Kang Rong
SAIL: Self-Amplified Iterative Learning for Diffusion Model Alignment with Minimal Human Feedback
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Aligning diffusion models with human preferences remains challenging, particularly when reward models are unavailable or impractical to obtain, and collecting large-scale preference datasets is prohibitively expensive. \textit{This raises a fundamental question: can we achieve effective alignment using only minimal human feedback, without auxiliary reward models, by unlocking the latent capabilities within diffusion models themselves?} In this paper, we propose \textbf{SAIL} (\textbf{S}elf-\textbf{A}mplified \textbf{I}terative \textbf{L}earning), a novel framework that enables diffusion models to act as their own teachers through iterative self-improvement. Starting from a minimal seed set of human-annotated preference pairs, SAIL operates in a closed-loop manner where the model progressively generates diverse samples, self-annotates preferences based on its evolving understanding, and refines itself using this self-augmented dataset. To ensure robust learning and prevent catastrophic forgetting, we introduce a ranked preference mixup strategy that carefully balances exploration with adherence to initial human priors. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SAIL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple benchmarks while using merely 6\% of the preference data required by existing approaches, revealing that diffusion models possess remarkable self-improvement capabilities that, when properly harnessed, can effectively replace both large-scale human annotation and external reward models.
WeThink: Toward General-purpose Vision-Language Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Building on the success of text-based reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1, extending these capabilities to multimodal reasoning holds great promise. While recent works have attempted to adapt DeepSeek-R1-style reinforcement learning (RL) training paradigms to multimodal large language models (MLLM), focusing on domain-specific tasks like math and visual perception, a critical question remains: How can we achieve the general-purpose visual-language reasoning through RL? To address this challenge, we make three key efforts: (1) A novel Scalable Multimodal QA Synthesis pipeline that autonomously generates context-aware, reasoning-centric question-answer (QA) pairs directly from the given images. (2) The open-source WeThink dataset containing over 120K multimodal QA pairs with annotated reasoning paths, curated from 18 diverse dataset sources and covering various question domains. (3) A comprehensive exploration of RL on our dataset, incorporating a hybrid reward mechanism that combines rule-based verification with model-based assessment to optimize RL training efficiency across various task domains. Across 14 diverse MLLM benchmarks, we demonstrate that our WeThink dataset significantly enhances performance, from mathematical reasoning to diverse general multimodal tasks. Moreover, we show that our automated data pipeline can continuously increase data diversity to further improve model performance.
Instruction-Oriented Preference Alignment for Enhancing Multi-Modal Comprehension Capability of MLLMs
Mar 26, 2025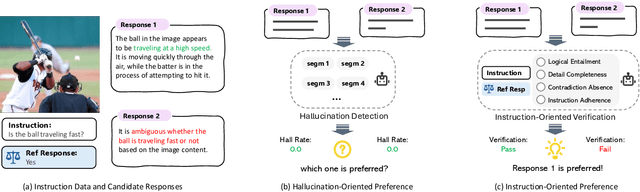
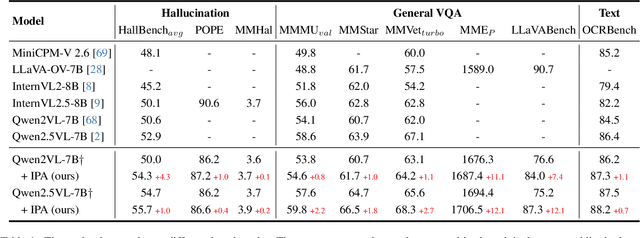
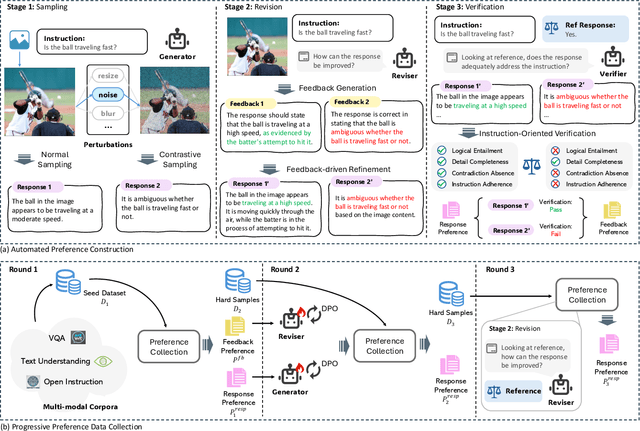
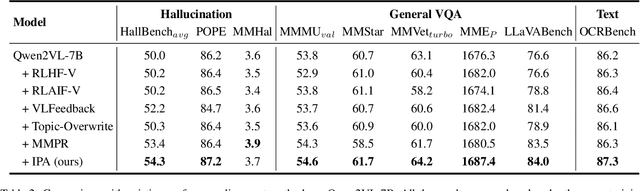
Abstract:Preference alignment has emerged as an effective strategy to enhance the performance of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) following supervised fine-tuning. While existing preference alignment methods predominantly target hallucination factors, they overlook the factors essential for multi-modal comprehension capabilities, often narrowing their improvements on hallucination mitigation. To bridge this gap, we propose Instruction-oriented Preference Alignment (IPA), a scalable framework designed to automatically construct alignment preferences grounded in instruction fulfillment efficacy. Our method involves an automated preference construction coupled with a dedicated verification process that identifies instruction-oriented factors, avoiding significant variability in response representations. Additionally, IPA incorporates a progressive preference collection pipeline, further recalling challenging samples through model self-evolution and reference-guided refinement. Experiments conducted on Qwen2VL-7B demonstrate IPA's effectiveness across multiple benchmarks, including hallucination evaluation, visual question answering, and text understanding tasks, highlighting its capability to enhance general comprehension.
Automated Multi-level Preference for MLLMs
May 18, 2024



Abstract:Current multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) suffer from ``hallucination'', occasionally generating responses that are not grounded in the input images. To tackle this challenge, one promising path is to utilize reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which steers MLLMs towards learning superior responses while avoiding inferior ones. We rethink the common practice of using binary preferences (\emph{i.e.}, superior, inferior), and find that adopting multi-level preferences (\emph{e.g.}, superior, medium, inferior) is better for two benefits: 1) It narrows the gap between adjacent levels, thereby encouraging MLLMs to discern subtle differences. 2) It further integrates cross-level comparisons (beyond adjacent-level comparisons), thus providing a broader range of comparisons with hallucination examples. To verify our viewpoint, we present the Automated Multi-level Preference (\textbf{AMP}) framework for MLLMs. To facilitate this framework, we first develop an automated dataset generation pipeline that provides high-quality multi-level preference datasets without any human annotators. Furthermore, we design the Multi-level Direct Preference Optimization (MDPO) algorithm to robustly conduct complex multi-level preference learning. Additionally, we propose a new hallucination benchmark, MRHal-Bench. Extensive experiments across public hallucination and general benchmarks, as well as our MRHal-Bench, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
HARIS: Human-Like Attention for Reference Image Segmentation
May 17, 2024Abstract:Referring image segmentation (RIS) aims to locate the particular region corresponding to the language expression. Existing methods incorporate features from different modalities in a \emph{bottom-up} manner. This design may get some unnecessary image-text pairs, which leads to an inaccurate segmentation mask. In this paper, we propose a referring image segmentation method called HARIS, which introduces the Human-Like Attention mechanism and uses the parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) framework. To be specific, the Human-Like Attention gets a \emph{feedback} signal from multi-modal features, which makes the network center on the specific objects and discard the irrelevant image-text pairs. Besides, we introduce the PEFT framework to preserve the zero-shot ability of pre-trained encoders. Extensive experiments on three widely used RIS benchmarks and the PhraseCut dataset demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and great zero-shot ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge