nCRT and total mesorectal excision surgery 6-12 weeks after completion of nCRT. Gross tumor volume (GTV) contours were drawn by an experienced radiation oncologist on DWIs. The patient-cohort was split into the responder group (n=22) and the non-responder group (n=21) based on the post-nCRT response assessed by postoperative pathology, MRI or colonoscopy. Handcrafted and DL-based features were extracted from the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map of the DWI using conventional computer-aided diagnosis methods and a pre-trained convolution neural network, respectively. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-logistic regression models were constructed using extracted features for predicting treatment response. The model performance was evaluated with repeated 20 times stratified 4-fold cross-validation using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and compared using the corrected resampled t-test. The model built with handcrafted features achieved the mean area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.64, while the one built with DL-based features yielded the mean AUC of 0.73. The corrected resampled t-test on AUC showed P-value < 0.05. DL-based features extracted from pre-treatment DWIs achieved significantly better classification performance compared with handcrafted features for predicting nCRT response in patients with LARC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge