Idan Kligvasser
Anchored Diffusion for Video Face Reenactment
Jul 21, 2024
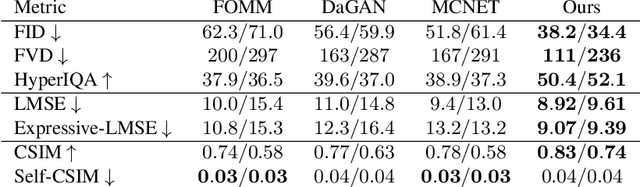
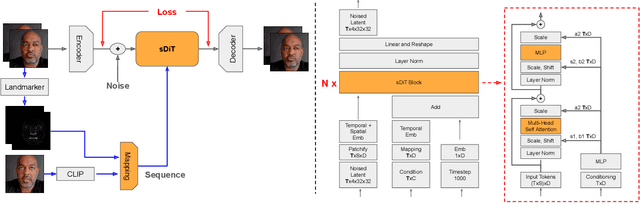
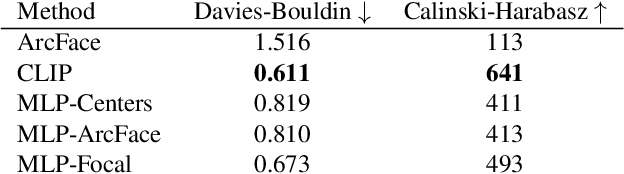
Abstract:Video generation has drawn significant interest recently, pushing the development of large-scale models capable of producing realistic videos with coherent motion. Due to memory constraints, these models typically generate short video segments that are then combined into long videos. The merging process poses a significant challenge, as it requires ensuring smooth transitions and overall consistency. In this paper, we introduce Anchored Diffusion, a novel method for synthesizing relatively long and seamless videos. We extend Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) to incorporate temporal information, creating our sequence-DiT (sDiT) model for generating short video segments. Unlike previous works, we train our model on video sequences with random non-uniform temporal spacing and incorporate temporal information via external guidance, increasing flexibility and allowing it to capture both short and long-term relationships. Furthermore, during inference, we leverage the transformer architecture to modify the diffusion process, generating a batch of non-uniform sequences anchored to a common frame, ensuring consistency regardless of temporal distance. To demonstrate our method, we focus on face reenactment, the task of creating a video from a source image that replicates the facial expressions and movements from a driving video. Through comprehensive experiments, we show our approach outperforms current techniques in producing longer consistent high-quality videos while offering editing capabilities.
Looks Too Good To Be True: An Information-Theoretic Analysis of Hallucinations in Generative Restoration Models
May 26, 2024



Abstract:The pursuit of high perceptual quality in image restoration has driven the development of revolutionary generative models, capable of producing results often visually indistinguishable from real data. However, as their perceptual quality continues to improve, these models also exhibit a growing tendency to generate hallucinations - realistic-looking details that do not exist in the ground truth images. The presence of hallucinations introduces uncertainty regarding the reliability of the models' predictions, raising major concerns about their practical application. In this paper, we employ information-theory tools to investigate this phenomenon, revealing a fundamental tradeoff between uncertainty and perception. We rigorously analyze the relationship between these two factors, proving that the global minimal uncertainty in generative models grows in tandem with perception. In particular, we define the inherent uncertainty of the restoration problem and show that attaining perfect perceptual quality entails at least twice this uncertainty. Additionally, we establish a relation between mean squared-error distortion, uncertainty and perception, through which we prove the aforementioned uncertainly-perception tradeoff induces the well-known perception-distortion tradeoff. This work uncovers fundamental limitations of generative models in achieving both high perceptual quality and reliable predictions for image restoration. We demonstrate our theoretical findings through an analysis of single image super-resolution algorithms. Our work aims to raise awareness among practitioners about this inherent tradeoff, empowering them to make informed decisions and potentially prioritize safety over perceptual performance.
Uncertainty-Aware PPG-2-ECG for Enhanced Cardiovascular Diagnosis using Diffusion Models
May 19, 2024Abstract:Analyzing the cardiovascular system condition via Electrocardiography (ECG) is a common and highly effective approach, and it has been practiced and perfected over many decades. ECG sensing is non-invasive and relatively easy to acquire, and yet it is still cumbersome for holter monitoring tests that may span over hours and even days. A possible alternative in this context is Photoplethysmography (PPG): An optically-based signal that measures blood volume fluctuations, as typically sensed by conventional ``wearable devices''. While PPG presents clear advantages in acquisition, convenience, and cost-effectiveness, ECG provides more comprehensive information, allowing for a more precise detection of heart conditions. This implies that a conversion from PPG to ECG, as recently discussed in the literature, inherently involves an unavoidable level of uncertainty. In this paper we introduce a novel methodology for addressing the PPG-2-ECG conversion, and offer an enhanced classification of cardiovascular conditions using the given PPG, all while taking into account the uncertainties arising from the conversion process. We provide a mathematical justification for our proposed computational approach, and present empirical studies demonstrating its superior performance compared to state-of-the-art baseline methods.
Semi-supervised Quality Evaluation of Colonoscopy Procedures
May 17, 2023Abstract:Colonoscopy is the standard of care technique for detecting and removing polyps for the prevention of colorectal cancer. Nevertheless, gastroenterologists (GI) routinely miss approximately 25% of polyps during colonoscopies. These misses are highly operator dependent, influenced by the physician skills, experience, vigilance, and fatigue. Standard quality metrics, such as Withdrawal Time or Cecal Intubation Rate, have been shown to be well correlated with Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR). However, those metrics are limited in their ability to assess the quality of a specific procedure, and they do not address quality aspects related to the style or technique of the examination. In this work we design novel online and offline quality metrics, based on visual appearance quality criteria learned by an ML model in an unsupervised way. Furthermore, we evaluate the likelihood of detecting an existing polyp as a function of quality and use it to demonstrate high correlation of the proposed metric to polyp detection sensitivity. The proposed online quality metric can be used to provide real time quality feedback to the performing GI. By integrating the local metric over the withdrawal phase, we build a global, offline quality metric, which is shown to be highly correlated to the standard Polyp Per Colonoscopy (PPC) quality metric.
BlendGAN: Learning and Blending the Internal Distributions of Single Images by Spatial Image-Identity Conditioning
Dec 03, 2022Abstract:Training a generative model on a single image has drawn significant attention in recent years. Single image generative methods are designed to learn the internal patch distribution of a single natural image at multiple scales. These models can be used for drawing diverse samples that semantically resemble the training image, as well as for solving many image editing and restoration tasks that involve that particular image. Here, we introduce an extended framework, which allows to simultaneously learn the internal distributions of several images, by using a single model with spatially varying image-identity conditioning. Our BlendGAN opens the door to applications that are not supported by single-image models, including morphing, melding, and structure-texture fusion between two or more arbitrary images.
Sparsity Aware Normalization for GANs
Mar 03, 2021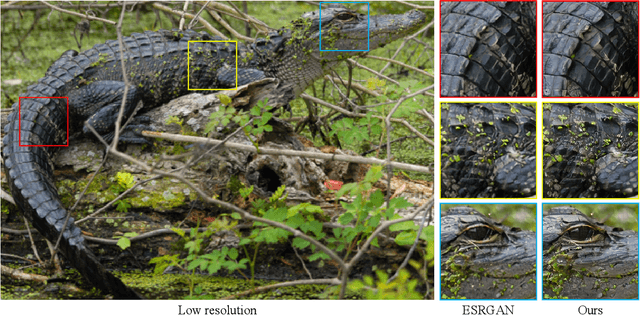
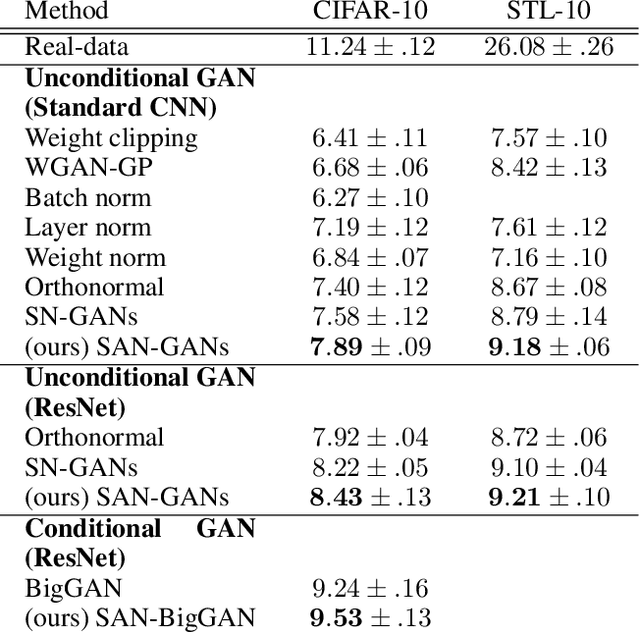
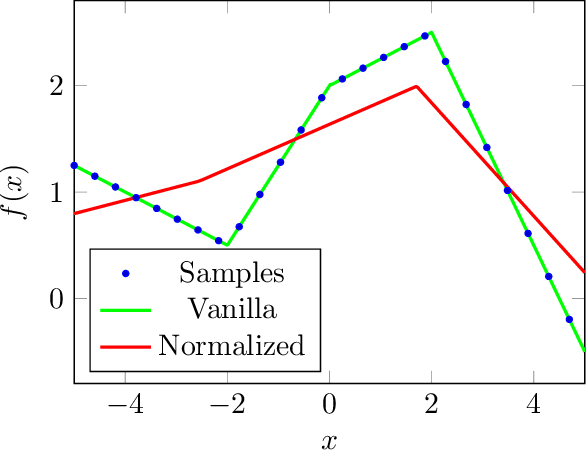
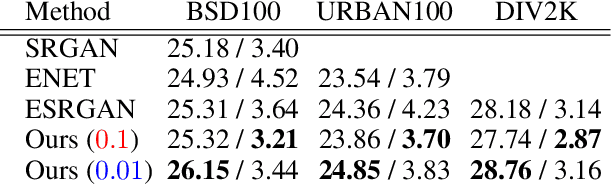
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are known to benefit from regularization or normalization of their critic (discriminator) network during training. In this paper, we analyze the popular spectral normalization scheme, find a significant drawback and introduce sparsity aware normalization (SAN), a new alternative approach for stabilizing GAN training. As opposed to other normalization methods, our approach explicitly accounts for the sparse nature of the feature maps in convolutional networks with ReLU activations. We illustrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive experiments with a variety of network architectures. As we show, sparsity is particularly dominant in critics used for image-to-image translation settings. In these cases our approach improves upon existing methods, in less training epochs and with smaller capacity networks, while requiring practically no computational overhead.
Dense xUnit Networks
Nov 27, 2018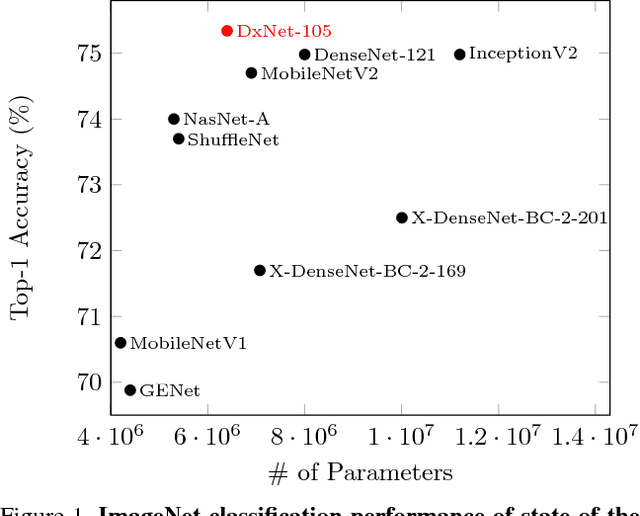
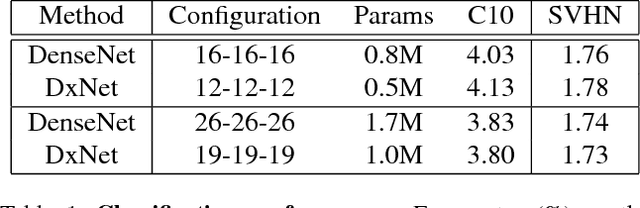
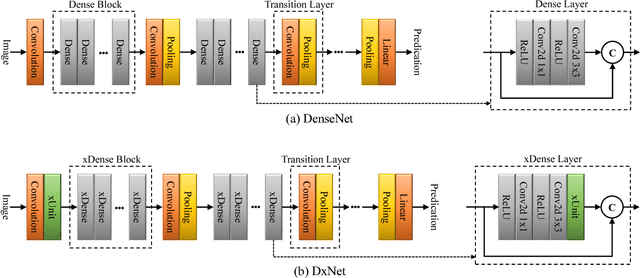
Abstract:Deep net architectures have constantly evolved over the past few years, leading to significant advancements in a wide array of computer vision tasks. However, besides high accuracy, many applications also require a low computational load and limited memory footprint. To date, efficiency has typically been achieved either by architectural choices at the macro level (e.g. using skip connections or pruning techniques) or modifications at the level of the individual layers (e.g. using depth-wise convolutions or channel shuffle operations). Interestingly, much less attention has been devoted to the role of the activation functions in constructing efficient nets. Recently, Kligvasser et al. showed that incorporating spatial connections within the activation functions, enables a significant boost in performance in image restoration tasks, at any given budget of parameters. However, the effectiveness of their xUnit module has only been tested on simple small models, which are not characteristic of those used in high-level vision tasks. In this paper, we adopt and improve the xUnit activation, show how it can be incorporated into the DenseNet architecture, and illustrate its high effectiveness for classification and image restoration tasks alike. While the DenseNet architecture is extremely efficient to begin with, our dense xUnit net (DxNet) can typically achieve the same performance with far fewer parameters. For example, on ImageNet, our DxNet outperforms a ReLU-based DenseNet having 30% more parameters and achieves state-of-the-art results for this budget of parameters. Furthermore, in denoising and super-resolution, DxNet significantly improves upon all existing lightweight solutions, including the xUnit-based nets of Kligvasser et al.
xUnit: Learning a Spatial Activation Function for Efficient Image Restoration
Mar 25, 2018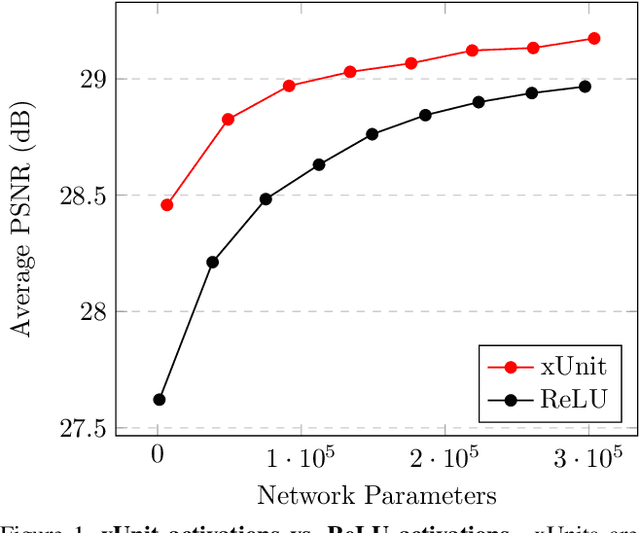
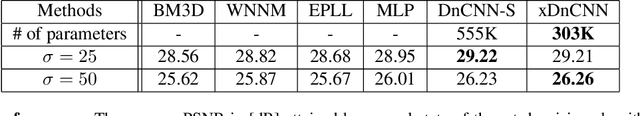
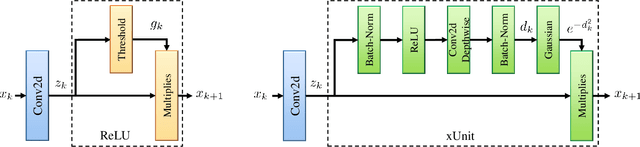
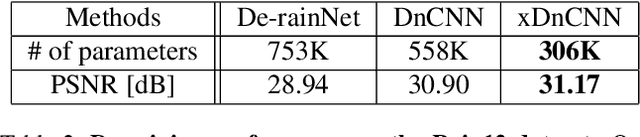
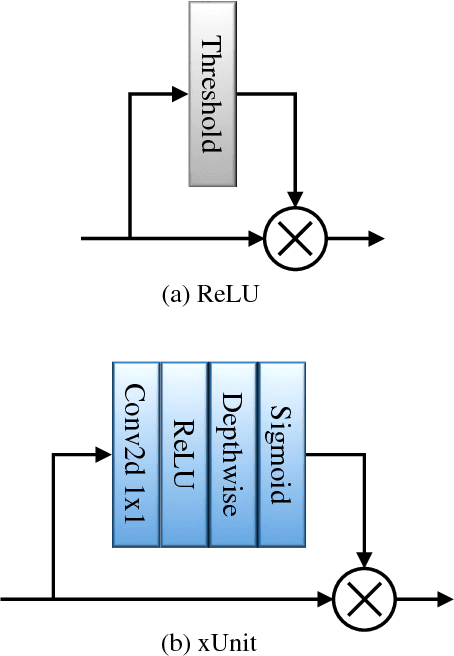
Abstract:In recent years, deep neural networks (DNNs) achieved unprecedented performance in many low-level vision tasks. However, state-of-the-art results are typically achieved by very deep networks, which can reach tens of layers with tens of millions of parameters. To make DNNs implementable on platforms with limited resources, it is necessary to weaken the tradeoff between performance and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a new activation unit, which is particularly suitable for image restoration problems. In contrast to the widespread per-pixel activation units, like ReLUs and sigmoids, our unit implements a learnable nonlinear function with spatial connections. This enables the net to capture much more complex features, thus requiring a significantly smaller number of layers in order to reach the same performance. We illustrate the effectiveness of our units through experiments with state-of-the-art nets for denoising, de-raining, and super resolution, which are already considered to be very small. With our approach, we are able to further reduce these models by nearly 50% without incurring any degradation in performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge