Ilhan Aslan
Huawei Technologies
Audio Enhancement for Computer Audition -- An Iterative Training Paradigm Using Sample Importance
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:Neural network models for audio tasks, such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and acoustic scene classification (ASC), are susceptible to noise contamination for real-life applications. To improve audio quality, an enhancement module, which can be developed independently, is explicitly used at the front-end of the target audio applications. In this paper, we present an end-to-end learning solution to jointly optimise the models for audio enhancement (AE) and the subsequent applications. To guide the optimisation of the AE module towards a target application, and especially to overcome difficult samples, we make use of the sample-wise performance measure as an indication of sample importance. In experiments, we consider four representative applications to evaluate our training paradigm, i.e., ASR, speech command recognition (SCR), speech emotion recognition (SER), and ASC. These applications are associated with speech and non-speech tasks concerning semantic and non-semantic features, transient and global information, and the experimental results indicate that our proposed approach can considerably boost the noise robustness of the models, especially at low signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), for a wide range of computer audition tasks in everyday-life noisy environments.
Modeling Emotional Trajectories in Written Stories Utilizing Transformers and Weakly-Supervised Learning
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Telling stories is an integral part of human communication which can evoke emotions and influence the affective states of the audience. Automatically modeling emotional trajectories in stories has thus attracted considerable scholarly interest. However, as most existing works have been limited to unsupervised dictionary-based approaches, there is no benchmark for this task. We address this gap by introducing continuous valence and arousal labels for an existing dataset of children's stories originally annotated with discrete emotion categories. We collect additional annotations for this data and map the categorical labels to the continuous valence and arousal space. For predicting the thus obtained emotionality signals, we fine-tune a DeBERTa model and improve upon this baseline via a weakly supervised learning approach. The best configuration achieves a Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) of $.8221$ for valence and $.7125$ for arousal on the test set, demonstrating the efficacy of our proposed approach. A detailed analysis shows the extent to which the results vary depending on factors such as the author, the individual story, or the section within the story. In addition, we uncover the weaknesses of our approach by investigating examples that prove to be difficult to predict.
Automatic Emotion Modelling in Written Stories
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:Telling stories is an integral part of human communication which can evoke emotions and influence the affective states of the audience. Automatically modelling emotional trajectories in stories has thus attracted considerable scholarly interest. However, as most existing works have been limited to unsupervised dictionary-based approaches, there is no labelled benchmark for this task. We address this gap by introducing continuous valence and arousal annotations for an existing dataset of children's stories annotated with discrete emotion categories. We collect additional annotations for this data and map the originally categorical labels to the valence and arousal space. Leveraging recent advances in Natural Language Processing, we propose a set of novel Transformer-based methods for predicting valence and arousal signals over the course of written stories. We explore several strategies for fine-tuning a pretrained ELECTRA model and study the benefits of considering a sentence's context when inferring its emotionality. Moreover, we experiment with additional LSTM and Transformer layers. The best configuration achieves a Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) of .7338 for valence and .6302 for arousal on the test set, demonstrating the suitability of our proposed approach. Our code and additional annotations are made available at https://github.com/lc0197/emotion_modelling_stories.
An Overview & Analysis of Sequence-to-Sequence Emotional Voice Conversion
Mar 29, 2022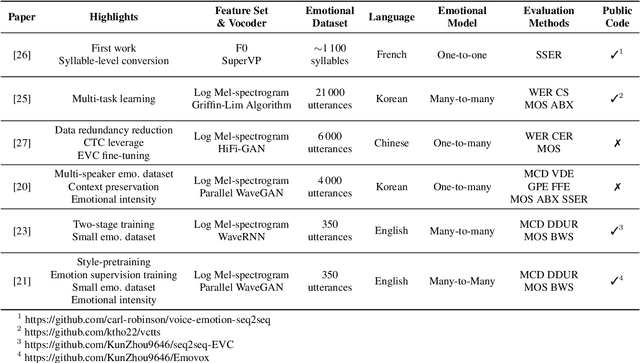
Abstract:Emotional voice conversion (EVC) focuses on converting a speech utterance from a source to a target emotion; it can thus be a key enabling technology for human-computer interaction applications and beyond. However, EVC remains an unsolved research problem with several challenges. In particular, as speech rate and rhythm are two key factors of emotional conversion, models have to generate output sequences of differing length. Sequence-to-sequence modelling is recently emerging as a competitive paradigm for models that can overcome those challenges. In an attempt to stimulate further research in this promising new direction, recent sequence-to-sequence EVC papers were systematically investigated and reviewed from six perspectives: their motivation, training strategies, model architectures, datasets, model inputs, and evaluation methods. This information is organised to provide the research community with an easily digestible overview of the current state-of-the-art. Finally, we discuss existing challenges of sequence-to-sequence EVC.
On the Impact of Word Error Rate on Acoustic-Linguistic Speech Emotion Recognition: An Update for the Deep Learning Era
Apr 20, 2021



Abstract:Text encodings from automatic speech recognition (ASR) transcripts and audio representations have shown promise in speech emotion recognition (SER) ever since. Yet, it is challenging to explain the effect of each information stream on the SER systems. Further, more clarification is required for analysing the impact of ASR's word error rate (WER) on linguistic emotion recognition per se and in the context of fusion with acoustic information exploitation in the age of deep ASR systems. In order to tackle the above issues, we create transcripts from the original speech by applying three modern ASR systems, including an end-to-end model trained with recurrent neural network-transducer loss, a model with connectionist temporal classification loss, and a wav2vec framework for self-supervised learning. Afterwards, we use pre-trained textual models to extract text representations from the ASR outputs and the gold standard. For extraction and learning of acoustic speech features, we utilise openSMILE, openXBoW, DeepSpectrum, and auDeep. Finally, we conduct decision-level fusion on both information streams -- acoustics and linguistics. Using the best development configuration, we achieve state-of-the-art unweighted average recall values of $73.6\,\%$ and $73.8\,\%$ on the speaker-independent development and test partitions of IEMOCAP, respectively.
Towards Tool-Support for Interactive-Machine Learning Applications in the Android Ecosystem
Mar 27, 2021

Abstract:Consumer applications are becoming increasingly smarter and most of them have to run on device ecosystems. Potential benefits are for example enabling cross-device interaction and seamless user experiences. Essential for today's smart solutions with high performance are machine learning models. However, these models are often developed separately by AI engineers for one specific device and do not consider the challenges and potentials associated with a device ecosystem in which their models have to run. We believe that there is a need for tool-support for AI engineers to address the challenges of implementing, testing, and deploying machine learning models for a next generation of smart interactive consumer applications. This paper presents preliminary results of a series of inquiries, including interviews with AI engineers and experiments for an interactive machine learning use case with a Smartwatch and Smartphone. We identified the themes through interviews and hands-on experience working on our use case and proposed features, such as data collection from sensors and easy testing of the resources consumption of running pre-processing code on the target device, which will serve as tool-support for AI engineers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge