Hsuan-Jui Chen
Once-for-All Sequence Compression for Self-Supervised Speech Models
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:The sequence length along the time axis is often the dominant factor of the computational cost of self-supervised speech models. Works have been proposed to reduce the sequence length for lowering the computational cost. However, different downstream tasks have different tolerance of sequence compressing, so a model that produces a fixed compressing rate may not fit all tasks. In this work, we introduce a once-for-all (OFA) sequence compression framework for self-supervised speech models that supports a continuous range of compressing rates. The framework is evaluated on various tasks, showing marginal degradation compared to the fixed compressing rate variants with a smooth performance-efficiency trade-off. We further explore adaptive compressing rate learning, demonstrating the ability to select task-specific preferred frame periods without needing a grid search.
On Compressing Sequences for Self-Supervised Speech Models
Oct 14, 2022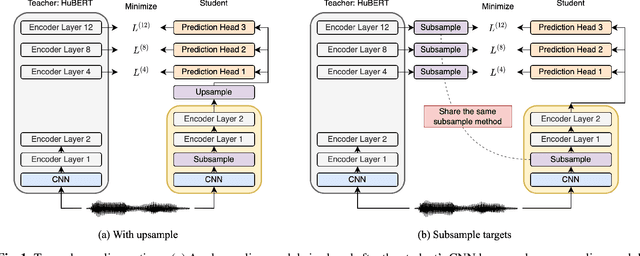
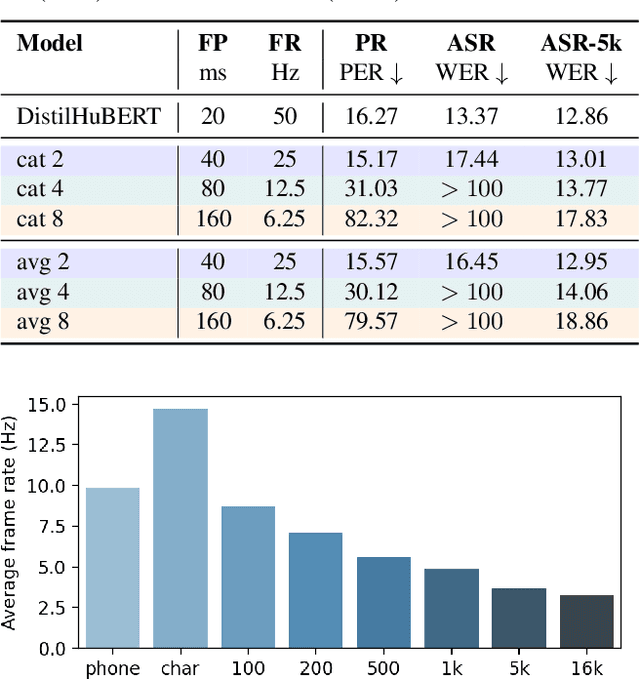
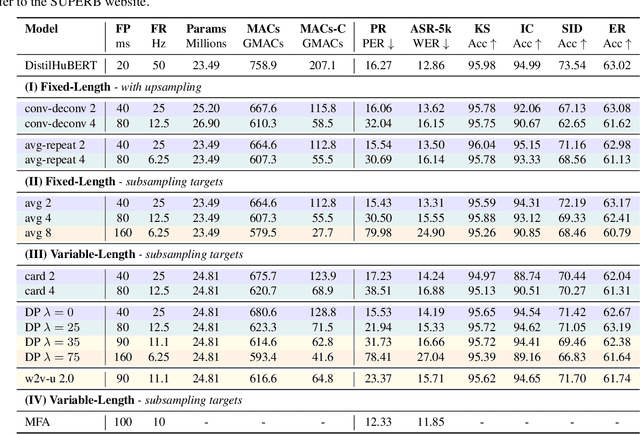
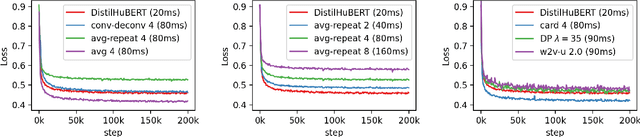
Abstract:Compressing self-supervised models has become increasingly necessary, as self-supervised models become larger. While previous approaches have primarily focused on compressing the model size, shortening sequences is also effective in reducing the computational cost. In this work, we study fixed-length and variable-length subsampling along the time axis in self-supervised learning. We explore how individual downstream tasks are sensitive to input frame rates. Subsampling while training self-supervised models not only improves the overall performance on downstream tasks under certain frame rates, but also brings significant speed-up in inference. Variable-length subsampling performs particularly well under low frame rates. In addition, if we have access to phonetic boundaries, we find no degradation in performance for an average frame rate as low as 10 Hz.
DUAL: Discrete Spoken Unit Adaptive Learning for Textless Spoken Question Answering
Mar 26, 2022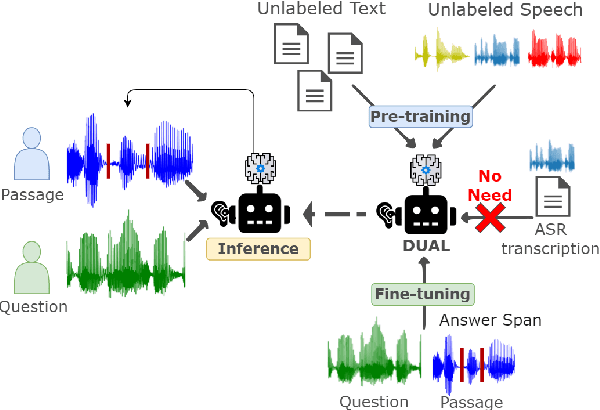
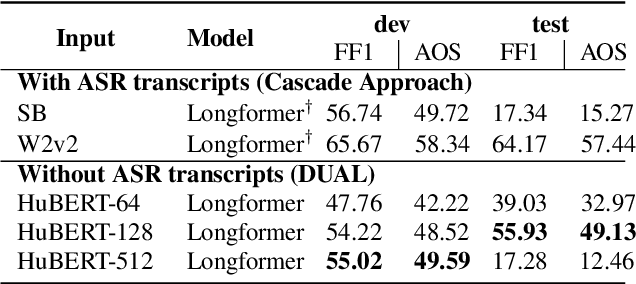
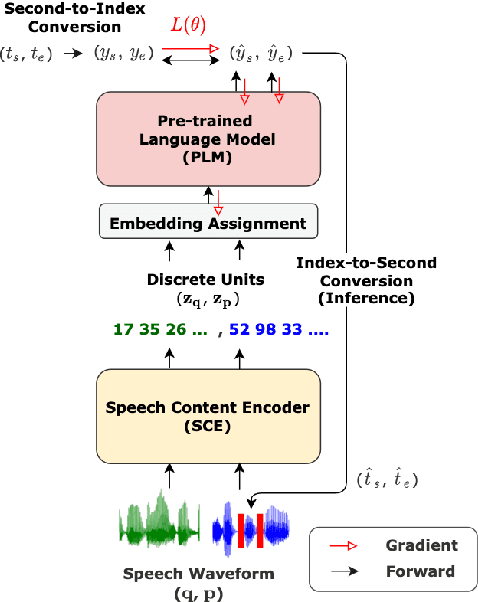
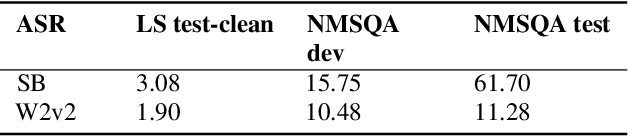
Abstract:Spoken Question Answering (SQA) is to find the answer from a spoken document given a question, which is crucial for personal assistants when replying to the queries from the users. Existing SQA methods all rely on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) transcripts. Not only does ASR need to be trained with massive annotated data that are time and cost-prohibitive to collect for low-resourced languages, but more importantly, very often the answers to the questions include name entities or out-of-vocabulary words that cannot be recognized correctly. Also, ASR aims to minimize recognition errors equally over all words, including many function words irrelevant to the SQA task. Therefore, SQA without ASR transcripts (textless) is always highly desired, although known to be very difficult. This work proposes Discrete Spoken Unit Adaptive Learning (DUAL), leveraging unlabeled data for pre-training and fine-tuned by the SQA downstream task. The time intervals of spoken answers can be directly predicted from spoken documents. We also release a new SQA benchmark corpus, NMSQA, for data with more realistic scenarios. We empirically showed that DUAL yields results comparable to those obtained by cascading ASR and text QA model and robust to real-world data. Our code and model will be open-sourced.
SUPERB-SG: Enhanced Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark for Semantic and Generative Capabilities
Mar 14, 2022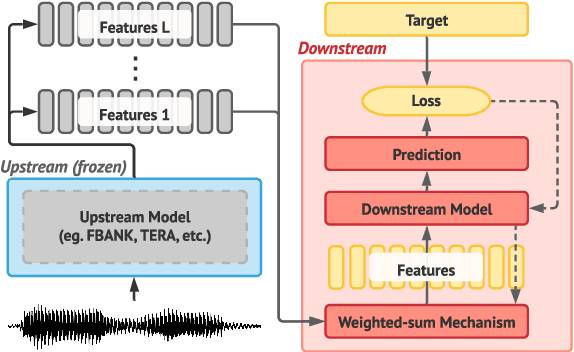
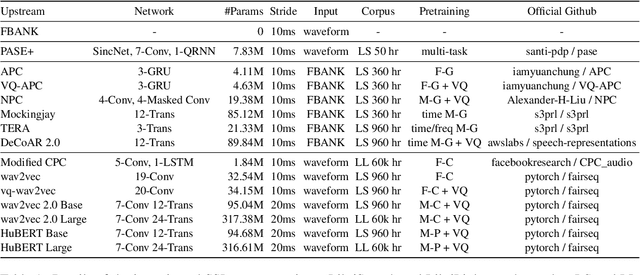
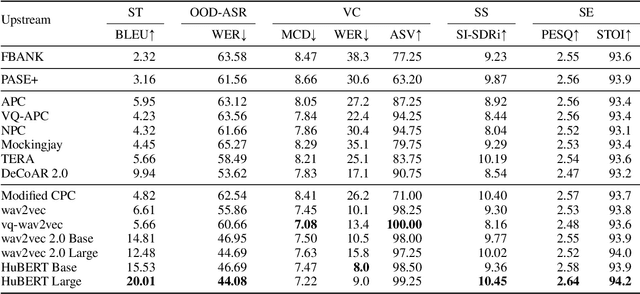
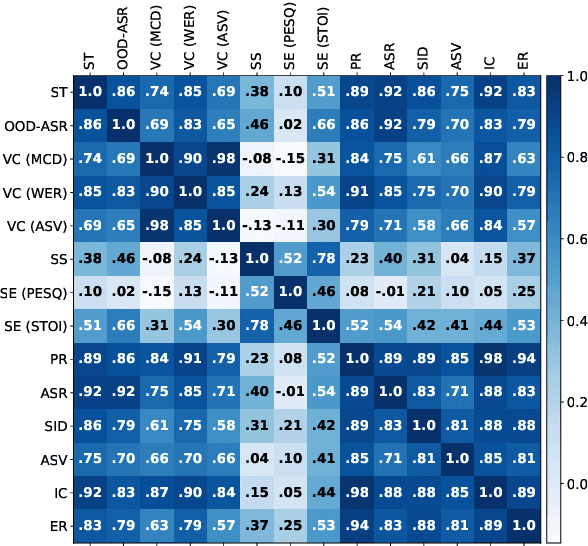
Abstract:Transfer learning has proven to be crucial in advancing the state of speech and natural language processing research in recent years. In speech, a model pre-trained by self-supervised learning transfers remarkably well on multiple tasks. However, the lack of a consistent evaluation methodology is limiting towards a holistic understanding of the efficacy of such models. SUPERB was a step towards introducing a common benchmark to evaluate pre-trained models across various speech tasks. In this paper, we introduce SUPERB-SG, a new benchmark focused on evaluating the semantic and generative capabilities of pre-trained models by increasing task diversity and difficulty over SUPERB. We use a lightweight methodology to test the robustness of representations learned by pre-trained models under shifts in data domain and quality across different types of tasks. It entails freezing pre-trained model parameters, only using simple task-specific trainable heads. The goal is to be inclusive of all researchers, and encourage efficient use of computational resources. We also show that the task diversity of SUPERB-SG coupled with limited task supervision is an effective recipe for evaluating the generalizability of model representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge