Jeremy Watson
University of Canterbury
One-Shot Price Forecasting with Covariate-Guided Experts under Privacy Constraints
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Forecasting in power systems often involves multivariate time series with complex dependencies and strict privacy constraints across regions. Traditional forecasting methods require significant expert knowledge and struggle to generalize across diverse deployment scenarios. Recent advancements in pre-trained time series models offer new opportunities, but their zero-shot performance on domain-specific tasks remains limited. To address these challenges, we propose a novel MoE Encoder module that augments pretrained forecasting models by injecting a sparse mixture-of-experts layer between tokenization and encoding. This design enables two key capabilities: (1) trans forming multivariate forecasting into an expert-guided univariate task, allowing the model to effectively capture inter-variable relations, and (2) supporting localized training and lightweight parameter sharing in federated settings where raw data cannot be exchanged. Extensive experiments on public multivariate datasets demonstrate that MoE-Encoder significantly improves forecasting accuracy compared to strong baselines. We further simulate federated environments and show that transferring only MoE-Encoder parameters allows efficient adaptation to new regions, with minimal performance degradation. Our findings suggest that MoE-Encoder provides a scalable and privacy-aware extension to foundation time series models.
Flatland Competition 2020: MAPF and MARL for Efficient Train Coordination on a Grid World
Mar 30, 2021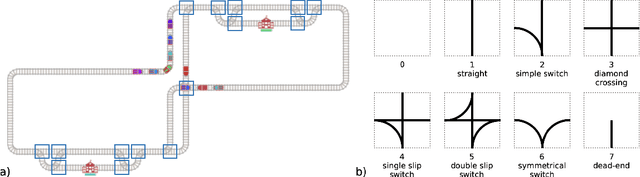
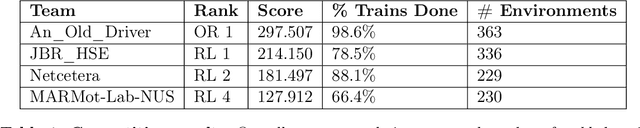
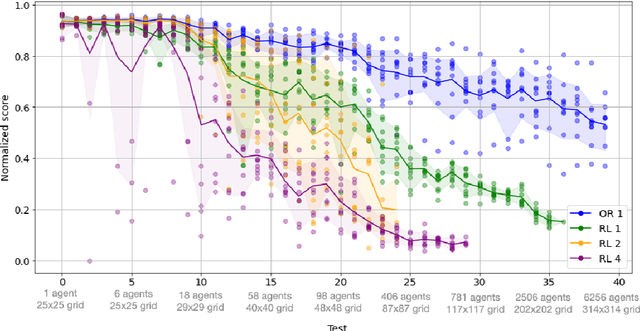
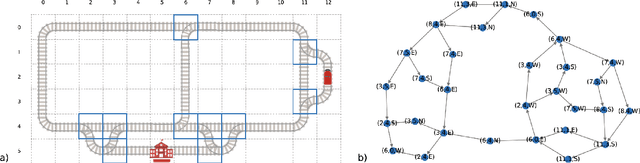
Abstract:The Flatland competition aimed at finding novel approaches to solve the vehicle re-scheduling problem (VRSP). The VRSP is concerned with scheduling trips in traffic networks and the re-scheduling of vehicles when disruptions occur, for example the breakdown of a vehicle. While solving the VRSP in various settings has been an active area in operations research (OR) for decades, the ever-growing complexity of modern railway networks makes dynamic real-time scheduling of traffic virtually impossible. Recently, multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has successfully tackled challenging tasks where many agents need to be coordinated, such as multiplayer video games. However, the coordination of hundreds of agents in a real-life setting like a railway network remains challenging and the Flatland environment used for the competition models these real-world properties in a simplified manner. Submissions had to bring as many trains (agents) to their target stations in as little time as possible. While the best submissions were in the OR category, participants found many promising MARL approaches. Using both centralized and decentralized learning based approaches, top submissions used graph representations of the environment to construct tree-based observations. Further, different coordination mechanisms were implemented, such as communication and prioritization between agents. This paper presents the competition setup, four outstanding solutions to the competition, and a cross-comparison between them.
Flatland-RL : Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning on Trains
Dec 11, 2020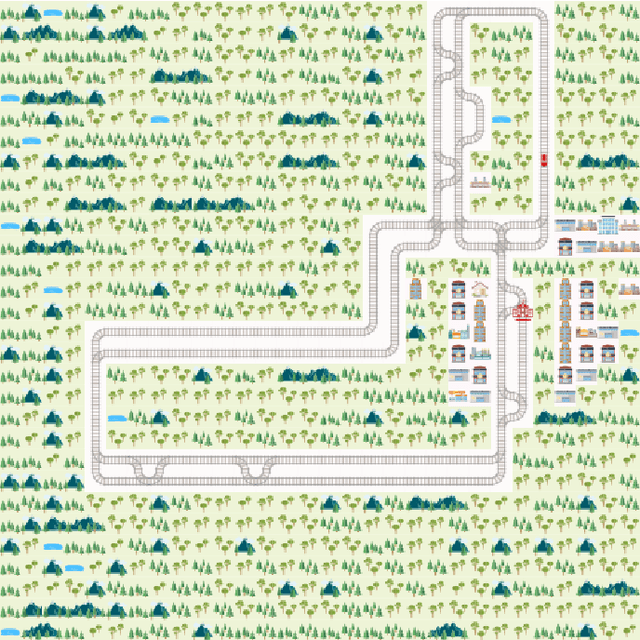


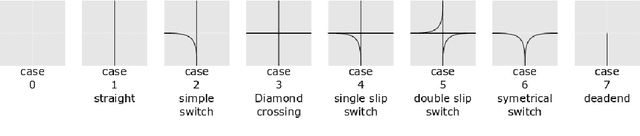
Abstract:Efficient automated scheduling of trains remains a major challenge for modern railway systems. The underlying vehicle rescheduling problem (VRSP) has been a major focus of Operations Research (OR) since decades. Traditional approaches use complex simulators to study VRSP, where experimenting with a broad range of novel ideas is time consuming and has a huge computational overhead. In this paper, we introduce a two-dimensional simplified grid environment called "Flatland" that allows for faster experimentation. Flatland does not only reduce the complexity of the full physical simulation, but also provides an easy-to-use interface to test novel approaches for the VRSP, such as Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Imitation Learning (IL). In order to probe the potential of Machine Learning (ML) research on Flatland, we (1) ran a first series of RL and IL experiments and (2) design and executed a public Benchmark at NeurIPS 2020 to engage a large community of researchers to work on this problem. Our own experimental results, on the one hand, demonstrate that ML has potential in solving the VRSP on Flatland. On the other hand, we identify key topics that need further research. Overall, the Flatland environment has proven to be a robust and valuable framework to investigate the VRSP for railway networks. Our experiments provide a good starting point for further research and for the participants of the NeurIPS 2020 Flatland Benchmark. All of these efforts together have the potential to have a substantial impact on shaping the mobility of the future.
Artificial Intelligence for Prosthetics - challenge solutions
Feb 07, 2019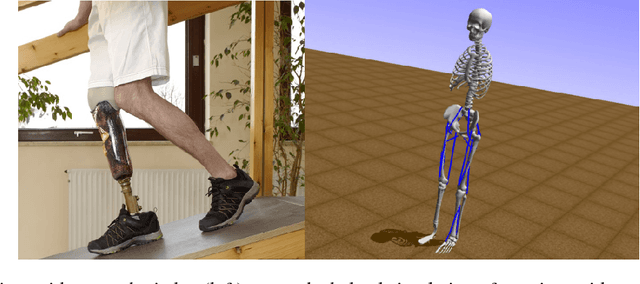
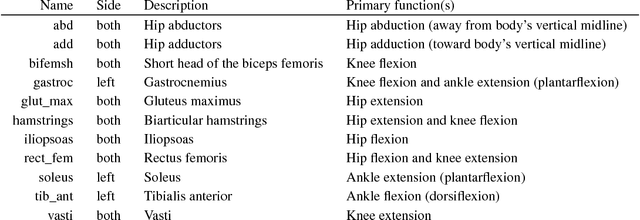
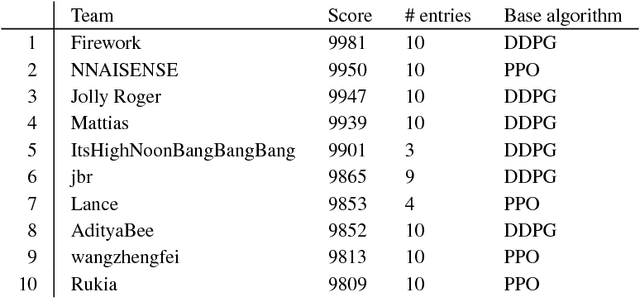
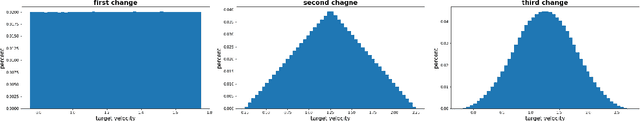
Abstract:In the NeurIPS 2018 Artificial Intelligence for Prosthetics challenge, participants were tasked with building a controller for a musculoskeletal model with a goal of matching a given time-varying velocity vector. Top participants were invited to describe their algorithms. In this work, we describe the challenge and present thirteen solutions that used deep reinforcement learning approaches. Many solutions use similar relaxations and heuristics, such as reward shaping, frame skipping, discretization of the action space, symmetry, and policy blending. However, each team implemented different modifications of the known algorithms by, for example, dividing the task into subtasks, learning low-level control, or by incorporating expert knowledge and using imitation learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge