Jinzhu Yang
SynMatch: Rethinking Consistency in Medical Image Segmentation with Sparse Annotations
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Label scarcity remains a major challenge in deep learning-based medical image segmentation. Recent studies use strong-weak pseudo supervision to leverage unlabeled data. However, performance is often hindered by inconsistencies between pseudo labels and their corresponding unlabeled images. In this work, we propose \textbf{SynMatch}, a novel framework that sidesteps the need for improving pseudo labels by synthesizing images to match them instead. Specifically, SynMatch synthesizes images using texture and shape features extracted from the same segmentation model that generates the corresponding pseudo labels for unlabeled images. This design enables the generation of highly consistent synthesized-image-pseudo-label pairs without requiring any training parameters for image synthesis. We extensively evaluate SynMatch across diverse medical image segmentation tasks under semi-supervised learning (SSL), weakly-supervised learning (WSL), and barely-supervised learning (BSL) settings with increasingly limited annotations. The results demonstrate that SynMatch achieves superior performance, especially in the most challenging BSL setting. For example, it outperforms the recent strong-weak pseudo supervision-based method by 29.71\% and 10.05\% on the polyp segmentation task with 5\% and 10\% scribble annotations, respectively. The code will be released at https://github.com/Senyh/SynMatch.
ConStyX: Content Style Augmentation for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Medical images are usually collected from multiple domains, leading to domain shifts that impair the performance of medical image segmentation models. Domain Generalization (DG) aims to address this issue by training a robust model with strong generalizability. Recently, numerous domain randomization-based DG methods have been proposed. However, these methods suffer from the following limitations: 1) constrained efficiency of domain randomization due to their exclusive dependence on image style perturbation, and 2) neglect of the adverse effects of over-augmented images on model training. To address these issues, we propose a novel domain randomization-based DG method, called content style augmentation (ConStyX), for generalizable medical image segmentation. Specifically, ConStyX 1) augments the content and style of training data, allowing the augmented training data to better cover a wider range of data domains, and 2) leverages well-augmented features while mitigating the negative effects of over-augmented features during model training. Extensive experiments across multiple domains demonstrate that our ConStyX achieves superior generalization performance. The code is available at https://github.com/jwxsp1/ConStyX.
Style Content Decomposition-based Data Augmentation for Domain Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Due to the domain shifts between training and testing medical images, learned segmentation models often experience significant performance degradation during deployment. In this paper, we first decompose an image into its style code and content map and reveal that domain shifts in medical images involve: \textbf{style shifts} (\emph{i.e.}, differences in image appearance) and \textbf{content shifts} (\emph{i.e.}, variations in anatomical structures), the latter of which has been largely overlooked. To this end, we propose \textbf{StyCona}, a \textbf{sty}le \textbf{con}tent decomposition-based data \textbf{a}ugmentation method that innovatively augments both image style and content within the rank-one space, for domain generalizable medical image segmentation. StyCona is a simple yet effective plug-and-play module that substantially improves model generalization without requiring additional training parameters or modifications to the segmentation model architecture. Experiments on cross-sequence, cross-center, and cross-modality medical image segmentation settings with increasingly severe domain shifts, demonstrate the effectiveness of StyCona and its superiority over state-of-the-arts. The code is available at https://github.com/Senyh/StyCona.
Adaptive Mix for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Mix-up is a key technique for consistency regularization-based semi-supervised learning methods, generating strong-perturbed samples for strong-weak pseudo-supervision. Existing mix-up operations are performed either randomly or with predefined rules, such as replacing low-confidence patches with high-confidence ones. The former lacks control over the perturbation degree, leading to overfitting on randomly perturbed samples, while the latter tends to generate images with trivial perturbations, both of which limit the effectiveness of consistency learning. This paper aims to answer the following question: How can image mix-up perturbation be adaptively performed during training? To this end, we propose an Adaptive Mix algorithm (AdaMix) for image mix-up in a self-paced learning manner. Given that, in general, a model's performance gradually improves during training, AdaMix is equipped with a self-paced curriculum that, in the initial training stage, provides relatively simple perturbed samples and then gradually increases the difficulty of perturbed images by adaptively controlling the perturbation degree based on the model's learning state estimated by a self-paced regularize. We develop three frameworks with our AdaMix, i.e., AdaMix-ST, AdaMix-MT, and AdaMix-CT, for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Extensive experiments on three public datasets, including both 2D and 3D modalities, show that the proposed frameworks are capable of achieving superior performance. For example, compared with the state-of-the-art, AdaMix-CT achieves relative improvements of 2.62% in Dice and 48.25% in average surface distance on the ACDC dataset with 10% labeled data. The results demonstrate that mix-up operations with dynamically adjusted perturbation strength based on the segmentation model's state can significantly enhance the effectiveness of consistency regularization.
Self-Paced Sample Selection for Barely-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:The existing barely-supervised medical image segmentation (BSS) methods, adopting a registration-segmentation paradigm, aim to learn from data with very few annotations to mitigate the extreme label scarcity problem. However, this paradigm poses a challenge: pseudo-labels generated by image registration come with significant noise. To address this issue, we propose a self-paced sample selection framework (SPSS) for BSS. Specifically, SPSS comprises two main components: 1) self-paced uncertainty sample selection (SU) for explicitly improving the quality of pseudo labels in the image space, and 2) self-paced bidirectional feature contrastive learning (SC) for implicitly improving the quality of pseudo labels through enhancing the separability between class semantics in the feature space. Both SU and SC are trained collaboratively in a self-paced learning manner, ensuring that SPSS can learn from high-quality pseudo labels for BSS. Extensive experiments on two public medical image segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of SPSS over the state-of-the-art. Our code is release at https://github.com/SuuuJM/SPSS.
Rethinking Barely-Supervised Segmentation from an Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Perspective
May 16, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates an extremely challenging problem, barely-supervised medical image segmentation (BSS), where the training dataset comprises limited labeled data with only single-slice annotations and numerous unlabeled images. Currently, state-of-the-art (SOTA) BSS methods utilize a registration-based paradigm, depending on image registration to propagate single-slice annotations into volumetric pseudo labels for constructing a complete labeled set. However, this paradigm has a critical limitation: the pseudo labels generated by image registration are unreliable and noisy. Motivated by this, we propose a new perspective: training a model using only single-annotated slices as the labeled set without relying on image registration. To this end, we formulate BSS as an unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) problem. Specifically, we first design a novel noise-free labeled data construction algorithm (NFC) for slice-to-volume labeled data synthesis, which may result in a side effect: domain shifts between the synthesized images and the original images. Then, a frequency and spatial mix-up strategy (FSX) is further introduced to mitigate the domain shifts for UDA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method provides a promising alternative for BSS. Remarkably, the proposed method with only one labeled slice achieves an 80.77% dice score on left atrial segmentation, outperforming the SOTA by 61.28%. The code will be released upon the publication of this paper.
A Clinical-oriented Multi-level Contrastive Learning Method for Disease Diagnosis in Low-quality Medical Images
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Representation learning offers a conduit to elucidate distinctive features within the latent space and interpret the deep models. However, the randomness of lesion distribution and the complexity of low-quality factors in medical images pose great challenges for models to extract key lesion features. Disease diagnosis methods guided by contrastive learning (CL) have shown significant advantages in lesion feature representation. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of CL is highly dependent on the quality of the positive and negative sample pairs. In this work, we propose a clinical-oriented multi-level CL framework that aims to enhance the model's capacity to extract lesion features and discriminate between lesion and low-quality factors, thereby enabling more accurate disease diagnosis from low-quality medical images. Specifically, we first construct multi-level positive and negative pairs to enhance the model's comprehensive recognition capability of lesion features by integrating information from different levels and qualities of medical images. Moreover, to improve the quality of the learned lesion embeddings, we introduce a dynamic hard sample mining method based on self-paced learning. The proposed CL framework is validated on two public medical image datasets, EyeQ and Chest X-ray, demonstrating superior performance compared to other state-of-the-art disease diagnostic methods.
Narrowing the semantic gaps in U-Net with learnable skip connections: The case of medical image segmentation
Dec 23, 2023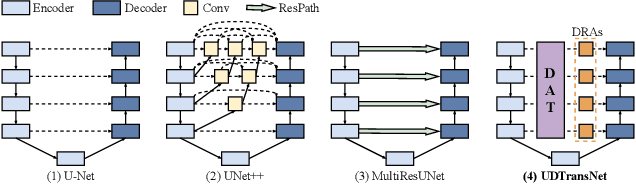
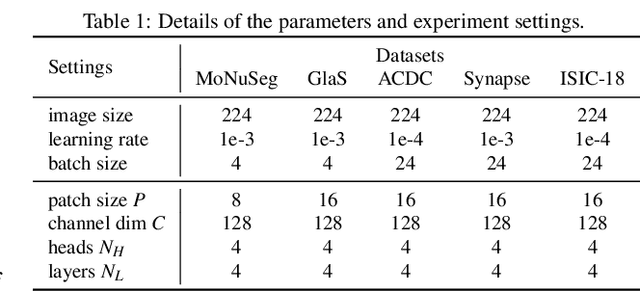
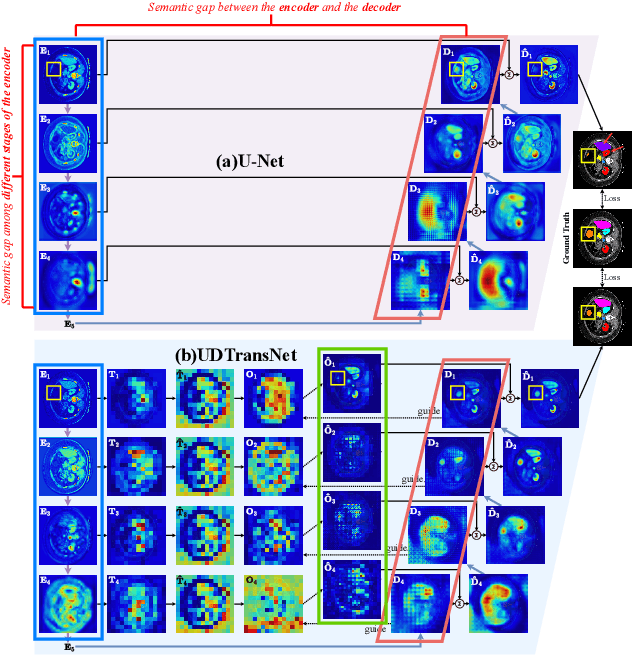
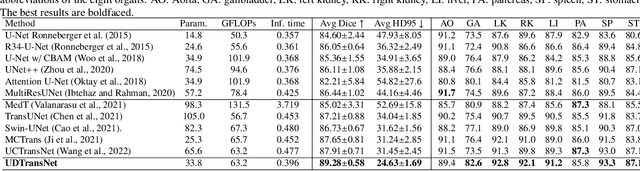
Abstract:Most state-of-the-art methods for medical image segmentation adopt the encoder-decoder architecture. However, this U-shaped framework still has limitations in capturing the non-local multi-scale information with a simple skip connection. To solve the problem, we firstly explore the potential weakness of skip connections in U-Net on multiple segmentation tasks, and find that i) not all skip connections are useful, each skip connection has different contribution; ii) the optimal combinations of skip connections are different, relying on the specific datasets. Based on our findings, we propose a new segmentation framework, named UDTransNet, to solve three semantic gaps in U-Net. Specifically, we propose a Dual Attention Transformer (DAT) module for capturing the channel- and spatial-wise relationships to better fuse the encoder features, and a Decoder-guided Recalibration Attention (DRA) module for effectively connecting the DAT tokens and the decoder features to eliminate the inconsistency. Hence, both modules establish a learnable connection to solve the semantic gaps between the encoder and the decoder, which leads to a high-performance segmentation model for medical images. Comprehensive experimental results indicate that our UDTransNet produces higher evaluation scores and finer segmentation results with relatively fewer parameters over the state-of-the-art segmentation methods on different public datasets. Code: https://github.com/McGregorWwww/UDTransNet.
Self-supervised Domain Adaptation for Breaking the Limits of Low-quality Fundus Image Quality Enhancement
Jan 17, 2023Abstract:Retinal fundus images have been applied for the diagnosis and screening of eye diseases, such as Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) or Diabetic Macular Edema (DME). However, both low-quality fundus images and style inconsistency potentially increase uncertainty in the diagnosis of fundus disease and even lead to misdiagnosis by ophthalmologists. Most of the existing image enhancement methods mainly focus on improving the image quality by leveraging the guidance of high-quality images, which is difficult to be collected in medical applications. In this paper, we tackle image quality enhancement in a fully unsupervised setting, i.e., neither paired images nor high-quality images. To this end, we explore the potential of the self-supervised task for improving the quality of fundus images without the requirement of high-quality reference images. Specifically, we construct multiple patch-wise domains via an auxiliary pre-trained quality assessment network and a style clustering. To achieve robust low-quality image enhancement and address style inconsistency, we formulate two self-supervised domain adaptation tasks to disentangle the features of image content, low-quality factor and style information by exploring intrinsic supervision signals within the low-quality images. Extensive experiments are conducted on EyeQ and Messidor datasets, and results show that our DASQE method achieves new state-of-the-art performance when only low-quality images are available.
Co-training with High-Confidence Pseudo Labels for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 11, 2023Abstract:High-quality pseudo labels are essential for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. Consistency regularization and pseudo labeling-based semi-supervised methods perform co-training using the pseudo labels from multi-view inputs. However, such co-training models tend to converge early to a consensus during training, so that the models degenerate to the self-training ones. Besides, the multi-view inputs are generated by perturbing or augmenting the original images, which inevitably introduces noise into the input leading to low-confidence pseudo labels. To address these issues, we propose an \textbf{U}ncertainty-guided Collaborative Mean-Teacher (UCMT) for semi-supervised semantic segmentation with the high-confidence pseudo labels. Concretely, UCMT consists of two main components: 1) collaborative mean-teacher (CMT) for encouraging model disagreement and performing co-training between the sub-networks, and 2) uncertainty-guided region mix (UMIX) for manipulating the input images according to the uncertainty maps of CMT and facilitating CMT to produce high-confidence pseudo labels. Combining the strengths of UMIX with CMT, UCMT can retain model disagreement and enhance the quality of pseudo labels for the co-training segmentation. Extensive experiments on four public medical image datasets including 2D and 3D modalities demonstrate the superiority of UCMT over the state-of-the-art. Code is available at: https://github.com/Senyh/UCMT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge