Restoring and Mining the Records of the Joseon Dynasty via Neural Language Modeling and Machine Translation
Paper and Code
May 07, 2021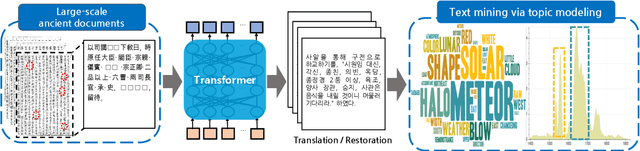
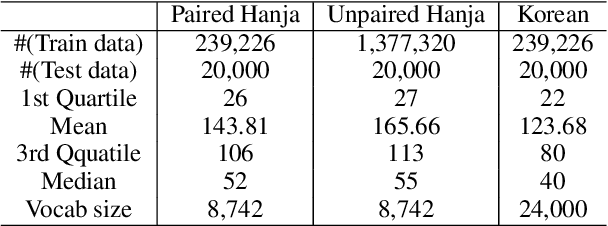

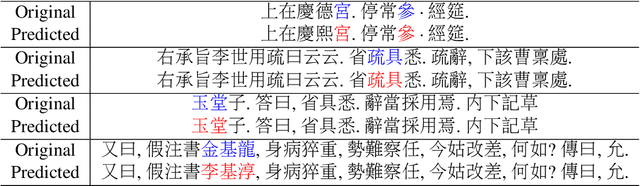
Understanding voluminous historical records provides clues on the past in various aspects, such as social and political issues and even natural science facts. However, it is generally difficult to fully utilize the historical records, since most of the documents are not written in a modern language and part of the contents are damaged over time. As a result, restoring the damaged or unrecognizable parts as well as translating the records into modern languages are crucial tasks. In response, we present a multi-task learning approach to restore and translate historical documents based on a self-attention mechanism, specifically utilizing two Korean historical records, ones of the most voluminous historical records in the world. Experimental results show that our approach significantly improves the accuracy of the translation task than baselines without multi-task learning. In addition, we present an in-depth exploratory analysis on our translated results via topic modeling, uncovering several significant historical events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge