Joonhyuk Kang
Beyond Fixed Rounds: Data-Free Early Stopping for Practical Federated Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) facilitates decentralized collaborative learning without transmitting raw data. However, reliance on fixed global rounds or validation data for hyperparameter tuning hinders practical deployment by incurring high computational costs and privacy risks. To address this, we propose a data-free early stopping framework that determines the optimal stopping point by monitoring the task vector's growth rate using solely server-side parameters. The numerical results on skin lesion/blood cell classification demonstrate that our approach is comparable to validation-based early stopping across various state-of-the-art FL methods. In particular, the proposed framework spends an average of 47/20 (skin lesion/blood cell) rounds to achieve over 12.5%/10.3% higher performance than early stopping based on validation data. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to propose an early stopping framework for FL methods without using any validation data.
When to Stop Federated Learning: Zero-Shot Generation of Synthetic Validation Data with Generative AI for Early Stopping
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across decentralized devices while preserving data privacy. However, FL methods typically run for a predefined number of global rounds, often leading to unnecessary computation when optimal performance is reached earlier. In addition, training may continue even when the model fails to achieve meaningful performance. To address this inefficiency, we introduce a zero-shot synthetic validation framework that leverages generative AI to monitor model performance and determine early stopping points. Our approach adaptively stops training near the optimal round, thereby conserving computational resources and enabling rapid hyperparameter adjustments. Numerical results on multi-label chest X-ray classification demonstrate that our method reduces training rounds by up to 74% while maintaining accuracy within 1% of the optimal.
VLF-MSC: Vision-Language Feature-Based Multimodal Semantic Communication System
Nov 13, 2025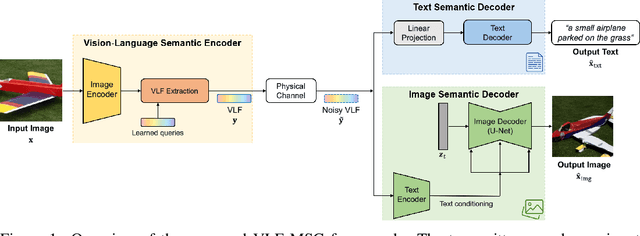
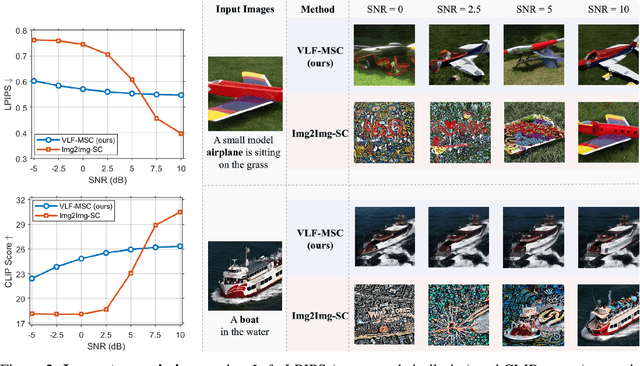
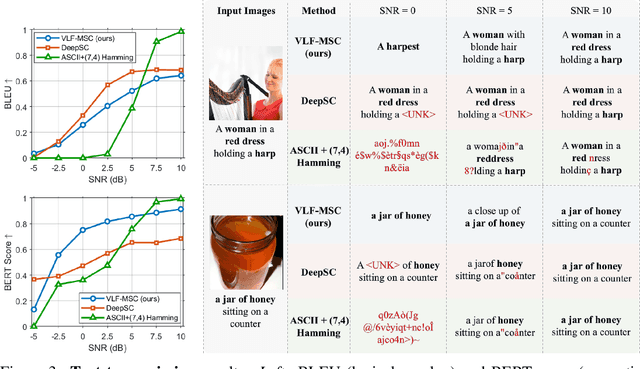
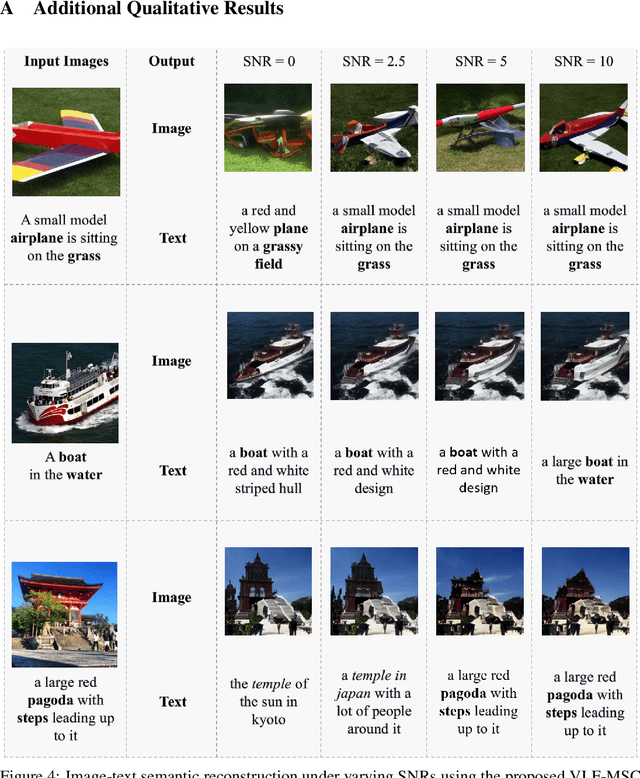
Abstract:We propose Vision-Language Feature-based Multimodal Semantic Communication (VLF-MSC), a unified system that transmits a single compact vision-language representation to support both image and text generation at the receiver. Unlike existing semantic communication techniques that process each modality separately, VLF-MSC employs a pre-trained vision-language model (VLM) to encode the source image into a vision-language semantic feature (VLF), which is transmitted over the wireless channel. At the receiver, a decoder-based language model and a diffusion-based image generator are both conditioned on the VLF to produce a descriptive text and a semantically aligned image. This unified representation eliminates the need for modality-specific streams or retransmissions, improving spectral efficiency and adaptability. By leveraging foundation models, the system achieves robustness to channel noise while preserving semantic fidelity. Experiments demonstrate that VLF-MSC outperforms text-only and image-only baselines, achieving higher semantic accuracy for both modalities under low SNR with significantly reduced bandwidth.
Forecasting-Based Biomedical Time-series Data Synthesis for Open Data and Robust AI
Oct 06, 2025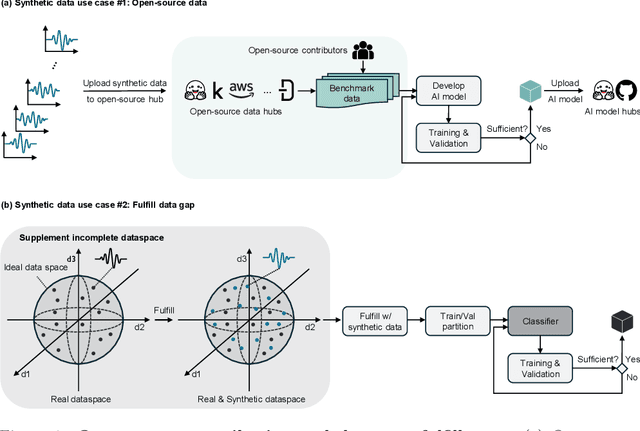
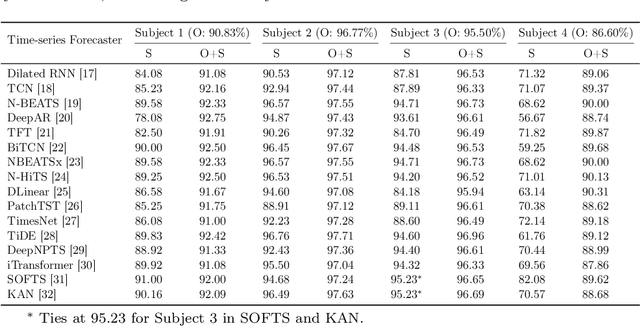
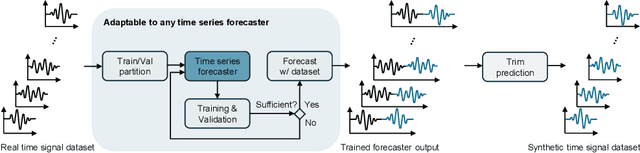
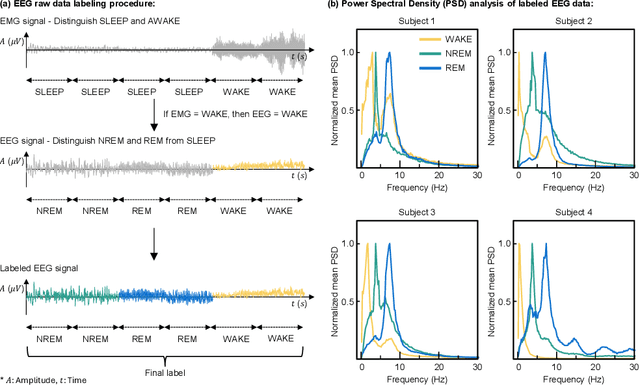
Abstract:The limited data availability due to strict privacy regulations and significant resource demands severely constrains biomedical time-series AI development, which creates a critical gap between data requirements and accessibility. Synthetic data generation presents a promising solution by producing artificial datasets that maintain the statistical properties of real biomedical time-series data without compromising patient confidentiality. We propose a framework for synthetic biomedical time-series data generation based on advanced forecasting models that accurately replicates complex electrophysiological signals such as EEG and EMG with high fidelity. These synthetic datasets preserve essential temporal and spectral properties of real data, which enables robust analysis while effectively addressing data scarcity and privacy challenges. Our evaluations across multiple subjects demonstrate that the generated synthetic data can serve as an effective substitute for real data and also significantly boost AI model performance. The approach maintains critical biomedical features while provides high scalability for various applications and integrates seamlessly into open-source repositories, substantially expanding resources for AI-driven biomedical research.
SHEFL: Resource-Aware Aggregation and Sparsification in Heterogeneous Ensemble Federated Learning
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Federated learning enables distributed training with private data of clients, but its convergence is hindered by data and system heterogeneity in realistic communication scenarios. Most existing system heterogeneous FL schemes utilize global pruning or ensemble distillation, yet they often overlook typical constraints required for communication efficiency. Meanwhile, deep ensembles can aggregate predictions from individually trained models to improve performance, but current ensemble-based FL methods fall short in fully capturing the diversity of model predictions. In this work, we propose SHEFL, a global ensemble-based federated learning framework suited for clients with diverse computational capacities. We allocate different numbers of global models to clients based on their available resources. We further introduce a novel aggregation scheme that accounts for bias between clients with different computational capabilities. To reduce the computational burden of training deep ensembles and mitigate data bias, we dynamically adjust the resource ratio across clients - aggressively reducing the influence of underpowered clients in constrained scenarios, while increasing their weight in the opposite case. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively addresses computational heterogeneity, significantly improving both fairness and overall performance compared to existing approaches.
Energy-Efficient Secure Communications via Joint Optimization of UAV Trajectory and Movable-Antenna Array Beamforming
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the potential of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with movable-antenna (MA) arrays to strengthen security in wireless communication systems. We propose a novel framework that jointly optimizes the UAV trajectory and the reconfigurable beamforming of the MA array to maximize secrecy energy efficiency, while ensuring reliable communication with legitimate users. By exploiting the spatial degrees of freedom enabled by the MA array, the system can form highly directional beams and deep nulls, thereby significantly improving physical layer security. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves superior secrecy energy efficiency, attributed to the enhanced spatial flexibility provided by the movable antenna architecture.
Data-Efficient Prediction-Powered Calibration via Cross-Validation
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Calibration data are necessary to formally quantify the uncertainty of the decisions produced by an existing artificial intelligence (AI) model. To overcome the common issue of scarce calibration data, a promising approach is to employ synthetic labels produced by a (generally different) predictive model. However, fine-tuning the label-generating predictor on the inference task of interest, as well as estimating the residual bias of the synthetic labels, demand additional data, potentially exacerbating the calibration data scarcity problem. This paper introduces a novel approach that efficiently utilizes limited calibration data to simultaneously fine-tune a predictor and estimate the bias of the synthetic labels. The proposed method yields prediction sets with rigorous coverage guarantees for AI-generated decisions. Experimental results on an indoor localization problem validate the effectiveness and performance gains of our solution.
RIS-assisted ISAC Systems for Industrial Revolution 6.0: Exploring the Near-field and Far-field Coexistence
Jul 10, 2025



Abstract:The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has emerged as a key technology for realizing the vision of Industry 6.0, requiring the seamless integration of diverse connected devices. In particular, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) plays a critical role in supporting real-time control and automation within IIoT systems. In this paper, we explore reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted ISAC systems for IIoT in the coexistence of near-field and far-field regions. The system consists of a full-duplex access point (AP), a RIS and multiple IIoT devices, where the near-field devices simultaneously perform sensing and communication, while the far-field devices rely on a RIS-assisted communication. To enhance spectral efficiency for both sensing and communication functionalities, we consider the use of both traditional sensing-only (SO) and ISAC frequency bands. Moreover, uplink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is employed to facilitate the sequential decoding of superimposed communication and sensing signals from IIoT devices. To maximize sensing accuracy in terms of Cram${\Grave{\textrm{e}}}$r-Rao bound (CRB), we formulate a joint optimization of RIS phase shift, bandwidth splitting ratio and receive beamforming vector subject to the minimum data rate requirements of IIoT devices and resource budget constraints. The algorithmic solution is developed via the successive convex approximation (SCA)-based alternating optimization (AO) method with the semi-definite relaxation (SDR) technique. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms conventional methods relying solely on either ISAC or SO band by achieving superior performance across RIS and device configurations, while ensuring robust ISAC performance under the near-field and far-field coexistence scenarios.
Improving Generalizability of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks via Error-Correcting Output Codes
May 09, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) offer universal function approximation using univariate spline compositions without nonlinear activations. In this work, we integrate Error-Correcting Output Codes (ECOC) into the KAN framework to transform multi-class classification into multiple binary tasks, improving robustness via Hamming-distance decoding. Our proposed KAN with ECOC method outperforms vanilla KAN on a challenging blood cell classification dataset, achieving higher accuracy under diverse hyperparameter settings. Ablation studies further confirm that ECOC consistently enhances performance across FastKAN and FasterKAN variants. These results demonstrate that ECOC integration significantly boosts KAN generalizability in critical healthcare AI applications. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first integration of ECOC with KAN for enhancing multi-class medical image classification performance.
A Unified Benchmark of Federated Learning with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Medical Imaging
Apr 28, 2025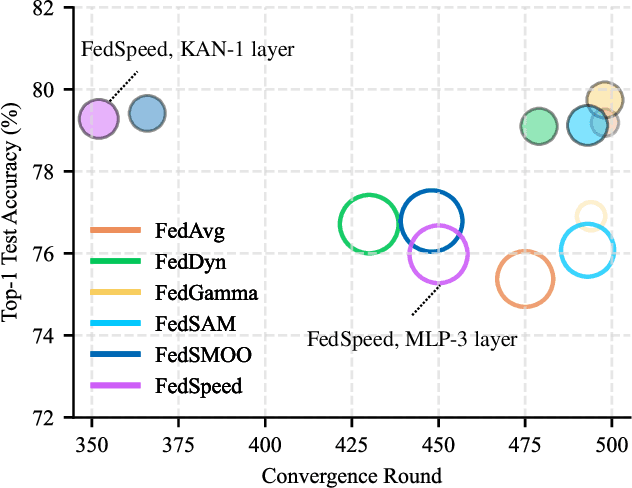
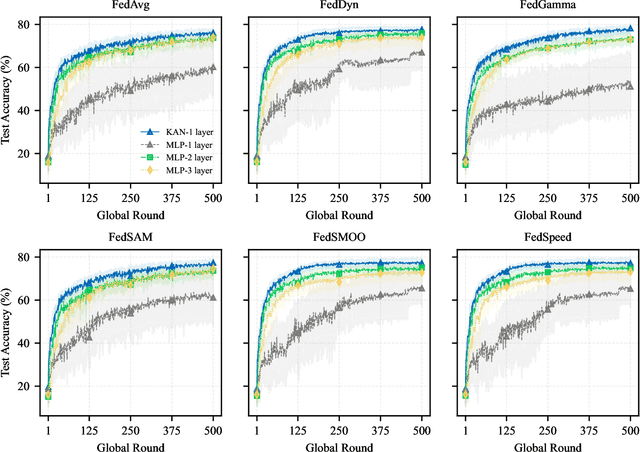
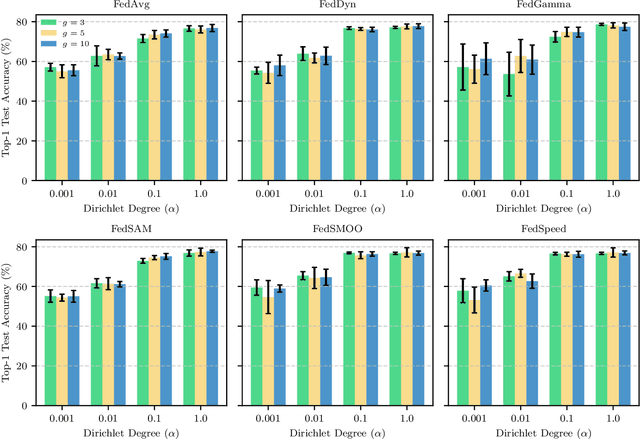
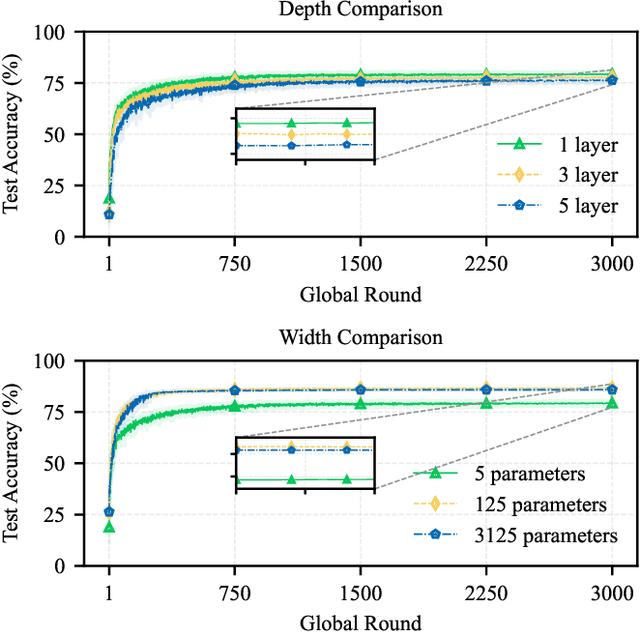
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables model training across decentralized devices without sharing raw data, thereby preserving privacy in sensitive domains like healthcare. In this paper, we evaluate Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) architectures against traditional MLP across six state-of-the-art FL algorithms on a blood cell classification dataset. Notably, our experiments demonstrate that KAN can effectively replace MLP in federated environments, achieving superior performance with simpler architectures. Furthermore, we analyze the impact of key hyperparameters-grid size and network architecture-on KAN performance under varying degrees of Non-IID data distribution. Additionally, our ablation studies reveal that optimizing KAN width while maintaining minimal depth yields the best performance in federated settings. As a result, these findings establish KAN as a promising alternative for privacy-preserving medical imaging applications in distributed healthcare. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive benchmark of KAN in FL settings for medical imaging task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge