Joon-myoung Kwon
ALFRED: Ask a Large-language model For Reliable ECG Diagnosis
Apr 30, 2025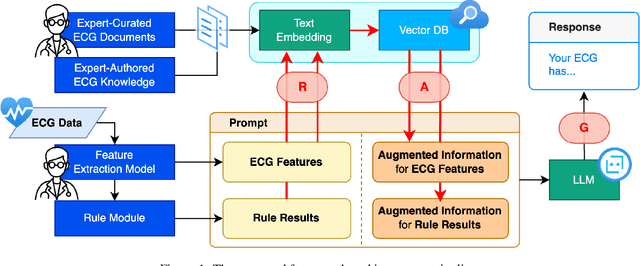
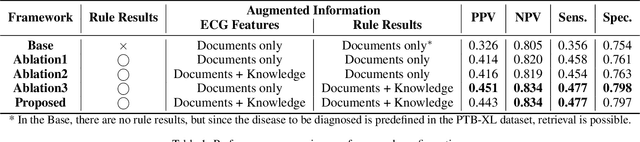
Abstract:Leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for analyzing medical data, particularly Electrocardiogram (ECG), offers high accuracy and convenience. However, generating reliable, evidence-based results in specialized fields like healthcare remains a challenge, as RAG alone may not suffice. We propose a Zero-shot ECG diagnosis framework based on RAG for ECG analysis that incorporates expert-curated knowledge to enhance diagnostic accuracy and explainability. Evaluation on the PTB-XL dataset demonstrates the framework's effectiveness, highlighting the value of structured domain expertise in automated ECG interpretation. Our framework is designed to support comprehensive ECG analysis, addressing diverse diagnostic needs with potential applications beyond the tested dataset.
New Test-Time Scenario for Biosignal: Concept and Its Approach
Nov 26, 2024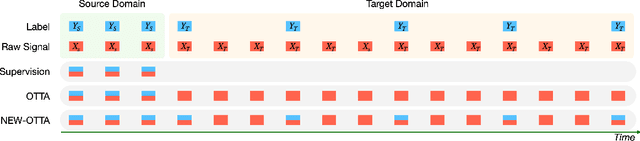
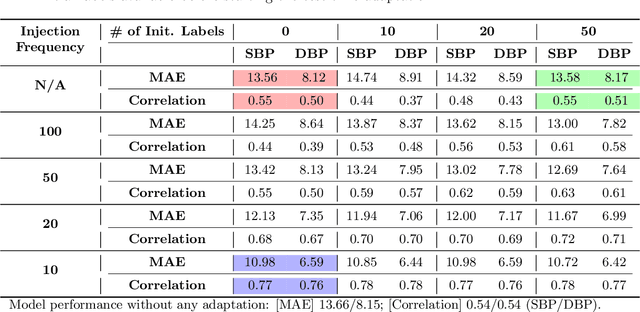
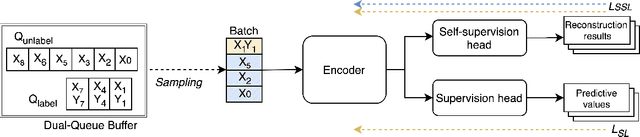
Abstract:Online Test-Time Adaptation (OTTA) enhances model robustness by updating pre-trained models with unlabeled data during testing. In healthcare, OTTA is vital for real-time tasks like predicting blood pressure from biosignals, which demand continuous adaptation. We introduce a new test-time scenario with streams of unlabeled samples and occasional labeled samples. Our framework combines supervised and self-supervised learning, employing a dual-queue buffer and weighted batch sampling to balance data types. Experiments show improved accuracy and adaptability under real-world conditions.
TADA: Temporal Adversarial Data Augmentation for Time Series Data
Jul 21, 2024Abstract:Domain generalization involves training machine learning models to perform robustly on unseen samples from out-of-distribution datasets. Adversarial Data Augmentation (ADA) is a commonly used approach that enhances model adaptability by incorporating synthetic samples, designed to simulate potential unseen samples. While ADA effectively addresses amplitude-related distribution shifts, it falls short in managing temporal shifts, which are essential for time series data. To address this limitation, we propose the Temporal Adversarial Data Augmentation for time teries Data (TADA), which incorporates a time warping technique specifically targeting temporal shifts. Recognizing the challenge of non-differentiability in traditional time warping, we make it differentiable by leveraging phase shifts in the frequency domain. Our evaluations across diverse domains demonstrate that TADA significantly outperforms existing ADA variants, enhancing model performance across time series datasets with varied distributions.
Foundation Models for Electrocardiograms
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Foundation models, enhanced by self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques, represent a cutting-edge frontier in biomedical signal analysis, particularly for electrocardiograms (ECGs), crucial for cardiac health monitoring and diagnosis. This study conducts a comprehensive analysis of foundation models for ECGs by employing and refining innovative SSL methodologies - namely, generative and contrastive learning - on a vast dataset of over 1.1 million ECG samples. By customizing these methods to align with the intricate characteristics of ECG signals, our research has successfully developed foundation models that significantly elevate the precision and reliability of cardiac diagnostics. These models are adept at representing the complex, subtle nuances of ECG data, thus markedly enhancing diagnostic capabilities. The results underscore the substantial potential of SSL-enhanced foundation models in clinical settings and pave the way for extensive future investigations into their scalable applications across a broader spectrum of medical diagnostics. This work sets a benchmark in the ECG field, demonstrating the profound impact of tailored, data-driven model training on the efficacy and accuracy of medical diagnostics.
ECG-QA: A Comprehensive Question Answering Dataset Combined With Electrocardiogram
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:Question answering (QA) in the field of healthcare has received much attention due to significant advancements in natural language processing. However, existing healthcare QA datasets primarily focus on medical images, clinical notes, or structured electronic health record tables. This leaves the vast potential of combining electrocardiogram (ECG) data with these systems largely untapped. To address this gap, we present ECG-QA, the first QA dataset specifically designed for ECG analysis. The dataset comprises a total of 70 question templates that cover a wide range of clinically relevant ECG topics, each validated by an ECG expert to ensure their clinical utility. As a result, our dataset includes diverse ECG interpretation questions, including those that require a comparative analysis of two different ECGs. In addition, we have conducted numerous experiments to provide valuable insights for future research directions. We believe that ECG-QA will serve as a valuable resource for the development of intelligent QA systems capable of assisting clinicians in ECG interpretations.
Text-to-ECG: 12-Lead Electrocardiogram Synthesis conditioned on Clinical Text Reports
Mar 09, 2023



Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) synthesis is the area of research focused on generating realistic synthetic ECG signals for medical use without concerns over annotation costs or clinical data privacy restrictions. Traditional ECG generation models consider a single ECG lead and utilize GAN-based generative models. These models can only generate single lead samples and require separate training for each diagnosis class. The diagnosis classes of ECGs are insufficient to capture the intricate differences between ECGs depending on various features (e.g. patient demographic details, co-existing diagnosis classes, etc.). To alleviate these challenges, we present a text-to-ECG task, in which textual inputs are used to produce ECG outputs. Then we propose Auto-TTE, an autoregressive generative model conditioned on clinical text reports to synthesize 12-lead ECGs, for the first time to our knowledge. We compare the performance of our model with other representative models in text-to-speech and text-to-image. Experimental results show the superiority of our model in various quantitative evaluations and qualitative analysis. Finally, we conduct a user study with three board-certified cardiologists to confirm the fidelity and semantic alignment of generated samples. our code will be available at https://github.com/TClife/text_to_ecg
Automatic Detection of Noisy Electrocardiogram Signals without Explicit Noise Labels
Aug 08, 2022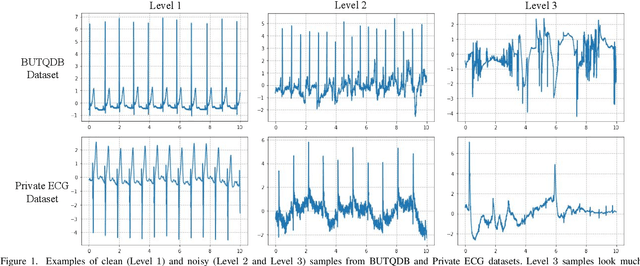
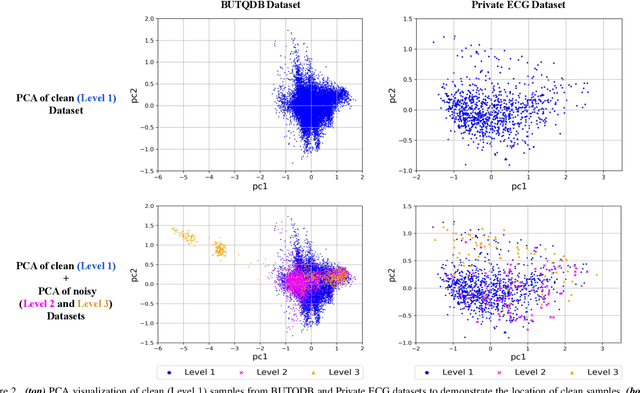
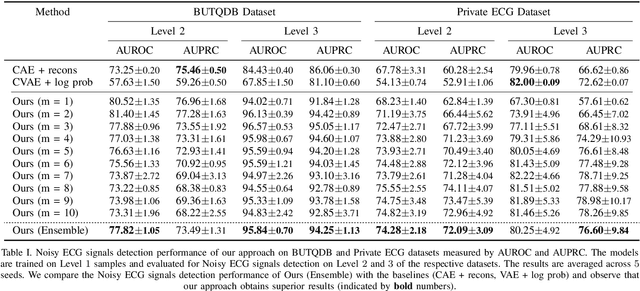
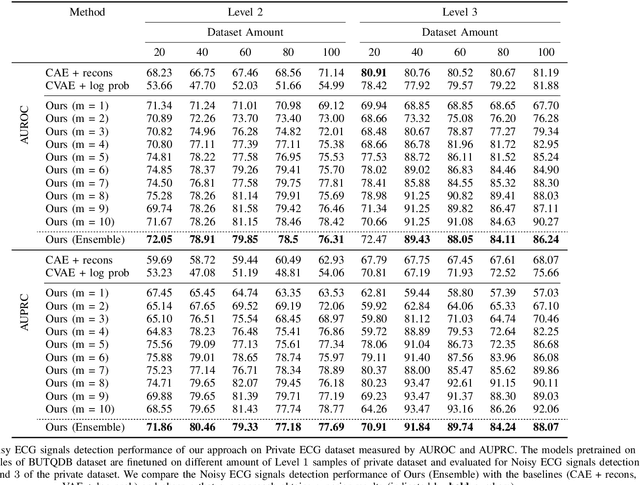
Abstract:Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are beneficial in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases, which are one of the leading causes of death. However, they are often contaminated by noise artifacts and affect the automatic and manual diagnosis process. Automatic deep learning-based examination of ECG signals can lead to inaccurate diagnosis, and manual analysis involves rejection of noisy ECG samples by clinicians, which might cost extra time. To address this limitation, we present a two-stage deep learning-based framework to automatically detect the noisy ECG samples. Through extensive experiments and analysis on two different datasets, we observe that the deep learning-based framework can detect slightly and highly noisy ECG samples effectively. We also study the transfer of the model learned on one dataset to another dataset and observe that the framework effectively detects noisy ECG samples.
Lead-agnostic Self-supervised Learning for Local and Global Representations of Electrocardiogram
Mar 18, 2022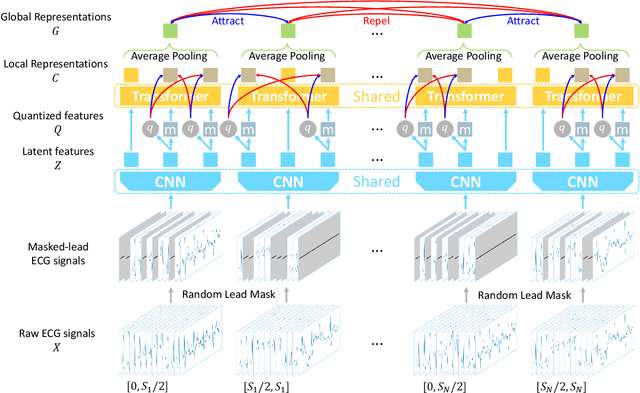
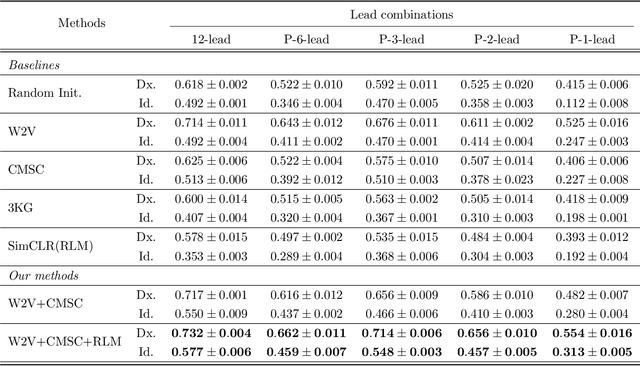
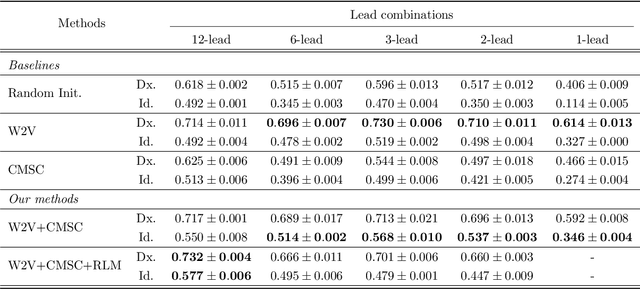
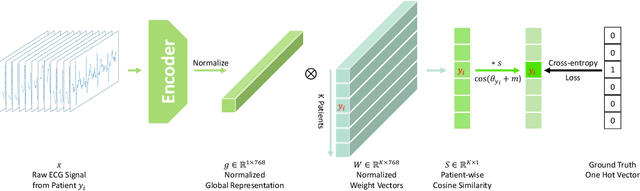
Abstract:In recent years, self-supervised learning methods have shown significant improvement for pre-training with unlabeled data and have proven helpful for electrocardiogram signals. However, most previous pre-training methods for electrocardiogram focused on capturing only global contextual representations. This inhibits the models from learning fruitful representation of electrocardiogram, which results in poor performance on downstream tasks. Additionally, they cannot fine-tune the model with an arbitrary set of electrocardiogram leads unless the models were pre-trained on the same set of leads. In this work, we propose an ECG pre-training method that learns both local and global contextual representations for better generalizability and performance on downstream tasks. In addition, we propose random lead masking as an ECG-specific augmentation method to make our proposed model robust to an arbitrary set of leads. Experimental results on two downstream tasks, cardiac arrhythmia classification and patient identification, show that our proposed approach outperforms other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge