Konrad Habel
ViewSparsifier: Killing Redundancy in Multi-View Plant Phenotyping
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Plant phenotyping involves analyzing observable characteristics of plants to better understand their growth, health, and development. In the context of deep learning, this analysis is often approached through single-view classification or regression models. However, these methods often fail to capture all information required for accurate estimation of target phenotypic traits, which can adversely affect plant health assessment and harvest readiness prediction. To address this, the Growth Modelling (GroMo) Grand Challenge at ACM Multimedia 2025 provides a multi-view dataset featuring multiple plants and two tasks: Plant Age Prediction and Leaf Count Estimation. Each plant is photographed from multiple heights and angles, leading to significant overlap and redundancy in the captured information. To learn view-invariant embeddings, we incorporate 24 views, referred to as the selection vector, in a random selection. Our ViewSparsifier approach won both tasks. For further improvement and as a direction for future research, we also experimented with randomized view selection across all five height levels (120 views total), referred to as selection matrices.
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
SoccerNet 2024 Challenges Results
Sep 16, 2024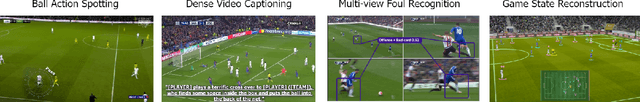
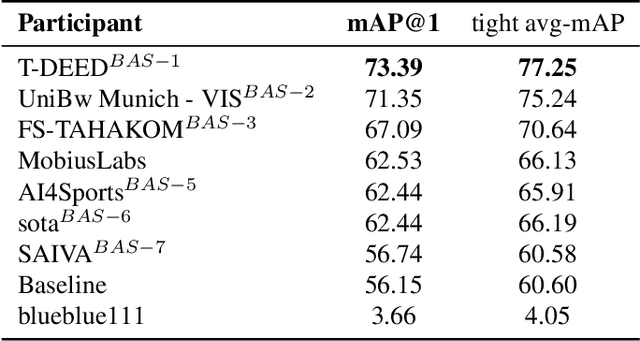
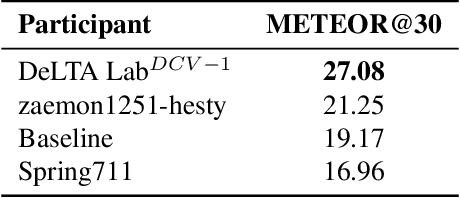
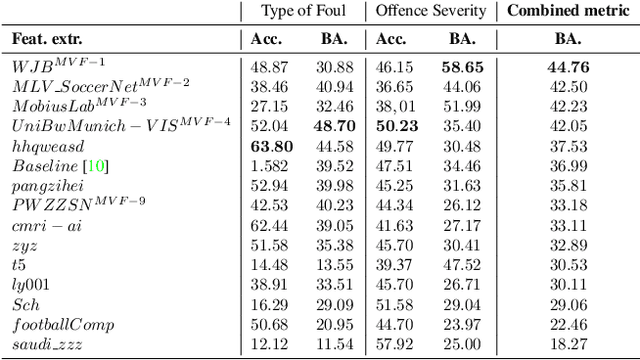
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2024 challenges represent the fourth annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. These challenges aim to advance research across multiple themes in football, including broadcast video understanding, field understanding, and player understanding. This year, the challenges encompass four vision-based tasks. (1) Ball Action Spotting, focusing on precisely localizing when and which soccer actions related to the ball occur, (2) Dense Video Captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps, (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, a novel task focusing on analyzing multiple viewpoints of a potential foul incident to classify whether a foul occurred and assess its severity, (4) Game State Reconstruction, another novel task focusing on reconstructing the game state from broadcast videos onto a 2D top-view map of the field. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
SoccerNet 2023 Challenges Results
Sep 12, 2023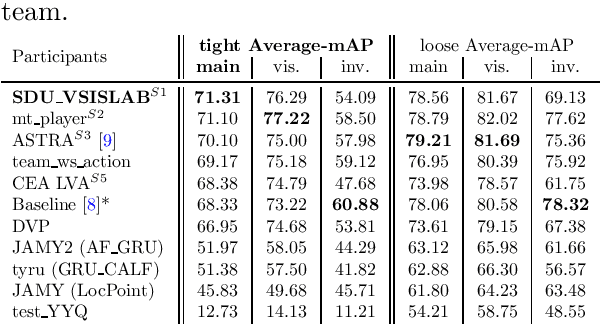
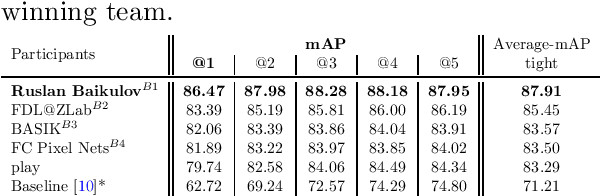
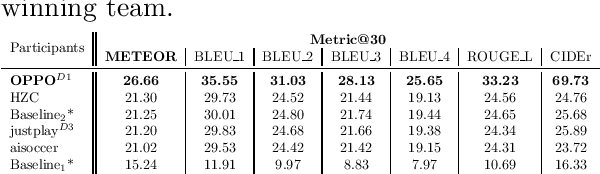
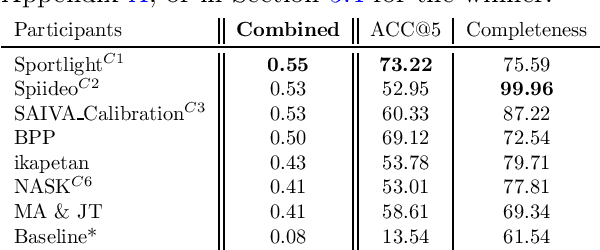
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2023 challenges were the third annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. For this third edition, the challenges were composed of seven vision-based tasks split into three main themes. The first theme, broadcast video understanding, is composed of three high-level tasks related to describing events occurring in the video broadcasts: (1) action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to global actions in soccer, (2) ball action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to the soccer ball change of state, and (3) dense video captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps. The second theme, field understanding, relates to the single task of (4) camera calibration, focusing on retrieving the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from images. The third and last theme, player understanding, is composed of three low-level tasks related to extracting information about the players: (5) re-identification, focusing on retrieving the same players across multiple views, (6) multiple object tracking, focusing on tracking players and the ball through unedited video streams, and (7) jersey number recognition, focusing on recognizing the jersey number of players from tracklets. Compared to the previous editions of the SoccerNet challenges, tasks (2-3-7) are novel, including new annotations and data, task (4) was enhanced with more data and annotations, and task (6) now focuses on end-to-end approaches. More information on the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards are available on https://www.soccer-net.org. Baselines and development kits can be found on https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Orientation-Guided Contrastive Learning for UAV-View Geo-Localisation
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:Retrieving relevant multimedia content is one of the main problems in a world that is increasingly data-driven. With the proliferation of drones, high quality aerial footage is now available to a wide audience for the first time. Integrating this footage into applications can enable GPS-less geo-localisation or location correction. In this paper, we present an orientation-guided training framework for UAV-view geo-localisation. Through hierarchical localisation orientations of the UAV images are estimated in relation to the satellite imagery. We propose a lightweight prediction module for these pseudo labels which predicts the orientation between the different views based on the contrastive learned embeddings. We experimentally demonstrate that this prediction supports the training and outperforms previous approaches. The extracted pseudo-labels also enable aligned rotation of the satellite image as augmentation to further strengthen the generalisation. During inference, we no longer need this orientation module, which means that no additional computations are required. We achieve state-of-the-art results on both the University-1652 and University-160k datasets.
Sample4Geo: Hard Negative Sampling For Cross-View Geo-Localisation
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:Cross-View Geo-Localisation is still a challenging task where additional modules, specific pre-processing or zooming strategies are necessary to determine accurate positions of images. Since different views have different geometries, pre-processing like polar transformation helps to merge them. However, this results in distorted images which then have to be rectified. Adding hard negatives to the training batch could improve the overall performance but with the default loss functions in geo-localisation it is difficult to include them. In this article, we present a simplified but effective architecture based on contrastive learning with symmetric InfoNCE loss that outperforms current state-of-the-art results. Our framework consists of a narrow training pipeline that eliminates the need of using aggregation modules, avoids further pre-processing steps and even increases the generalisation capability of the model to unknown regions. We introduce two types of sampling strategies for hard negatives. The first explicitly exploits geographically neighboring locations to provide a good starting point. The second leverages the visual similarity between the image embeddings in order to mine hard negative samples. Our work shows excellent performance on common cross-view datasets like CVUSA, CVACT, University-1652 and VIGOR. A comparison between cross-area and same-area settings demonstrate the good generalisation capability of our model.
CLIP-ReIdent: Contrastive Training for Player Re-Identification
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:Sports analytics benefits from recent advances in machine learning providing a competitive advantage for teams or individuals. One important task in this context is the performance measurement of individual players to provide reports and log files for subsequent analysis. During sport events like basketball, this involves the re-identification of players during a match either from multiple camera viewpoints or from a single camera viewpoint at different times. In this work, we investigate whether it is possible to transfer the out-standing zero-shot performance of pre-trained CLIP models to the domain of player re-identification. For this purpose we reformulate the contrastive language-to-image pre-training approach from CLIP to a contrastive image-to-image training approach using the InfoNCE loss as training objective. Unlike previous work, our approach is entirely class-agnostic and benefits from large-scale pre-training. With a fine-tuned CLIP ViT-L/14 model we achieve 98.44 % mAP on the MMSports 2022 Player Re-Identification challenge. Furthermore we show that the CLIP Vision Transformers have already strong OCR capabilities to identify useful player features like shirt numbers in a zero-shot manner without any fine-tuning on the dataset. By applying the Score-CAM algorithm we visualise the most important image regions that our fine-tuned model identifies when calculating the similarity score between two images of a player.
Less Is More: Linear Layers on CLIP Features as Powerful VizWiz Model
Jun 10, 2022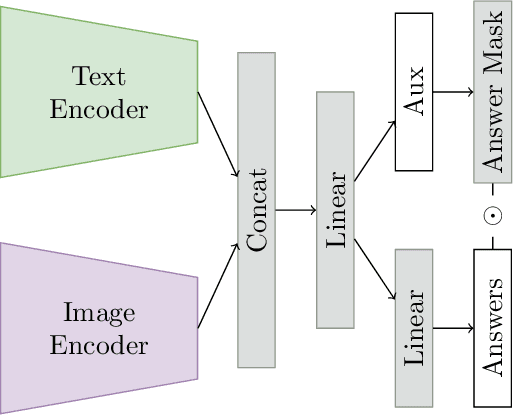
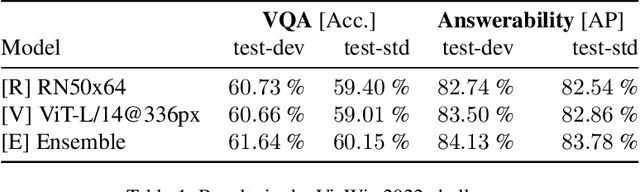
Abstract:Current architectures for multi-modality tasks such as visual question answering suffer from their high complexity. As a result, these architectures are difficult to train and require high computational resources. To address these problems we present a CLIP-based architecture that does not require any fine-tuning of the feature extractors. A simple linear classifier is used on the concatenated features of the image and text encoder. During training an auxiliary loss is added which operates on the answer types. The resulting classification is then used as an attention gate on the answer class selection. On the VizWiz 2022 Visual Question Answering Challenge we achieve 60.15 % accuracy on Task 1: Predict Answer to a Visual Question and AP score of 83.78 % on Task 2: Predict Answerability of a Visual Question.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge