Kyohoon Jin
SUMMPILOT: Bridging Efficiency and Customization for Interactive Summarization System
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:This paper incorporates the efficiency of automatic summarization and addresses the challenge of generating personalized summaries tailored to individual users' interests and requirements. To tackle this challenge, we introduce SummPilot, an interaction-based customizable summarization system. SummPilot leverages a large language model to facilitate both automatic and interactive summarization. Users can engage with the system to understand document content and personalize summaries through interactive components such as semantic graphs, entity clustering, and explainable evaluation. Our demo and user studies demonstrate SummPilot's adaptability and usefulness for customizable summarization.
GRADE: Generating multi-hop QA and fine-gRAined Difficulty matrix for RAG Evaluation
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems are widely adopted in knowledge-intensive NLP tasks, but current evaluations often overlook the structural complexity and multi-step reasoning required in real-world scenarios. These benchmarks overlook key factors such as the interaction between retrieval difficulty and reasoning depth. To address this gap, we propose \textsc{GRADE}, a novel evaluation framework that models task difficulty along two orthogonal dimensions: (1) reasoning depth, defined by the number of inference steps (hops), and (2) semantic distance between the query and its supporting evidence. We construct a synthetic multi-hop QA dataset from factual news articles by extracting knowledge graphs and augmenting them through semantic clustering to recover missing links, allowing us to generate diverse and difficulty-controlled queries. Central to our framework is a 2D difficulty matrix that combines generator-side and retriever-side difficulty. Experiments across multiple domains and models show that error rates strongly correlate with our difficulty measures, validating their diagnostic utility. \textsc{GRADE} enables fine-grained analysis of RAG performance and provides a scalable foundation for evaluating and improving multi-hop reasoning in real-world applications.
Plug-in and Fine-tuning: Bridging the Gap between Small Language Models and Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are renowned for their extensive linguistic knowledge and strong generalization capabilities, but their high computational demands make them unsuitable for resource-constrained environments. In contrast, small language models (SLMs) are computationally efficient but often lack the broad generalization capacity of LLMs. To bridge this gap, we propose PiFi, a novel framework that combines the strengths of both LLMs and SLMs to achieve high performance while maintaining efficiency. PiFi integrates a single frozen layer from an LLM into a SLM and fine-tunes the combined model for specific tasks, boosting performance without a significant increase in computational cost. We show that PiFi delivers consistent performance improvements across a range of natural language processing tasks, including both natural language understanding and generation. Moreover, our findings demonstrate PiFi's ability to effectively leverage LLM knowledge, enhancing generalization to unseen domains and facilitating the transfer of linguistic abilities.
Multi-News+: Cost-efficient Dataset Cleansing via LLM-based Data Annotation
Apr 15, 2024
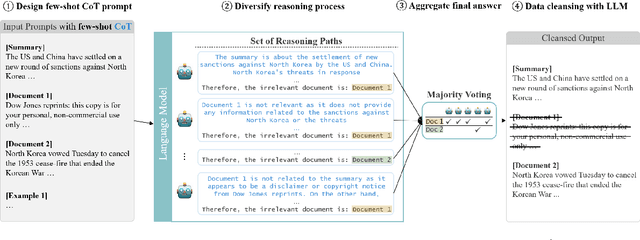
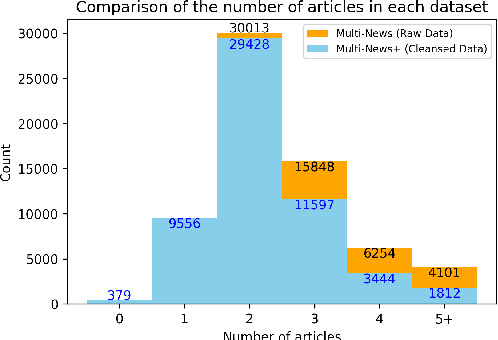
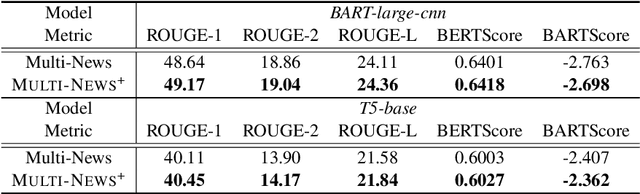
Abstract:The quality of the dataset is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability of downstream task models. However, datasets often contain noisy data inadvertently included during the construction process. Numerous attempts have been made to correct this issue through human annotators. However, hiring and managing human annotators is expensive and time-consuming. As an alternative, recent studies are exploring the use of large language models (LLMs) for data annotation. In this study, we present a case study that extends the application of LLM-based data annotation to enhance the quality of existing datasets through a cleansing strategy. Specifically, we leverage approaches such as chain-of-thought (CoT) and majority voting to imitate human annotation and classify unrelated documents from the Multi-News dataset, which is widely used for the multi-document summarization task. Through our proposed cleansing method, we introduce an enhanced Multi-News+. By employing LLMs for data cleansing, we demonstrate an efficient and effective approach to improving dataset quality without relying on expensive human annotation efforts.
Enhancing Effectiveness and Robustness in a Low-Resource Regime via Decision-Boundary-aware Data Augmentation
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:Efforts to leverage deep learning models in low-resource regimes have led to numerous augmentation studies. However, the direct application of methods such as mixup and cutout to text data, is limited due to their discrete characteristics. While methods using pretrained language models have exhibited efficiency, they require additional considerations for robustness. Inspired by recent studies on decision boundaries, this paper proposes a decision-boundary-aware data augmentation strategy to enhance robustness using pretrained language models. The proposed technique first focuses on shifting the latent features closer to the decision boundary, followed by reconstruction to generate an ambiguous version with a soft label. Additionally, mid-K sampling is suggested to enhance the diversity of the generated sentences. This paper demonstrates the performance of the proposed augmentation strategy compared to other methods through extensive experiments. Furthermore, the ablation study reveals the effect of soft labels and mid-K sampling and the extensibility of the method with curriculum data augmentation.
SoftEDA: Rethinking Rule-Based Data Augmentation with Soft Labels
Feb 08, 2024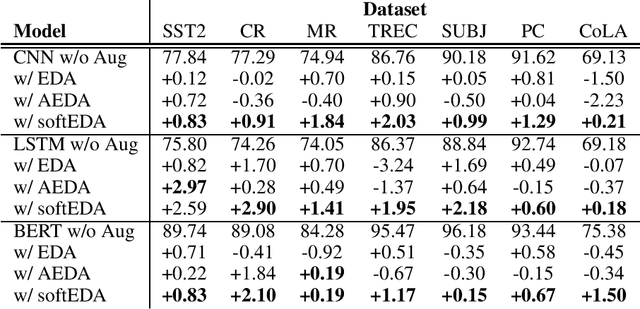
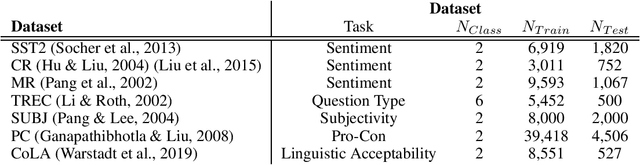
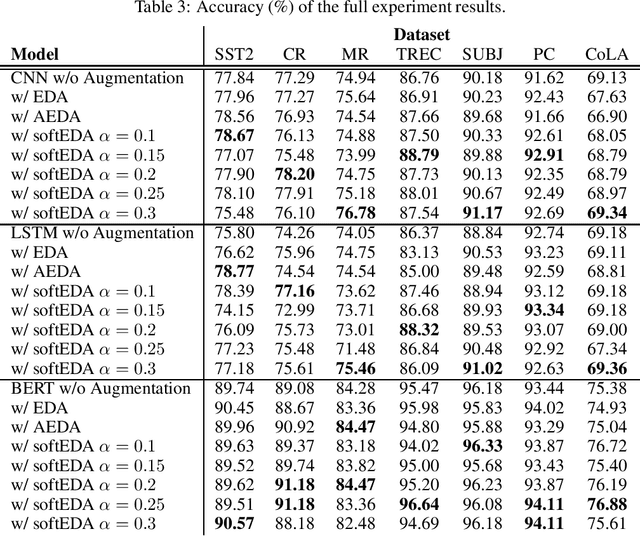
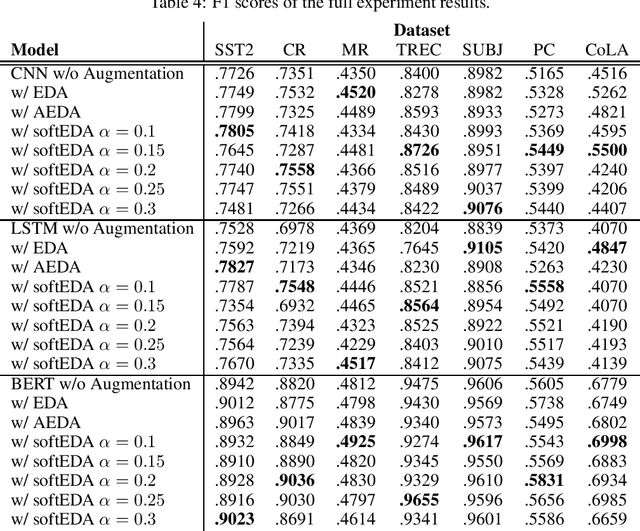
Abstract:Rule-based text data augmentation is widely used for NLP tasks due to its simplicity. However, this method can potentially damage the original meaning of the text, ultimately hurting the performance of the model. To overcome this limitation, we propose a straightforward technique for applying soft labels to augmented data. We conducted experiments across seven different classification tasks and empirically demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed approach. We have publicly opened our source code for reproducibility.
AutoAugment Is What You Need: Enhancing Rule-based Augmentation Methods in Low-resource Regimes
Feb 08, 2024


Abstract:Text data augmentation is a complex problem due to the discrete nature of sentences. Although rule-based augmentation methods are widely adopted in real-world applications because of their simplicity, they suffer from potential semantic damage. Previous researchers have suggested easy data augmentation with soft labels (softEDA), employing label smoothing to mitigate this problem. However, finding the best factor for each model and dataset is challenging; therefore, using softEDA in real-world applications is still difficult. In this paper, we propose adapting AutoAugment to solve this problem. The experimental results suggest that the proposed method can boost existing augmentation methods and that rule-based methods can enhance cutting-edge pre-trained language models. We offer the source code.
GPTs Are Multilingual Annotators for Sequence Generation Tasks
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:Data annotation is an essential step for constructing new datasets. However, the conventional approach of data annotation through crowdsourcing is both time-consuming and expensive. In addition, the complexity of this process increases when dealing with low-resource languages owing to the difference in the language pool of crowdworkers. To address these issues, this study proposes an autonomous annotation method by utilizing large language models, which have been recently demonstrated to exhibit remarkable performance. Through our experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed method is not just cost-efficient but also applicable for low-resource language annotation. Additionally, we constructed an image captioning dataset using our approach and are committed to open this dataset for future study. We have opened our source code for further study and reproducibility.
Restoring and Mining the Records of the Joseon Dynasty via Neural Language Modeling and Machine Translation
May 07, 2021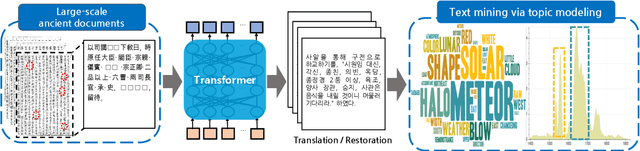
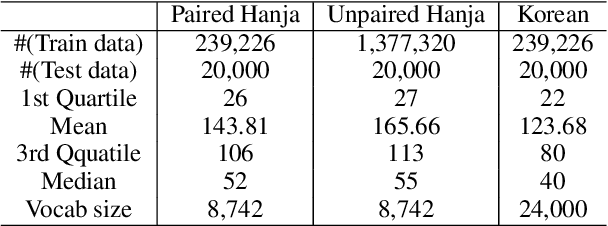

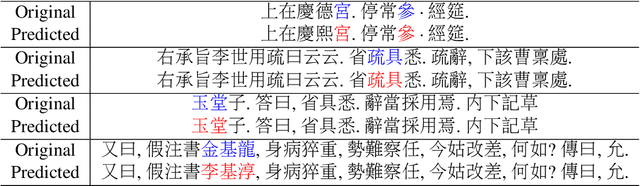
Abstract:Understanding voluminous historical records provides clues on the past in various aspects, such as social and political issues and even natural science facts. However, it is generally difficult to fully utilize the historical records, since most of the documents are not written in a modern language and part of the contents are damaged over time. As a result, restoring the damaged or unrecognizable parts as well as translating the records into modern languages are crucial tasks. In response, we present a multi-task learning approach to restore and translate historical documents based on a self-attention mechanism, specifically utilizing two Korean historical records, ones of the most voluminous historical records in the world. Experimental results show that our approach significantly improves the accuracy of the translation task than baselines without multi-task learning. In addition, we present an in-depth exploratory analysis on our translated results via topic modeling, uncovering several significant historical events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge