Kipton Barros
Ensemble Knowledge Distillation for Machine Learning Interatomic Potentials
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) are a promising tool to accelerate atomistic simulations and molecular property prediction. The quality of MLIPs strongly depends on the quantity of available training data as well as the quantum chemistry (QC) level of theory used to generate that data. Datasets generated with high-fidelity QC methods, such as coupled cluster, are typically restricted to small molecules and may be missing energy gradients. With this limited quantity of data, it is often difficult to train good MLIP models. We present an ensemble knowledge distillation (EKD) method to improve MLIP accuracy when trained to energy-only datasets. In our EKD approach, first, multiple teacher models are trained to QC energies and then used to generate atomic forces for all configurations in the dataset. Next, a student MLIP is trained to both QC energies and to ensemble-averaged forces generated by the teacher models. We apply this workflow on the ANI-1ccx dataset which consists of organic molecules with configuration energies computed at the coupled cluster level of theory. The resulting student MLIPs achieve new state-of-the-art accuracy on the out-of-sample COMP6 benchmark and improved stability for molecular dynamics simulations. The EKD approach for MLIP is broadly applicable for chemical, biomolecular and materials science simulations.
Teacher-student training improves accuracy and efficiency of machine learning inter-atomic potentials
Feb 07, 2025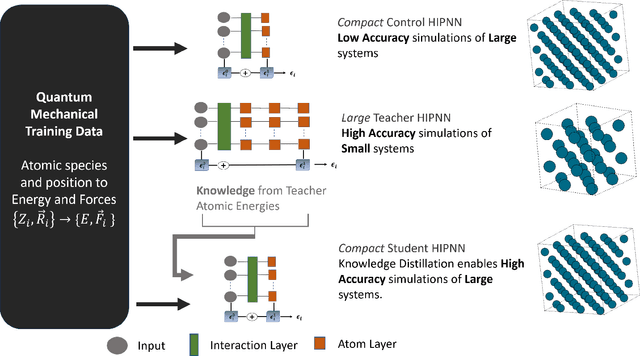

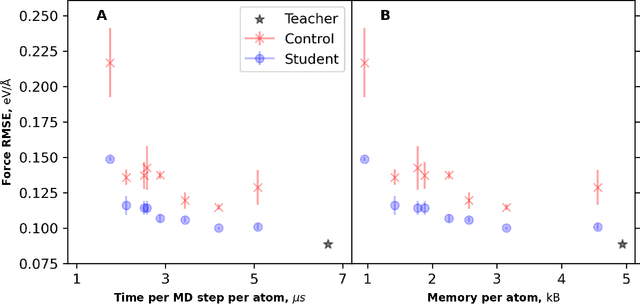
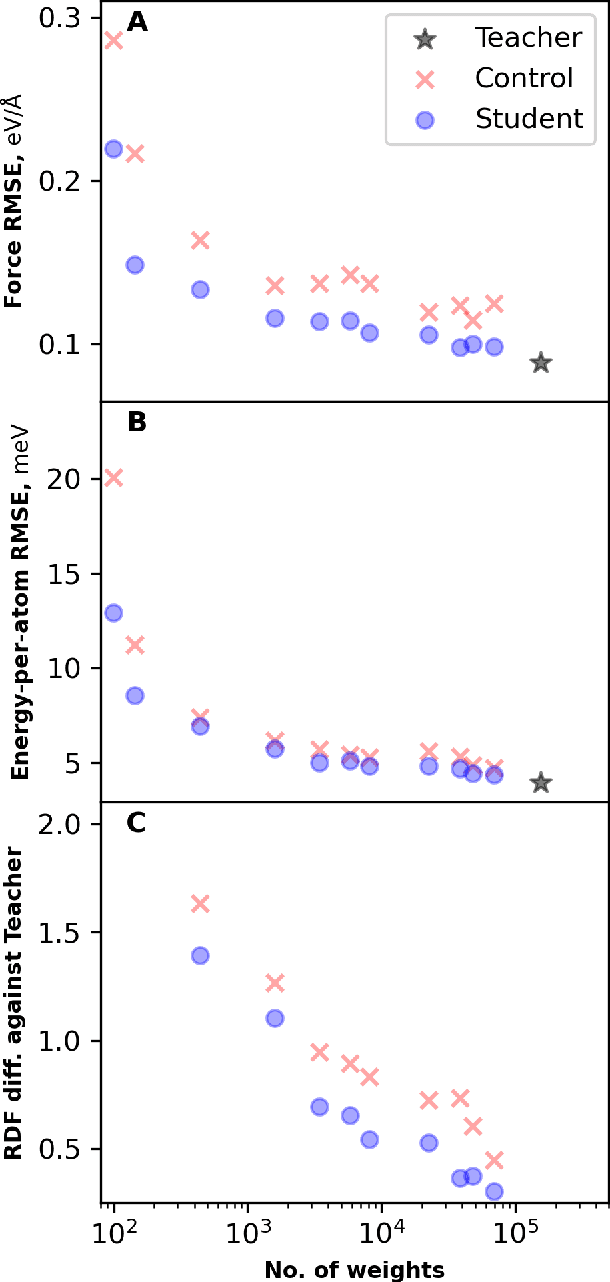
Abstract:Machine learning inter-atomic potentials (MLIPs) are revolutionizing the field of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Recent MLIPs have tended towards more complex architectures trained on larger datasets. The resulting increase in computational and memory costs may prohibit the application of these MLIPs to perform large-scale MD simulations. Here, we present a teacher-student training framework in which the latent knowledge from the teacher (atomic energies) is used to augment the students' training. We show that the light-weight student MLIPs have faster MD speeds at a fraction of the memory footprint compared to the teacher models. Remarkably, the student models can even surpass the accuracy of the teachers, even though both are trained on the same quantum chemistry dataset. Our work highlights a practical method for MLIPs to reduce the resources required for large-scale MD simulations.
Machine-learning Kondo physics using variational autoencoders
Jul 16, 2021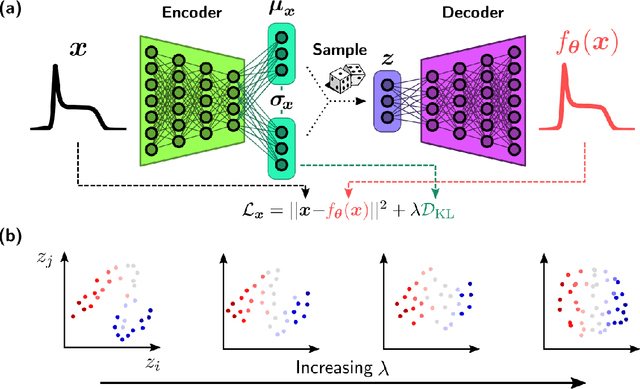
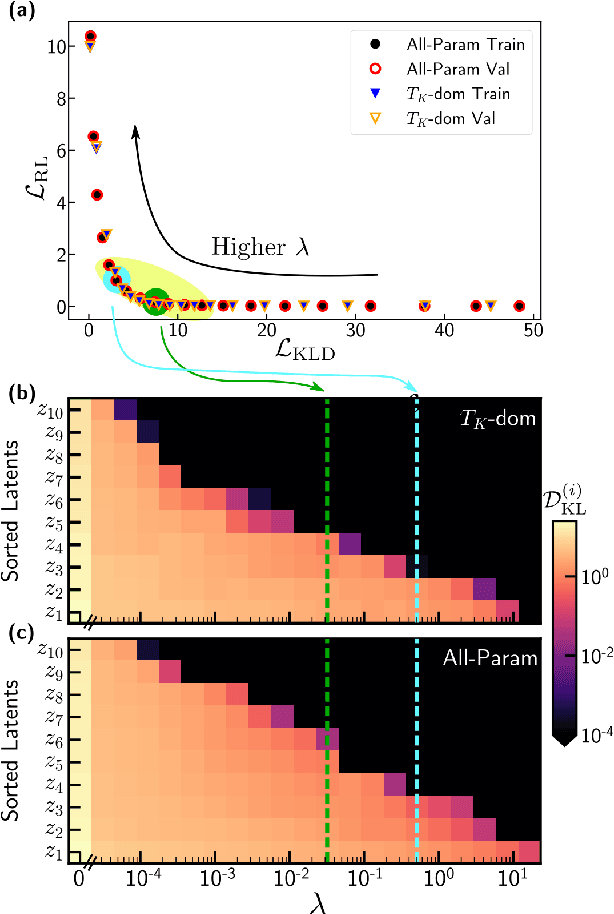
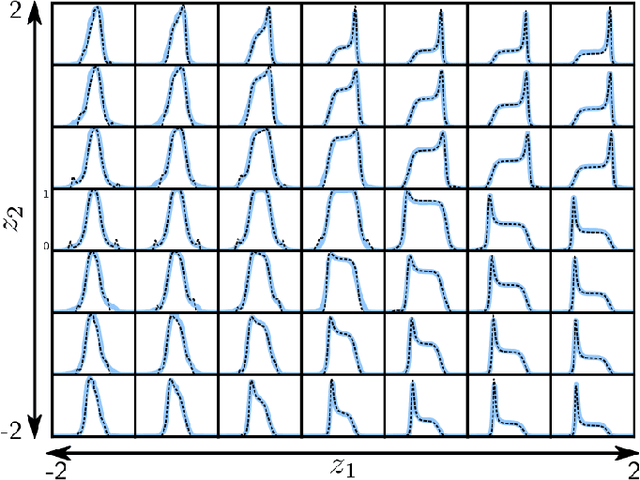
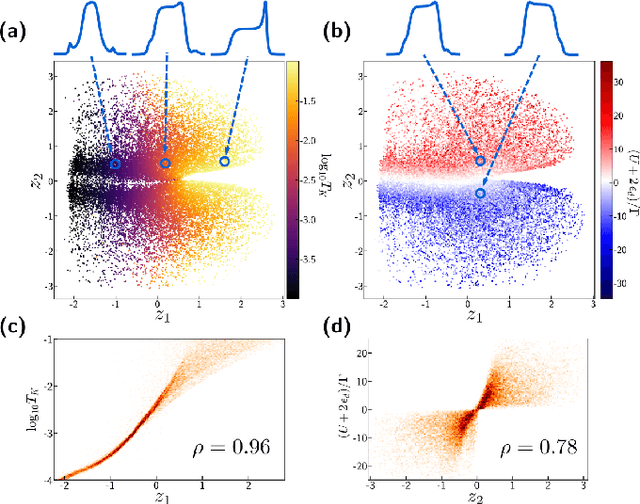
Abstract:We employ variational autoencoders to extract physical insight from a dataset of one-particle Anderson impurity model spectral functions. Autoencoders are trained to find a low-dimensional, latent space representation that faithfully characterizes each element of the training set, as measured by a reconstruction error. Variational autoencoders, a probabilistic generalization of standard autoencoders, further condition the learned latent space to promote highly interpretable features. In our study, we find that the learned latent space components strongly correlate with well known, but nontrivial, parameters that characterize emergent behaviors in the Anderson impurity model. In particular, one latent space component correlates with particle-hole asymmetry, while another is in near one-to-one correspondence with the Kondo temperature, a dynamically generated low-energy scale in the impurity model. With symbolic regression, we model this component as a function of bare physical input parameters and "rediscover" the non-perturbative formula for the Kondo temperature. The machine learning pipeline we develop opens opportunities to discover new domain knowledge in other physical systems.
Simple and efficient algorithms for training machine learning potentials to force data
Jun 09, 2020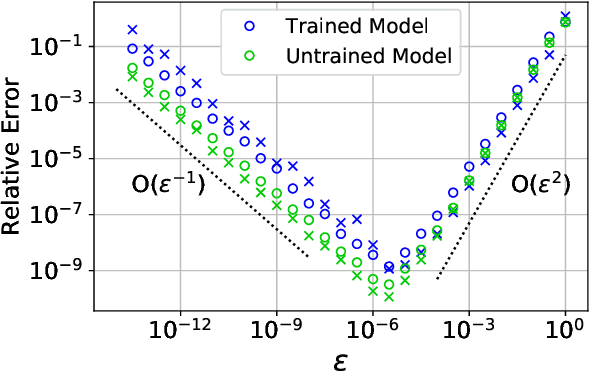
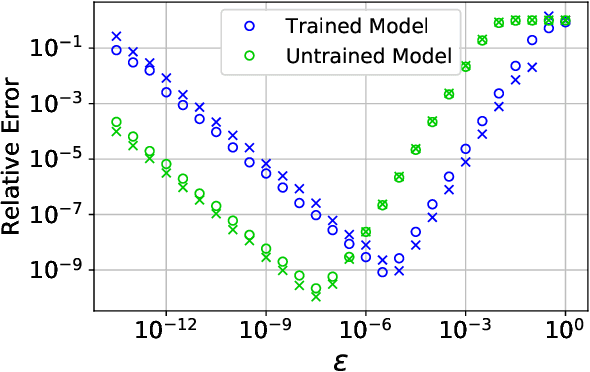
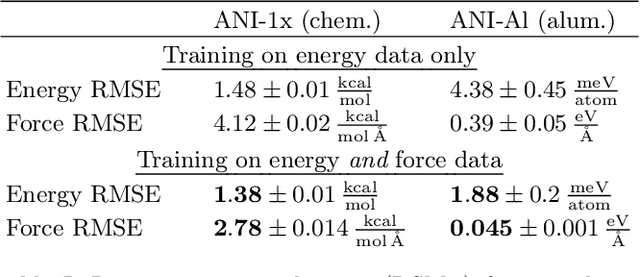
Abstract:Abstract Machine learning models, trained on data from ab initio quantum simulations, are yielding molecular dynamics potentials with unprecedented accuracy. One limiting factor is the quantity of available training data, which can be expensive to obtain. A quantum simulation often provides all atomic forces, in addition to the total energy of the system. These forces provide much more information than the energy alone. It may appear that training a model to this large quantity of force data would introduce significant computational costs. Actually, training to all available force data should only be a few times more expensive than training to energies alone. Here, we present a new algorithm for efficient force training, and benchmark its accuracy by training to forces from real-world datasets for organic chemistry and bulk aluminum.
Automated discovery of a robust interatomic potential for aluminum
Mar 10, 2020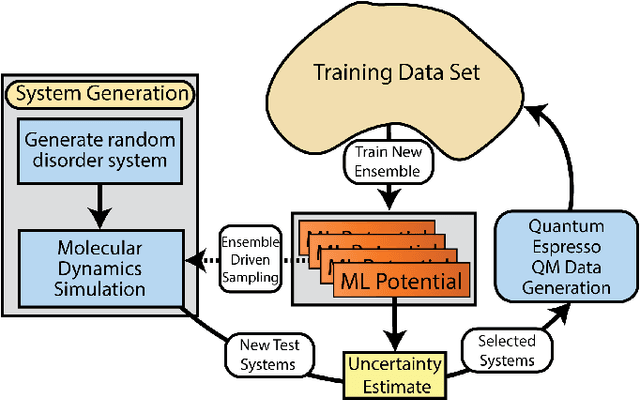
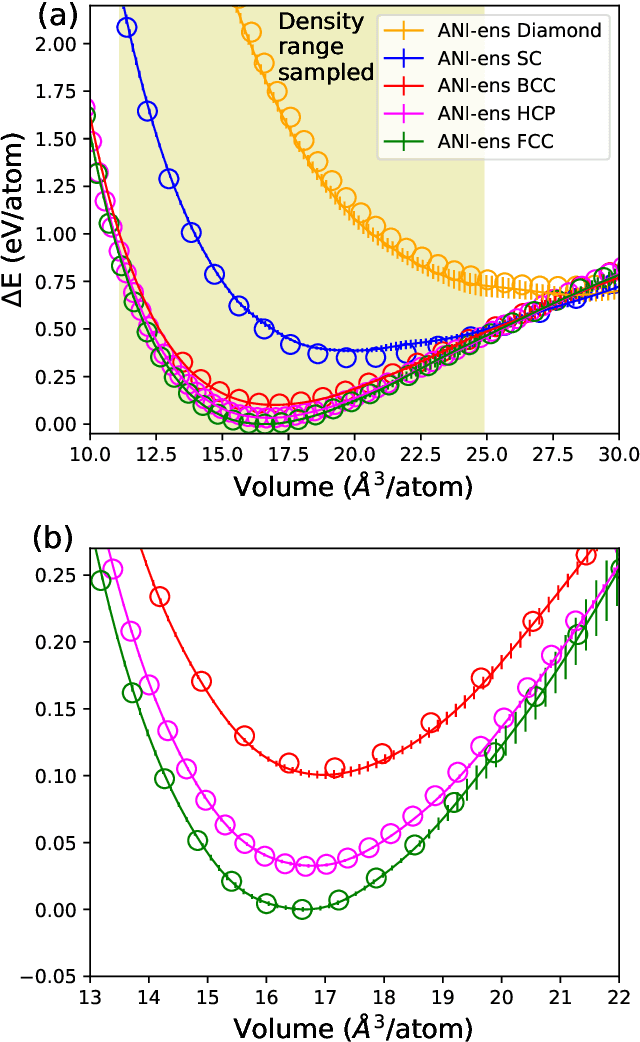
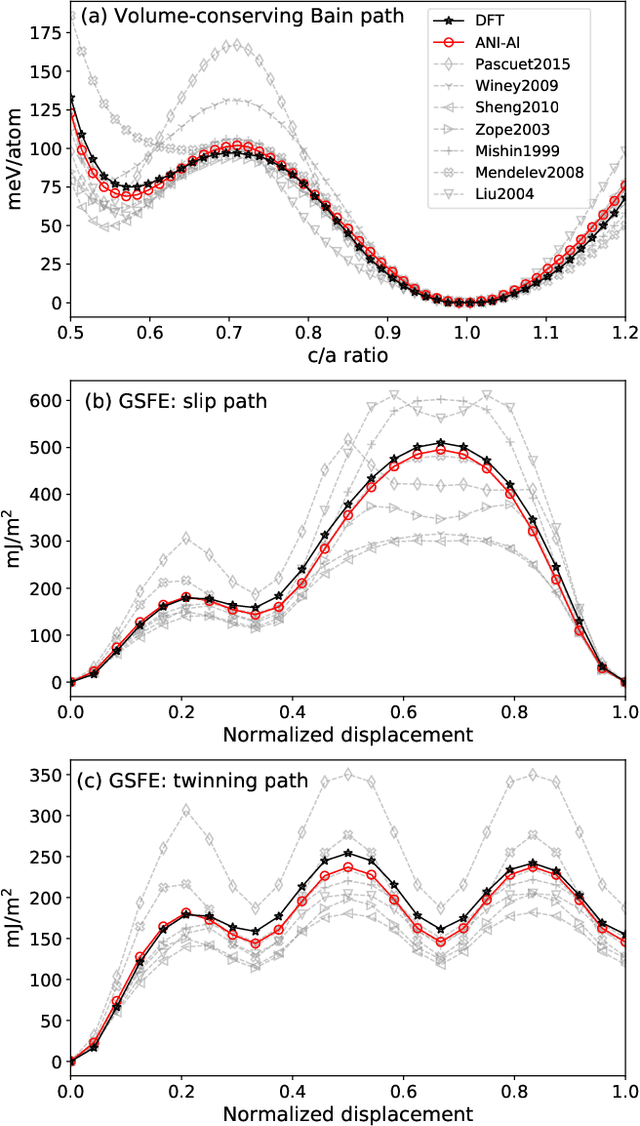
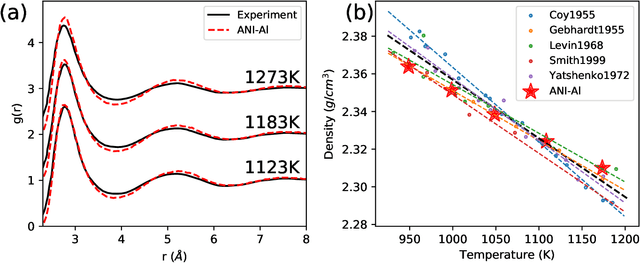
Abstract:Atomistic molecular dynamics simulation is an important tool for predicting materials properties. Accuracy depends crucially on the model for the interatomic potential. The gold standard would be quantum mechanics (QM) based force calculations, but such a first-principles approach becomes prohibitively expensive at large system sizes. Efficient machine learning models (ML) have become increasingly popular as surrogates for QM. Neural networks with many thousands of parameters excel in capturing structure within a large dataset, but may struggle to extrapolate beyond the scope of the available data. Here we present a highly automated active learning approach to iteratively collect new QM data that best resolves weaknesses in the existing ML model. We exemplify our approach by developing a general potential for elemental aluminum. At each active learning iteration, the method (1) trains an ANI-style neural network potential from the available data, (2) uses this potential to drive molecular dynamics simulations, and (3) collects new QM data whenever the neural network identifies an atomic configuration for which it cannot make a good prediction. All molecular dynamics simulations are initialized to a disordered configuration, and then driven according to randomized, time-varying temperatures. This nonequilibrium molecular dynamics forms a variety of crystalline and defected configurations. By training on all such automatically collected data, we produce ANI-Al, our new interatomic potential for aluminum. We demonstrate the remarkable transferability of ANI-Al by benchmarking against experimental data, e.g., the radial distribution function in melt, various properties of the stable face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal, and the coexistence curve between melt and FCC.
Hierarchical modeling of molecular energies using a deep neural network
Sep 29, 2017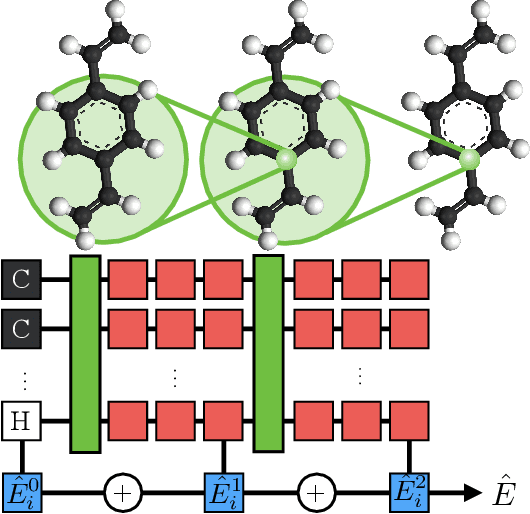
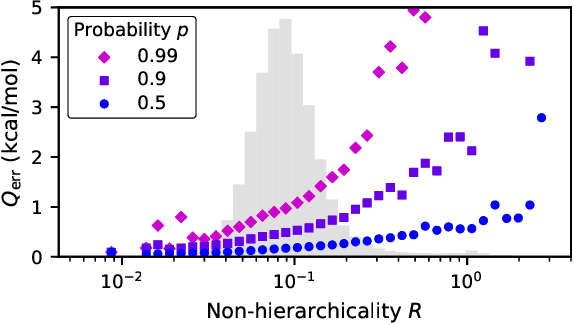
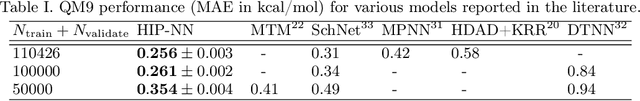
Abstract:We introduce the Hierarchically Interacting Particle Neural Network (HIP-NN) to model molecular properties from datasets of quantum calculations. Inspired by a many-body expansion, HIP-NN decomposes properties, such as energy, as a sum over hierarchical terms. These terms are generated from a neural network--a composition of many nonlinear transformations--acting on a representation of the molecule. HIP-NN achieves state-of-the-art performance on a dataset of 131k ground state organic molecules, and predicts energies with 0.26 kcal/mol mean absolute error. With minimal tuning, our model is also competitive on a dataset of molecular dynamics trajectories. In addition to enabling accurate energy predictions, the hierarchical structure of HIP-NN helps to identify regions of model uncertainty.
Inferring low-dimensional microstructure representations using convolutional neural networks
Nov 08, 2016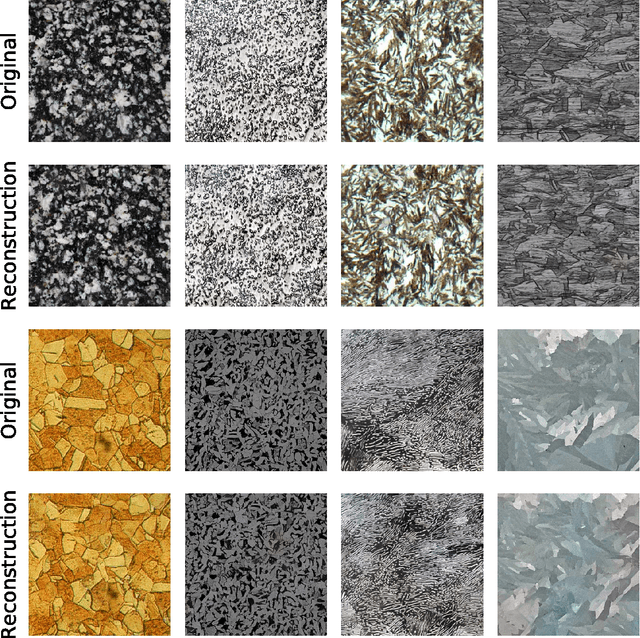
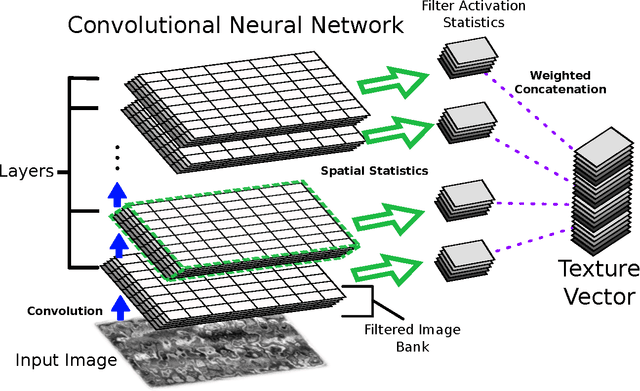
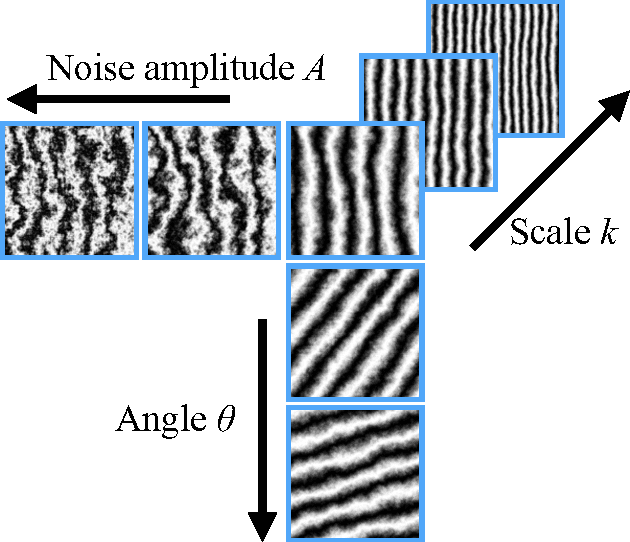
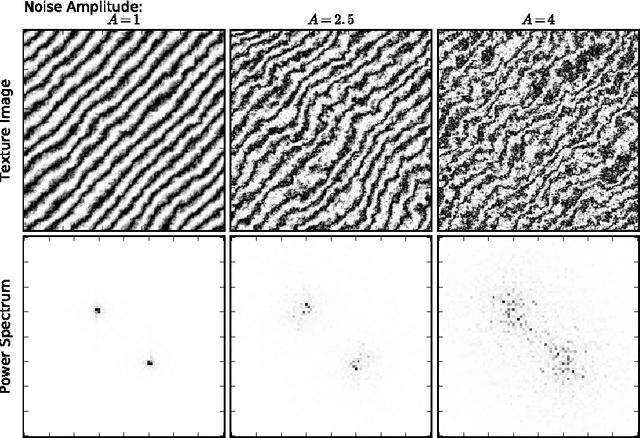
Abstract:We apply recent advances in machine learning and computer vision to a central problem in materials informatics: The statistical representation of microstructural images. We use activations in a pre-trained convolutional neural network to provide a high-dimensional characterization of a set of synthetic microstructural images. Next, we use manifold learning to obtain a low-dimensional embedding of this statistical characterization. We show that the low-dimensional embedding extracts the parameters used to generate the images. According to a variety of metrics, the convolutional neural network method yields dramatically better embeddings than the analogous method derived from two-point correlations alone.
* 25 Pages, 12 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge