Jin-Hyun Ahn
FedEFC: Federated Learning Using Enhanced Forward Correction Against Noisy Labels
Apr 08, 2025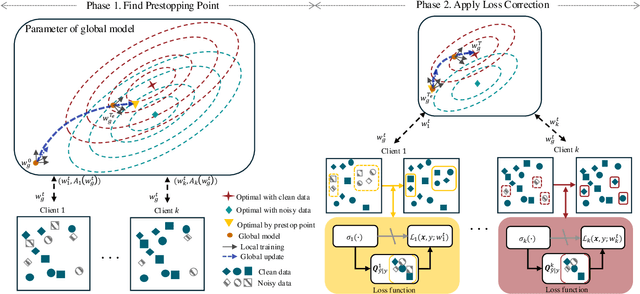
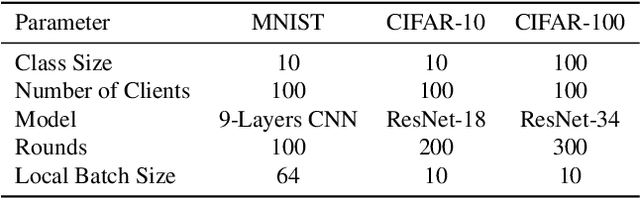
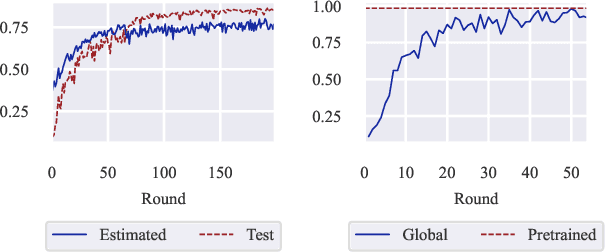
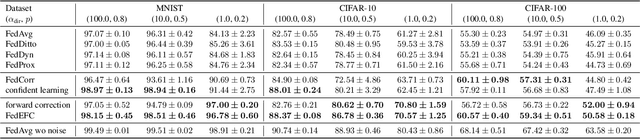
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a powerful framework for privacy-preserving distributed learning. It enables multiple clients to collaboratively train a global model without sharing raw data. However, handling noisy labels in FL remains a major challenge due to heterogeneous data distributions and communication constraints, which can severely degrade model performance. To address this issue, we propose FedEFC, a novel method designed to tackle the impact of noisy labels in FL. FedEFC mitigates this issue through two key techniques: (1) prestopping, which prevents overfitting to mislabeled data by dynamically halting training at an optimal point, and (2) loss correction, which adjusts model updates to account for label noise. In particular, we develop an effective loss correction tailored to the unique challenges of FL, including data heterogeneity and decentralized training. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical analysis, leveraging the composite proper loss property, to demonstrate that the FL objective function under noisy label distributions can be aligned with the clean label distribution. Extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that it consistently outperforms existing FL techniques in mitigating the impact of noisy labels, particularly under heterogeneous data settings (e.g., achieving up to 41.64% relative performance improvement over the existing loss correction method).
Federated Active Learning (F-AL): an Efficient Annotation Strategy for Federated Learning
Feb 07, 2022



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has been intensively investigated in terms of communication efficiency, privacy, and fairness. However, efficient annotation, which is a pain point in real-world FL applications, is less studied. In this project, we propose to apply active learning (AL) and sampling strategy into the FL framework to reduce the annotation workload. We expect that the AL and FL can improve the performance of each other complementarily. In our proposed federated active learning (F-AL) method, the clients collaboratively implement the AL to obtain the instances which are considered as informative to FL in a distributed optimization manner. We compare the test accuracies of the global FL models using the conventional random sampling strategy, client-level separate AL (S-AL), and the proposed F-AL. We empirically demonstrate that the F-AL outperforms baseline methods in image classification tasks.
Wireless Federated Distillation for Distributed Edge Learning with Heterogeneous Data
Jul 05, 2019



Abstract:Cooperative training methods for distributed machine learning typically assume noiseless and ideal communication channels. This work studies some of the opportunities and challenges arising from the presence of wireless communication links. We specifically consider wireless implementations of Federated Learning (FL) and Federated Distillation (FD), as well as of a novel Hybrid Federated Distillation (HFD) scheme. Both digital implementations based on separate source-channel coding and over-the-air computing implementations based on joint source-channel coding are proposed and evaluated over Gaussian multiple-access channels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge