Junfu Liu
Learn to Cluster Faces via Pairwise Classification
May 26, 2022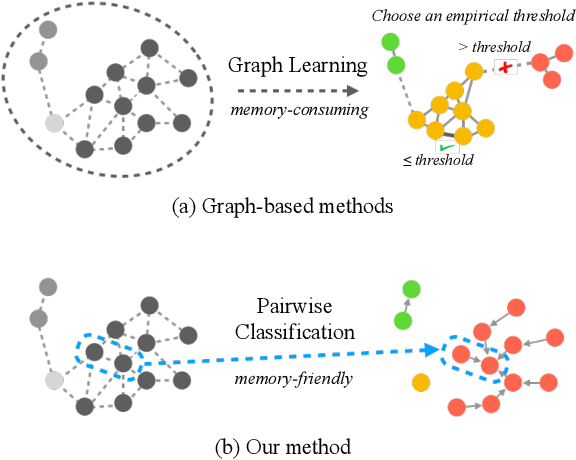

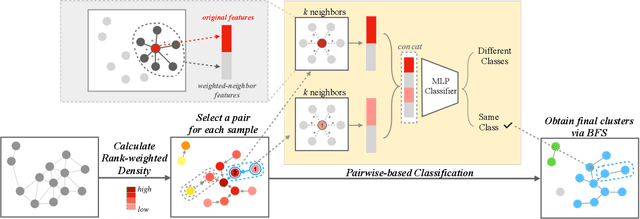

Abstract:Face clustering plays an essential role in exploiting massive unlabeled face data. Recently, graph-based face clustering methods are getting popular for their satisfying performances. However, they usually suffer from excessive memory consumption especially on large-scale graphs, and rely on empirical thresholds to determine the connectivities between samples in inference, which restricts their applications in various real-world scenes. To address such problems, in this paper, we explore face clustering from the pairwise angle. Specifically, we formulate the face clustering task as a pairwise relationship classification task, avoiding the memory-consuming learning on large-scale graphs. The classifier can directly determine the relationship between samples and is enhanced by taking advantage of the contextual information. Moreover, to further facilitate the efficiency of our method, we propose a rank-weighted density to guide the selection of pairs sent to the classifier. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performances on several public clustering benchmarks at the fastest speed and shows a great advantage in comparison with graph-based clustering methods on memory consumption.
CelebA-Spoof Challenge 2020 on Face Anti-Spoofing: Methods and Results
Feb 26, 2021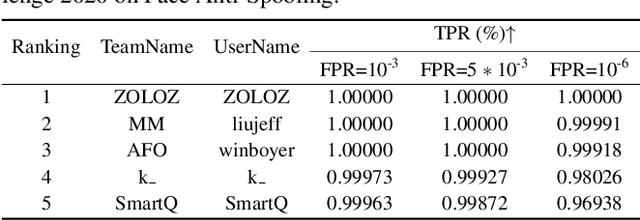
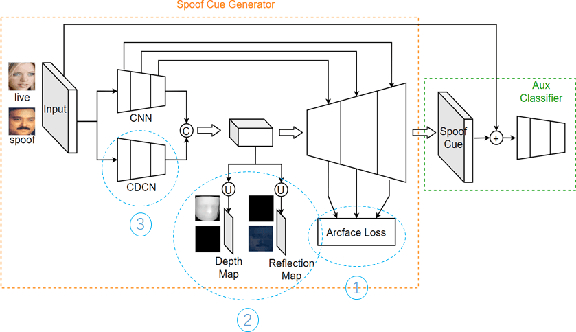
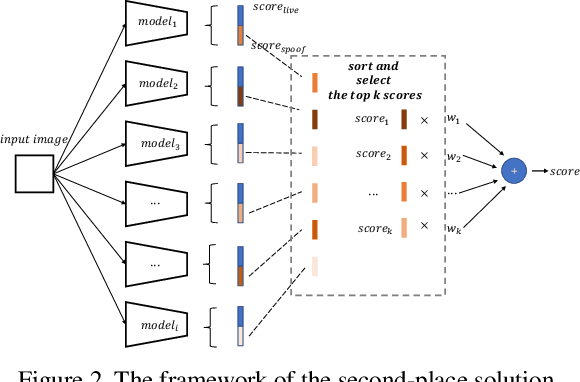
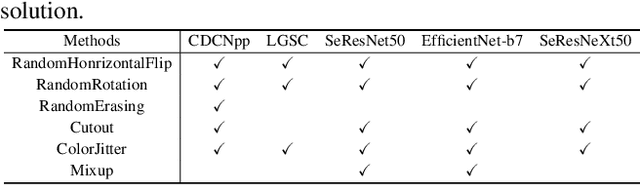
Abstract:As facial interaction systems are prevalently deployed, security and reliability of these systems become a critical issue, with substantial research efforts devoted. Among them, face anti-spoofing emerges as an important area, whose objective is to identify whether a presented face is live or spoof. Recently, a large-scale face anti-spoofing dataset, CelebA-Spoof which comprised of 625,537 pictures of 10,177 subjects has been released. It is the largest face anti-spoofing dataset in terms of the numbers of the data and the subjects. This paper reports methods and results in the CelebA-Spoof Challenge 2020 on Face AntiSpoofing which employs the CelebA-Spoof dataset. The model evaluation is conducted online on the hidden test set. A total of 134 participants registered for the competition, and 19 teams made valid submissions. We will analyze the top ranked solutions and present some discussion on future work directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge