JinTai Chen
Group-On: Boosting One-Shot Segmentation with Supportive Query
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:One-shot semantic segmentation aims to segment query images given only ONE annotated support image of the same class. This task is challenging because target objects in the support and query images can be largely different in appearance and pose (i.e., intra-class variation). Prior works suggested that incorporating more annotated support images in few-shot settings boosts performances but increases costs due to additional manual labeling. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for ONE-shot semantic segmentation, called Group-On, which packs multiple query images in batches for the benefit of mutual knowledge support within the same category. Specifically, after coarse segmentation masks of the batch of queries are predicted, query-mask pairs act as pseudo support data to enhance mask predictions mutually, under the guidance of a simple Group-On Voting module. Comprehensive experiments on three standard benchmarks show that, in the ONE-shot setting, our Group-On approach significantly outperforms previous works by considerable margins. For example, on the COCO-20i dataset, we increase mIoU scores by 8.21% and 7.46% on ASNet and HSNet baselines, respectively. With only one support image, Group-On can be even competitive with the counterparts using 5 annotated support images.
Fetal Brain Tissue Annotation and Segmentation Challenge Results
Apr 20, 2022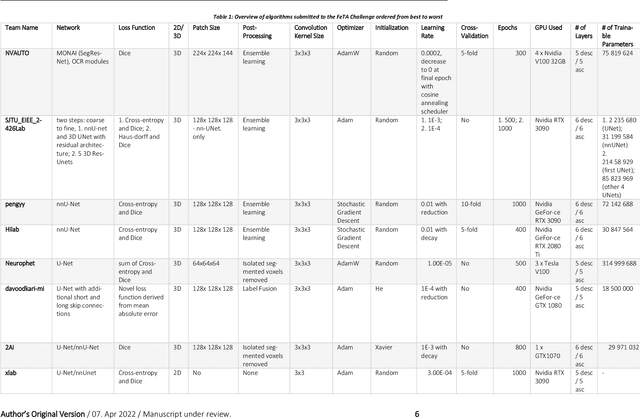
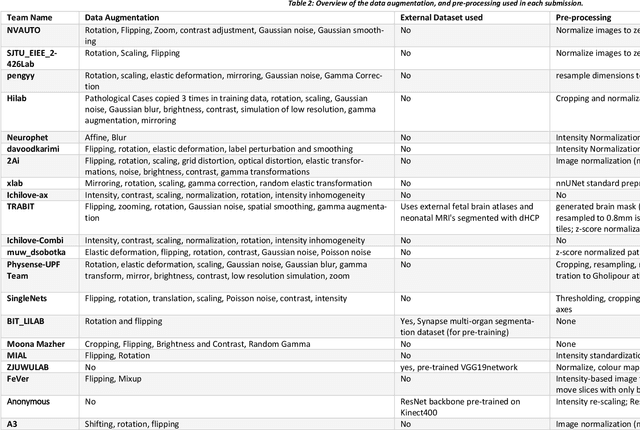
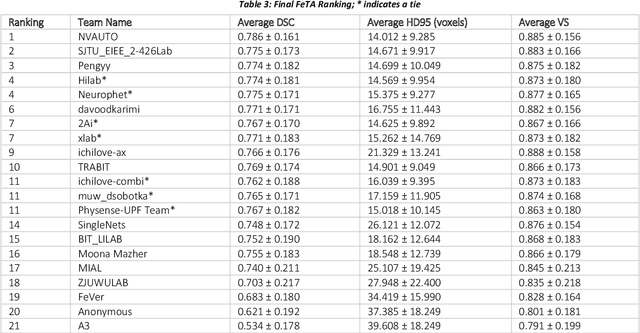
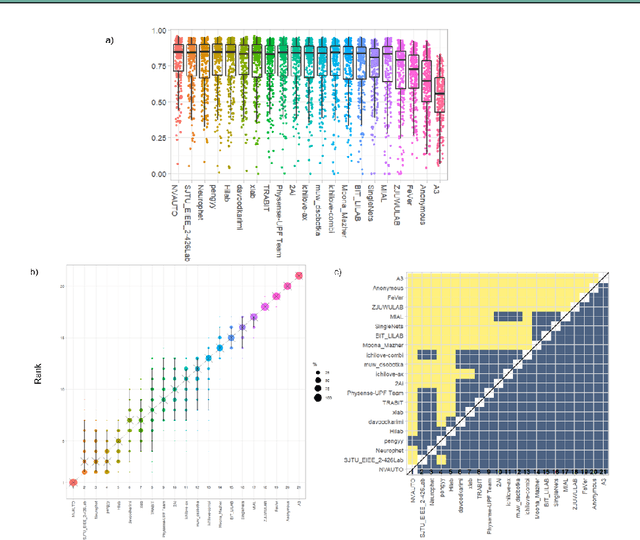
Abstract:In-utero fetal MRI is emerging as an important tool in the diagnosis and analysis of the developing human brain. Automatic segmentation of the developing fetal brain is a vital step in the quantitative analysis of prenatal neurodevelopment both in the research and clinical context. However, manual segmentation of cerebral structures is time-consuming and prone to error and inter-observer variability. Therefore, we organized the Fetal Tissue Annotation (FeTA) Challenge in 2021 in order to encourage the development of automatic segmentation algorithms on an international level. The challenge utilized FeTA Dataset, an open dataset of fetal brain MRI reconstructions segmented into seven different tissues (external cerebrospinal fluid, grey matter, white matter, ventricles, cerebellum, brainstem, deep grey matter). 20 international teams participated in this challenge, submitting a total of 21 algorithms for evaluation. In this paper, we provide a detailed analysis of the results from both a technical and clinical perspective. All participants relied on deep learning methods, mainly U-Nets, with some variability present in the network architecture, optimization, and image pre- and post-processing. The majority of teams used existing medical imaging deep learning frameworks. The main differences between the submissions were the fine tuning done during training, and the specific pre- and post-processing steps performed. The challenge results showed that almost all submissions performed similarly. Four of the top five teams used ensemble learning methods. However, one team's algorithm performed significantly superior to the other submissions, and consisted of an asymmetrical U-Net network architecture. This paper provides a first of its kind benchmark for future automatic multi-tissue segmentation algorithms for the developing human brain in utero.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge