Haoxuan Zhang
The Evolving Role of Large Language Models in Scientific Innovation: Evaluator, Collaborator, and Scientist
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Scientific innovation is undergoing a paradigm shift driven by the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs). As science faces mounting challenges including information overload, disciplinary silos, and diminishing returns on conventional research methods, LLMs are emerging as powerful agents capable not only of enhancing scientific workflows but also of participating in and potentially leading the innovation process. Existing surveys mainly focus on different perspectives, phrases, and tasks in scientific research and discovery, while they have limitations in understanding the transformative potential and role differentiation of LLM. This survey proposes a comprehensive framework to categorize the evolving roles of LLMs in scientific innovation across three hierarchical levels: Evaluator, Collaborator, and Scientist. We distinguish between LLMs' contributions to structured scientific research processes and open-ended scientific discovery, thereby offering a unified taxonomy that clarifies capability boundaries, evaluation criteria, and human-AI interaction patterns at each level. Through an extensive analysis of current methodologies, benchmarks, systems, and evaluation metrics, this survey delivers an in-depth and systematic synthesis on LLM-driven scientific innovation. We present LLMs not only as tools for automating existing processes, but also as catalysts capable of reshaping the epistemological foundations of science itself. This survey offers conceptual clarity, practical guidance, and theoretical foundations for future research, while also highlighting open challenges and ethical considerations in the pursuit of increasingly autonomous AI-driven science. Resources related to this survey can be accessed on GitHub at: https://github.com/haoxuan-unt2024/llm4innovation.
Cooperative Payload Estimation by a Team of Mocobots
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Consider the following scenario: a human guides multiple mobile manipulators to grasp a common payload. For subsequent high-performance autonomous manipulation of the payload by the mobile manipulator team, or for collaborative manipulation with the human, the robots should be able to discover where the other robots are attached to the payload, as well as the payload's mass and inertial properties. In this paper, we describe a method for the robots to autonomously discover this information. The robots cooperatively manipulate the payload, and the twist, twist derivative, and wrench data at their grasp frames are used to estimate the transformation matrices between the grasp frames, the location of the payload's center of mass, and the payload's inertia matrix. The method is validated experimentally with a team of three mobile cobots, or mocobots.
MQENet: A Mesh Quality Evaluation Neural Network Based on Dynamic Graph Attention
Sep 03, 2023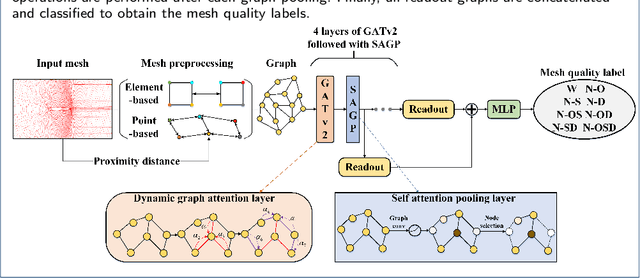

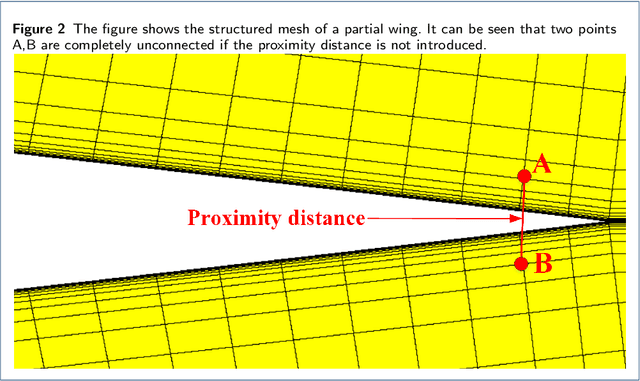

Abstract:With the development of computational fluid dynamics, the requirements for the fluid simulation accuracy in industrial applications have also increased. The quality of the generated mesh directly affects the simulation accuracy. However, previous mesh quality metrics and models cannot evaluate meshes comprehensively and objectively. To this end, we propose MQENet, a structured mesh quality evaluation neural network based on dynamic graph attention. MQENet treats the mesh evaluation task as a graph classification task for classifying the quality of the input structured mesh. To make graphs generated from structured meshes more informative, MQENet introduces two novel structured mesh preprocessing algorithms. These two algorithms can also improve the conversion efficiency of structured mesh data. Experimental results on the benchmark structured mesh dataset NACA-Market show the effectiveness of MQENet in the mesh quality evaluation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge