Kevin M. Lynch
Cooperative Payload Estimation by a Team of Mocobots
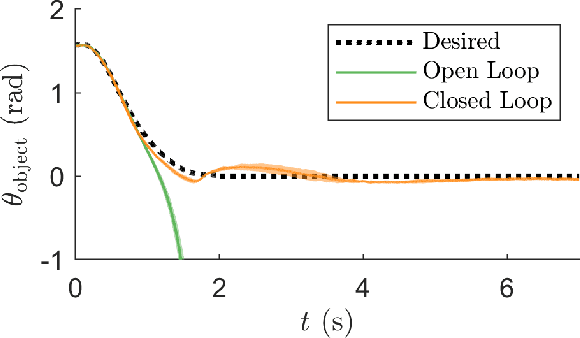
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Consider the following scenario: a human guides multiple mobile manipulators to grasp a common payload. For subsequent high-performance autonomous manipulation of the payload by the mobile manipulator team, or for collaborative manipulation with the human, the robots should be able to discover where the other robots are attached to the payload, as well as the payload's mass and inertial properties. In this paper, we describe a method for the robots to autonomously discover this information. The robots cooperatively manipulate the payload, and the twist, twist derivative, and wrench data at their grasp frames are used to estimate the transformation matrices between the grasp frames, the location of the payload's center of mass, and the payload's inertia matrix. The method is validated experimentally with a team of three mobile cobots, or mocobots.
Self-Healing Distributed Swarm Formation Control Using Image Moments
Dec 12, 2023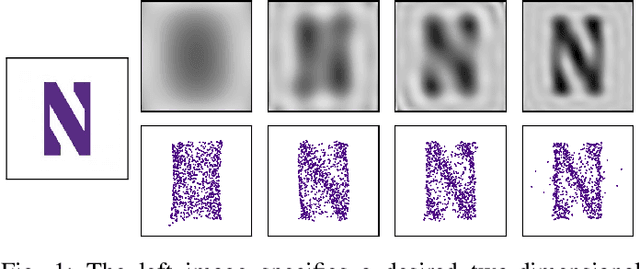
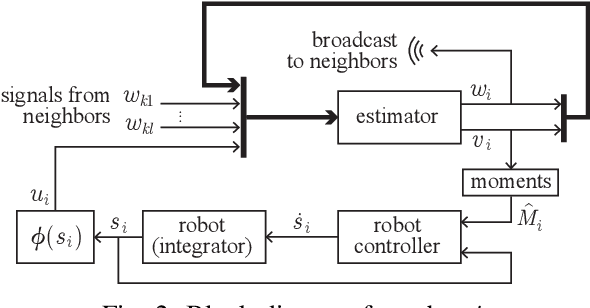
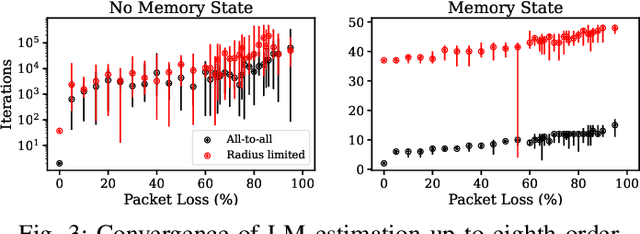
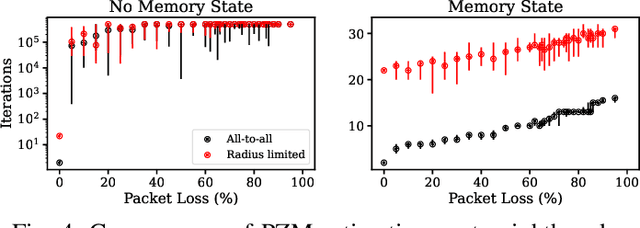
Abstract:Human-swarm interaction is facilitated by a low-dimensional encoding of the swarm formation, independent of the (possibly large) number of robots. We propose using image moments to encode two-dimensional formations of robots. Each robot knows the desired formation moments, and simultaneously estimates the current moments of the entire swarm while controlling its motion to better achieve the desired group moments. The estimator is a distributed optimization, requiring no centralized processing, and self-healing, meaning that the process is robust to initialization errors, packet drops, and robots being added to or removed from the swarm. Our experimental results with a swarm of 50 robots, suffering nearly 50% packet loss, show that distributed estimation and control of image moments effectively achieves desired swarm formations.
Efficient, Responsive, and Robust Hopping on Deformable Terrain
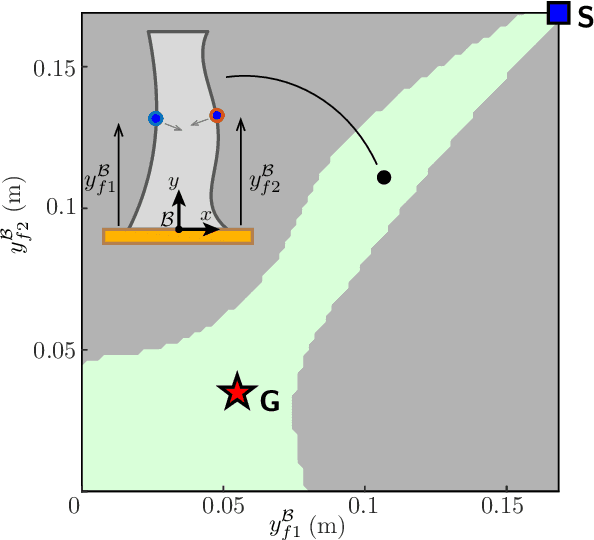
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Legged robot locomotion is hindered by a mismatch between applications where legs can outperform wheels or treads, most of which feature deformable substrates, and existing tools for planning and control, most of which assume flat, rigid substrates. In this study we focus on the ramifications of plastic terrain deformation on the hop-to-hop energy dynamics of a spring-legged monopedal hopping robot animated by a switched-compliance energy injection controller. From this deliberately simple robot-terrain model, we derive a hop-to-hop energy return map, and we use physical experiments and simulations to validate the hop-to-hop energy map for a real robot hopping on a real deformable substrate. The dynamical properties (fixed points, eigenvalues, basins of attraction) of this map provide insights into efficient, responsive, and robust locomotion on deformable terrain. Specifically, we identify constant-fixed-point surfaces in a controller parameter space that suggest it is possible to tune control parameters for efficiency or responsiveness while targeting a desired gait energy level. We also identify conditions under which fixed points of the energy map are globally stable, and we further characterize the basins of attraction of fixed points when these conditions are not satisfied. We conclude by discussing the implications of this hop-to-hop energy map for planning, control, and estimation for efficient, agile, and robust legged locomotion on deformable terrain.
Human-Multirobot Collaborative Mobile Manipulation: the Omnid Mocobots
Jun 28, 2022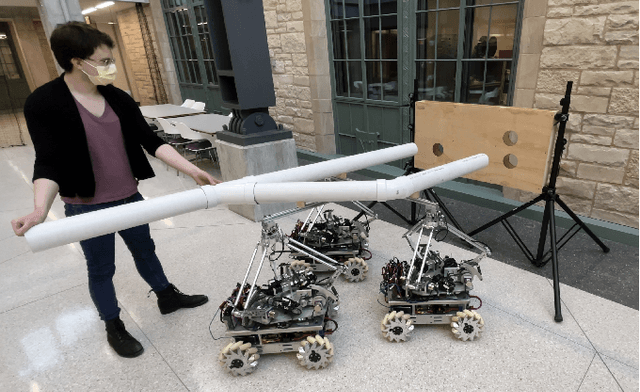
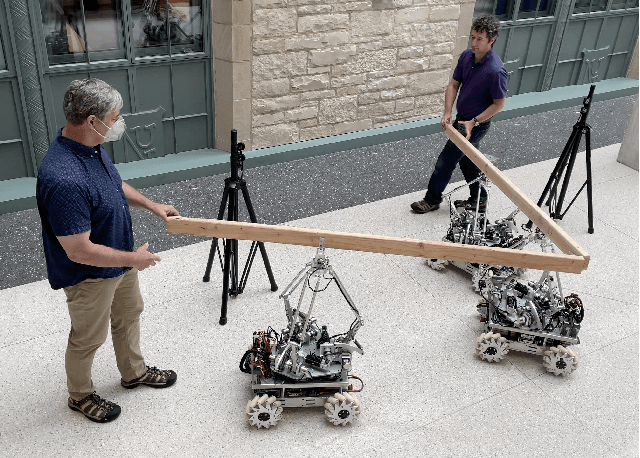
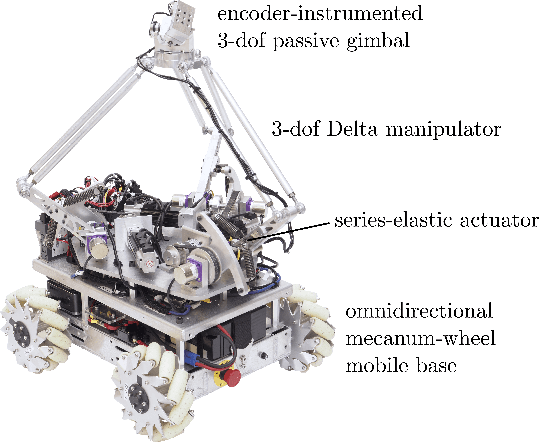
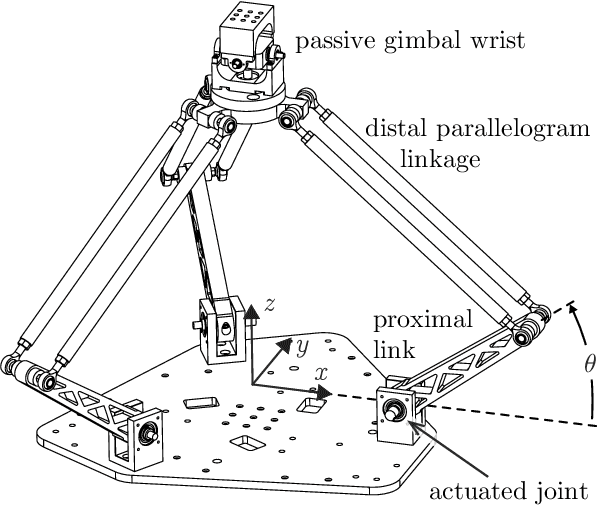
Abstract:The Omnid human-collaborative mobile manipulators are an experimental platform for testing control architectures for autonomous and human-collaborative multirobot mobile manipulation. An Omnid consists of a mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile base and a series-elastic Delta-type parallel manipulator, and it is a specific implementation of a broader class of mobile collaborative robots ("mocobots") suitable for safe human co-manipulation of delicate, flexible, and articulated payloads. Key features of mocobots include passive compliance, for the safety of the human and the payload, and high-fidelity end-effector force control independent of the potentially imprecise motions of the mobile base. We describe general considerations for the design of teams of mocobots; the design of the Omnids in light of these considerations; manipulator and mobile base controllers to achieve useful multirobot collaborative behaviors; and initial experiments in human-multirobot collaborative mobile manipulation of large, unwieldy payloads. For these experiments, the only communication among the humans and Omnids is mechanical, through the payload.
Robotic Contact Juggling
Feb 20, 2021
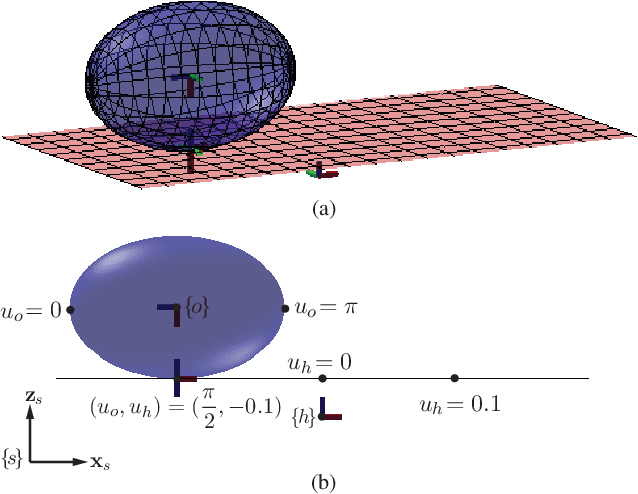

Abstract:We define "robotic contact juggling" to be the purposeful control of the motion of a three-dimensional smooth object as it rolls freely on a motion-controlled robot manipulator, or "hand." While specific examples of robotic contact juggling have been studied before, in this paper we provide the first general formulation and solution method for the case of an arbitrary smooth object in single-point rolling contact on an arbitrary smooth hand. Our formulation splits the problem into four subproblems: (1) deriving the second-order rolling kinematics; (2) deriving the three-dimensional rolling dynamics; (3) planning rolling motions that satisfy the rolling dynamics; and (4) feedback stabilization of planned rolling trajectories. The theoretical results are demonstrated in simulation and experiment using feedback from a high-speed vision system.
A Topological Approach to Gait Generation for Biped Robots
Jun 06, 2020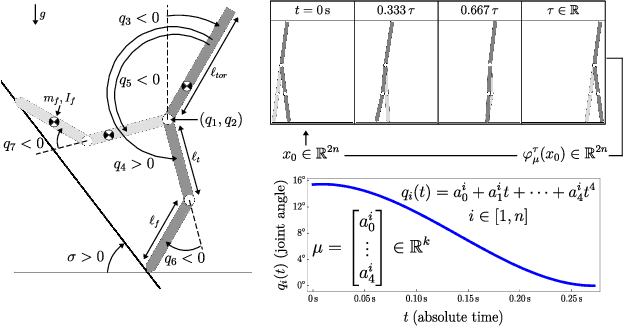
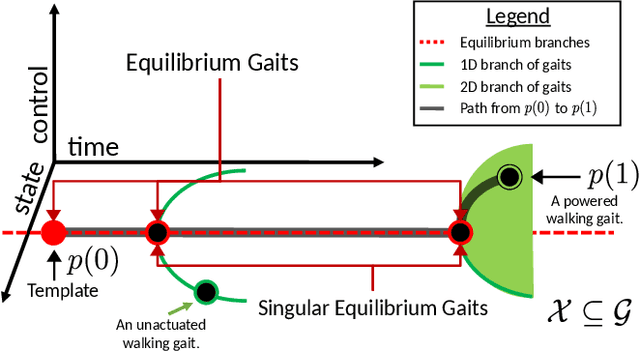
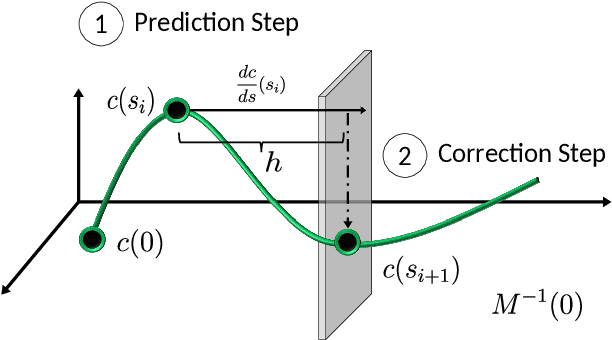

Abstract:This paper describes a topological approach to generating families of open- and closed-loop walking gaits for underactuated 2D and 3D biped walkers subject to configuration inequality constraints, physical holonomic constraints (e.g., closed chains), and virtual holonomic constraints (user-defined constraints enforced through feedback control). Our method constructs implicitly-defined manifolds of feasible periodic gaits within a state-time-control space that parameterizes the biped's hybrid trajectories. Since equilibrium configurations of the biped often belong to such manifolds, we use equilibria as "templates" from which to grow the gait families. Equilibria are reliable seeds for the construction of gait families, eliminating the need for random, intuited, or bio-inspired initial guesses at feasible trajectories in an optimization framework. We demonstrate the approach on several 2D and 3D biped walkers.
In-hand Sliding Regrasp with Spring-Sliding Compliance
Sep 22, 2019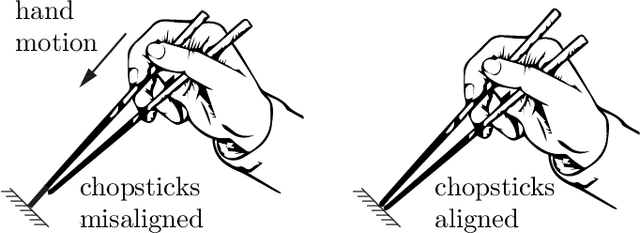
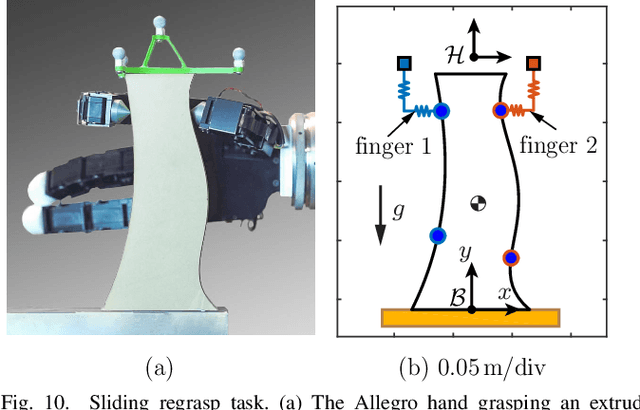
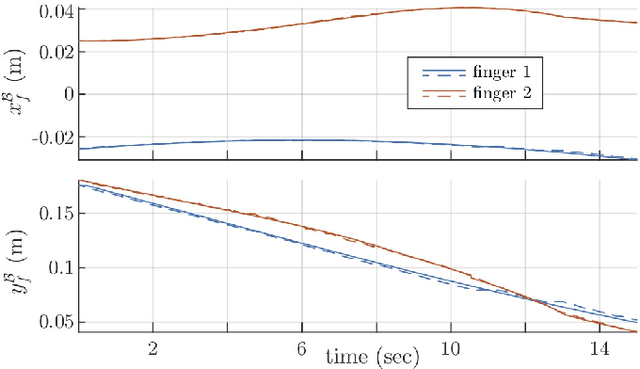
Abstract:We investigate in-hand regrasping by pushing an object against an external constraint and allowing sliding at the fingertips. Each fingertip is modeled as attached to a multidimensional spring mounted to a position-controlled anchor. Spring compliance maps contact forces to spring compressions, ensuring the fingers remain in contact, and sliding "compliance" governs the relationship between sliding motions and tangential contact forces. A spring-sliding compliant regrasp is achieved by controlling the finger anchor motions. We derive the fingertip sliding mechanics for multifingered sliding regrasps and analyze robust regrasping conditions in the presence of finger contact wrench uncertainties. The results are verified in simulation and experiment with a two-fingered sliding regrasp designed to maximize robustness of the operation.
The Soft Landing Problem: Minimizing Energy Loss by a Legged Robot Impacting Yielding Terrain
Sep 12, 2019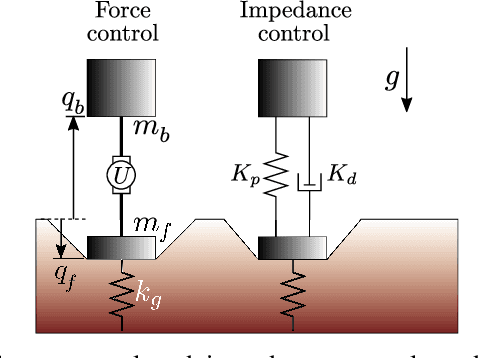
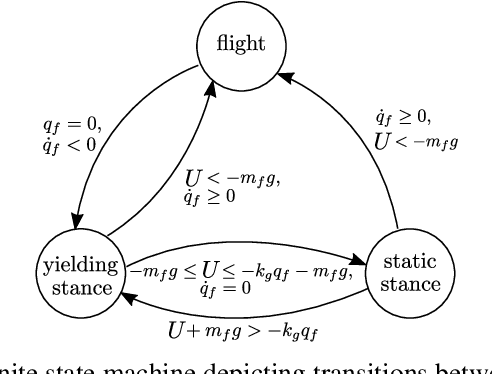
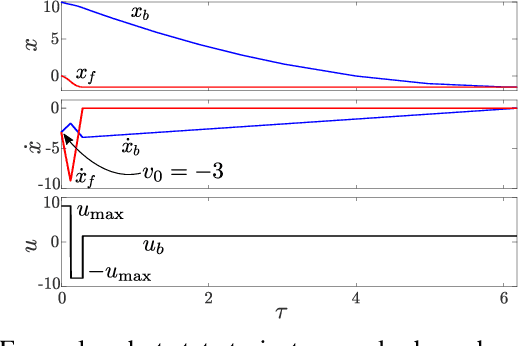
Abstract:Enabling robots to walk and run on yielding terrain is increasingly vital to endeavors ranging from disaster response to extraterrestrial exploration. While dynamic legged locomotion on rigid ground is challenging enough, yielding terrain presents additional challenges such as permanent ground deformation which dissipates energy. In this paper, we examine the soft landing problem: given some impact momentum, bring the robot to rest while minimizing foot penetration depth. To gain insight into properties of penetration depth-minimizing control policies, we formulate a constrained optimal control problem and obtain a bang-bang open-loop force profile. Motivated by examples from biology and recent advances in legged robotics, we also examine impedance-control solutions to the dimensionless soft landing problem. Through simulations, we find that optimal impedance reduces penetration depth nearly as much as the open-loop force profile, while remaining robust to model uncertainty. Through simulations and experiments, we find that the solution space is rich, exhibiting qualitatively different relationships between impact velocity and the optimal impedance for small and large dimensionless impact velocities. Lastly, we discuss the relevance of this work to minimum-cost-of-transport locomotion for several actuator design choices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge