Howard E. Morgan
Registration-Guided Deep Learning Image Segmentation for Cone Beam CT-based Online Adaptive Radiotherapy
Aug 19, 2021



Abstract:Adaptive radiotherapy (ART), especially online ART, effectively accounts for positioning errors and anatomical changes. One key component of online ART is accurately and efficiently delineating organs at risk (OARs) and targets on online images, such as CBCT, to meet the online demands of plan evaluation and adaptation. Deep learning (DL)-based automatic segmentation has gained great success in segmenting planning CT, but its applications to CBCT yielded inferior results due to the low image quality and limited available contour labels for training. To overcome these obstacles to online CBCT segmentation, we propose a registration-guided DL (RgDL) segmentation framework that integrates image registration algorithms and DL segmentation models. The registration algorithm generates initial contours, which were used as guidance by DL model to obtain accurate final segmentations. We had two implementations the proposed framework--Rig-RgDL (Rig for rigid body) and Def-RgDL (Def for deformable)--with rigid body (RB) registration or deformable image registration (DIR) as the registration algorithm respectively and U-Net as DL model architecture. The two implementations of RgDL framework were trained and evaluated on seven OARs in an institutional clinical Head and Neck (HN) dataset. Compared to the baseline approaches using the registration or the DL alone, RgDL achieved more accurate segmentation, as measured by higher mean Dice similarity coefficients (DSC) and other distance-based metrics. Rig-RgDL achieved a DSC of 84.5% on seven OARs on average, higher than RB or DL alone by 4.5% and 4.7%. The DSC of Def-RgDL is 86.5%, higher than DIR or DL alone by 2.4% and 6.7%. The inference time took by the DL model to generate final segmentations of seven OARs is less than one second in RgDL. The resulting segmentation accuracy and efficiency show the promise of applying RgDL framework for online ART.
A Proof-of-Concept Study of Artificial Intelligence Assisted Contour Revision
Jul 28, 2021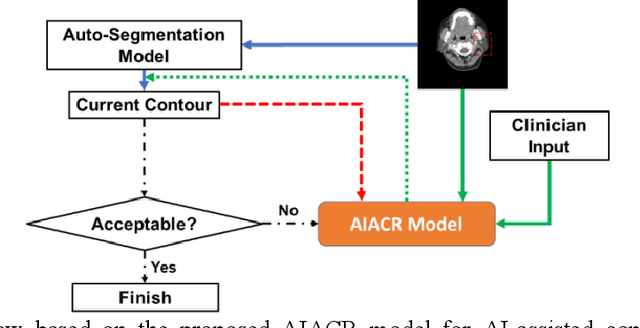

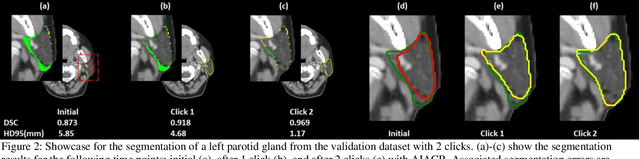
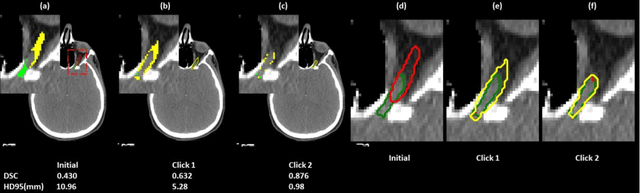
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of anatomical structures is critical for many medical applications. However, the results are not always clinically acceptable and require tedious manual revision. Here, we present a novel concept called artificial intelligence assisted contour revision (AIACR) and demonstrate its feasibility. The proposed clinical workflow of AIACR is as follows given an initial contour that requires a clinicians revision, the clinician indicates where a large revision is needed, and a trained deep learning (DL) model takes this input to update the contour. This process repeats until a clinically acceptable contour is achieved. The DL model is designed to minimize the clinicians input at each iteration and to minimize the number of iterations needed to reach acceptance. In this proof-of-concept study, we demonstrated the concept on 2D axial images of three head-and-neck cancer datasets, with the clinicians input at each iteration being one mouse click on the desired location of the contour segment. The performance of the model is quantified with Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and 95th percentile of Hausdorff Distance (HD95). The average DSC/HD95 (mm) of the auto-generated initial contours were 0.82/4.3, 0.73/5.6 and 0.67/11.4 for three datasets, which were improved to 0.91/2.1, 0.86/2.4 and 0.86/4.7 with three mouse clicks, respectively. Each DL-based contour update requires around 20 ms. We proposed a novel AIACR concept that uses DL models to assist clinicians in revising contours in an efficient and effective way, and we demonstrated its feasibility by using 2D axial CT images from three head-and-neck cancer datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge