Kairui Wen
SS3DM: Benchmarking Street-View Surface Reconstruction with a Synthetic 3D Mesh Dataset
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Reconstructing accurate 3D surfaces for street-view scenarios is crucial for applications such as digital entertainment and autonomous driving simulation. However, existing street-view datasets, including KITTI, Waymo, and nuScenes, only offer noisy LiDAR points as ground-truth data for geometric evaluation of reconstructed surfaces. These geometric ground-truths often lack the necessary precision to evaluate surface positions and do not provide data for assessing surface normals. To overcome these challenges, we introduce the SS3DM dataset, comprising precise \textbf{S}ynthetic \textbf{S}treet-view \textbf{3D} \textbf{M}esh models exported from the CARLA simulator. These mesh models facilitate accurate position evaluation and include normal vectors for evaluating surface normal. To simulate the input data in realistic driving scenarios for 3D reconstruction, we virtually drive a vehicle equipped with six RGB cameras and five LiDAR sensors in diverse outdoor scenes. Leveraging this dataset, we establish a benchmark for state-of-the-art surface reconstruction methods, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the associated challenges. For more information, visit our homepage at https://ss3dm.top.
FlightLLM: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with a Complete Mapping Flow on FPGAs
Jan 09, 2024
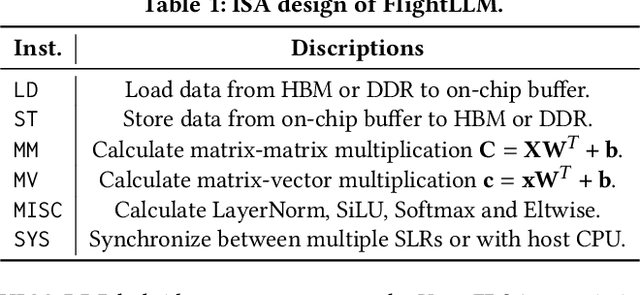


Abstract:Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) have made a significant impact on various domains. However, LLMs' efficiency suffers from both heavy computation and memory overheads. Compression techniques like sparsification and quantization are commonly used to mitigate the gap between LLM's computation/memory overheads and hardware capacity. However, existing GPU and transformer-based accelerators cannot efficiently process compressed LLMs, due to the following unresolved challenges: low computational efficiency, underutilized memory bandwidth, and large compilation overheads. This paper proposes FlightLLM, enabling efficient LLMs inference with a complete mapping flow on FPGAs. In FlightLLM, we highlight an innovative solution that the computation and memory overhead of LLMs can be solved by utilizing FPGA-specific resources (e.g., DSP48 and heterogeneous memory hierarchy). We propose a configurable sparse DSP chain to support different sparsity patterns with high computation efficiency. Second, we propose an always-on-chip decode scheme to boost memory bandwidth with mixed-precision support. Finally, to make FlightLLM available for real-world LLMs, we propose a length adaptive compilation method to reduce the compilation overhead. Implemented on the Xilinx Alveo U280 FPGA, FlightLLM achieves 6.0$\times$ higher energy efficiency and 1.8$\times$ better cost efficiency against commercial GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA V100S) on modern LLMs (e.g., LLaMA2-7B) using vLLM and SmoothQuant under the batch size of one. FlightLLM beats NVIDIA A100 GPU with 1.2$\times$ higher throughput using the latest Versal VHK158 FPGA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge