Jason Ingyu Choi
Wizard of Shopping: Target-Oriented E-commerce Dialogue Generation with Decision Tree Branching
Feb 03, 2025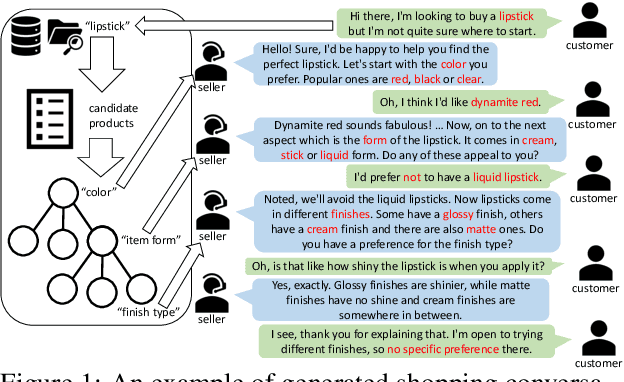

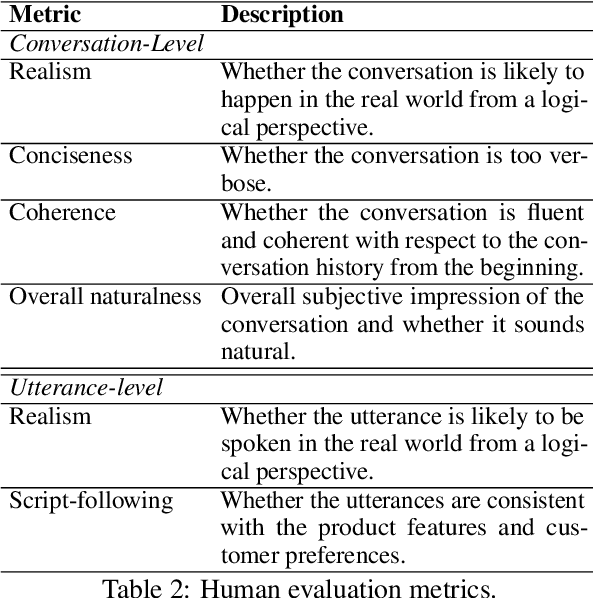
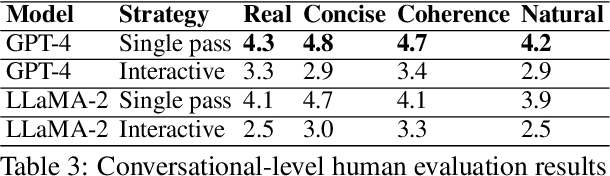
Abstract:The goal of conversational product search (CPS) is to develop an intelligent, chat-based shopping assistant that can directly interact with customers to understand shopping intents, ask clarification questions, and find relevant products. However, training such assistants is hindered mainly due to the lack of reliable and large-scale datasets. Prior human-annotated CPS datasets are extremely small in size and lack integration with real-world product search systems. We propose a novel approach, TRACER, which leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate realistic and natural conversations for different shopping domains. TRACER's novelty lies in grounding the generation to dialogue plans, which are product search trajectories predicted from a decision tree model, that guarantees relevant product discovery in the shortest number of search conditions. We also release the first target-oriented CPS dataset Wizard of Shopping (WoS), containing highly natural and coherent conversations (3.6k) from three shopping domains. Finally, we demonstrate the quality and effectiveness of WoS via human evaluations and downstream tasks.
Evaluation Metrics of Language Generation Models for Synthetic Traffic Generation Tasks
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:Many Natural Language Generation (NLG) tasks aim to generate a single output text given an input prompt. Other settings require the generation of multiple texts, e.g., for Synthetic Traffic Generation (STG). This generation task is crucial for training and evaluating QA systems as well as conversational agents, where the goal is to generate multiple questions or utterances resembling the linguistic variability of real users. In this paper, we show that common NLG metrics, like BLEU, are not suitable for evaluating STG. We propose and evaluate several metrics designed to compare the generated traffic to the distribution of real user texts. We validate our metrics with an automatic procedure to verify whether they capture different types of quality issues of generated data; we also run human annotations to verify the correlation with human judgements. Experiments on three tasks, i.e., Shopping Utterance Generation, Product Question Generation and Query Auto Completion, demonstrate that our metrics are effective for evaluating STG tasks, and improve the agreement with human judgement up to 20% with respect to common NLG metrics. We believe these findings can pave the way towards better solutions for estimating the representativeness of synthetic text data.
Offline and Online Satisfaction Prediction in Open-Domain Conversational Systems
Jun 02, 2020

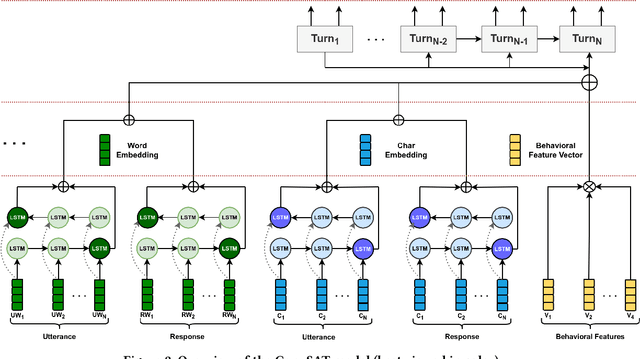

Abstract:Predicting user satisfaction in conversational systems has become critical, as spoken conversational assistants operate in increasingly complex domains. Online satisfaction prediction (i.e., predicting satisfaction of the user with the system after each turn) could be used as a new proxy for implicit user feedback, and offers promising opportunities to create more responsive and effective conversational agents, which adapt to the user's engagement with the agent. To accomplish this goal, we propose a conversational satisfaction prediction model specifically designed for open-domain spoken conversational agents, called ConvSAT. To operate robustly across domains, ConvSAT aggregates multiple representations of the conversation, namely the conversation history, utterance and response content, and system- and user-oriented behavioral signals. We first calibrate ConvSAT performance against state of the art methods on a standard dataset (Dialogue Breakdown Detection Challenge) in an online regime, and then evaluate ConvSAT on a large dataset of conversations with real users, collected as part of the Alexa Prize competition. Our experimental results show that ConvSAT significantly improves satisfaction prediction for both offline and online setting on both datasets, compared to the previously reported state-of-the-art approaches. The insights from our study can enable more intelligent conversational systems, which could adapt in real-time to the inferred user satisfaction and engagement.
Quantifying the Effects of Prosody Modulation on User Engagement and Satisfaction in Conversational Systems
Jun 02, 2020


Abstract:As voice-based assistants such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant become ubiquitous, users increasingly expect to maintain natural and informative conversations with such systems. However, for an open-domain conversational system to be coherent and engaging, it must be able to maintain the user's interest for extended periods, without sounding boring or annoying. In this paper, we investigate one natural approach to this problem, of modulating response prosody, i.e., changing the pitch and cadence of the response to indicate delight, sadness or other common emotions, as well as using pre-recorded interjections. Intuitively, this approach should improve the naturalness of the conversation, but attempts to quantify the effects of prosodic modulation on user satisfaction and engagement remain challenging. To accomplish this, we report results obtained from a large-scale empirical study that measures the effects of prosodic modulation on user behavior and engagement across multiple conversation domains, both immediately after each turn, and at the overall conversation level. Our results indicate that the prosody modulation significantly increases both immediate and overall user satisfaction. However, since the effects vary across different domains, we verify that prosody modulations do not substitute for coherent, informative content of the responses. Together, our results provide useful tools and insights for improving the naturalness of responses in conversational systems.
Contextual Dialogue Act Classification for Open-Domain Conversational Agents
May 28, 2020



Abstract:Classifying the general intent of the user utterance in a conversation, also known as Dialogue Act (DA), e.g., open-ended question, statement of opinion, or request for an opinion, is a key step in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) for conversational agents. While DA classification has been extensively studied in human-human conversations, it has not been sufficiently explored for the emerging open-domain automated conversational agents. Moreover, despite significant advances in utterance-level DA classification, full understanding of dialogue utterances requires conversational context. Another challenge is the lack of available labeled data for open-domain human-machine conversations. To address these problems, we propose a novel method, CDAC (Contextual Dialogue Act Classifier), a simple yet effective deep learning approach for contextual dialogue act classification. Specifically, we use transfer learning to adapt models trained on human-human conversations to predict dialogue acts in human-machine dialogues. To investigate the effectiveness of our method, we train our model on the well-known Switchboard human-human dialogue dataset, and fine-tune it for predicting dialogue acts in human-machine conversation data, collected as part of the Amazon Alexa Prize 2018 competition. The results show that the CDAC model outperforms an utterance-level state of the art baseline by 8.0% on the Switchboard dataset, and is comparable to the latest reported state-of-the-art contextual DA classification results. Furthermore, our results show that fine-tuning the CDAC model on a small sample of manually labeled human-machine conversations allows CDAC to more accurately predict dialogue acts in real users' conversations, suggesting a promising direction for future improvements.
ConCET: Entity-Aware Topic Classification for Open-Domain Conversational Agents
May 28, 2020



Abstract:Identifying the topic (domain) of each user's utterance in open-domain conversational systems is a crucial step for all subsequent language understanding and response tasks. In particular, for complex domains, an utterance is often routed to a single component responsible for that domain. Thus, correctly mapping a user utterance to the right domain is critical. To address this problem, we introduce ConCET: a Concurrent Entity-aware conversational Topic classifier, which incorporates entity-type information together with the utterance content features. Specifically, ConCET utilizes entity information to enrich the utterance representation, combining character, word, and entity-type embeddings into a single representation. However, for rich domains with millions of available entities, unrealistic amounts of labeled training data would be required. To complement our model, we propose a simple and effective method for generating synthetic training data, to augment the typically limited amounts of labeled training data, using commonly available knowledge bases to generate additional labeled utterances. We extensively evaluate ConCET and our proposed training method first on an openly available human-human conversational dataset called Self-Dialogue, to calibrate our approach against previous state-of-the-art methods; second, we evaluate ConCET on a large dataset of human-machine conversations with real users, collected as part of the Amazon Alexa Prize. Our results show that ConCET significantly improves topic classification performance on both datasets, including 8-10% improvements over state-of-the-art deep learning methods. We complement our quantitative results with detailed analysis of system performance, which could be used for further improvements of conversational agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge