Houda Bahig
Few-shot Adaptation of Medical Vision-Language Models
Sep 05, 2024Abstract:Integrating image and text data through multi-modal learning has emerged as a new approach in medical imaging research, following its successful deployment in computer vision. While considerable efforts have been dedicated to establishing medical foundation models and their zero-shot transfer to downstream tasks, the popular few-shot setting remains relatively unexplored. Following on from the currently strong emergence of this setting in computer vision, we introduce the first structured benchmark for adapting medical vision-language models (VLMs) in a strict few-shot regime and investigate various adaptation strategies commonly used in the context of natural images. Furthermore, we evaluate a simple generalization of the linear-probe adaptation baseline, which seeks an optimal blending of the visual prototypes and text embeddings via learnable class-wise multipliers. Surprisingly, such a text-informed linear probe yields competitive performances in comparison to convoluted prompt-learning and adapter-based strategies, while running considerably faster and accommodating the black-box setting. Our extensive experiments span three different medical modalities and specialized foundation models, nine downstream tasks, and several state-of-the-art few-shot adaptation methods. We made our benchmark and code publicly available to trigger further developments in this emergent subject: \url{https://github.com/FereshteShakeri/few-shot-MedVLMs}.
Boosting Vision-Language Models for Histopathology Classification: Predict all at once
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:The development of vision-language models (VLMs) for histo-pathology has shown promising new usages and zero-shot performances. However, current approaches, which decompose large slides into smaller patches, focus solely on inductive classification, i.e., prediction for each patch is made independently of the other patches in the target test data. We extend the capability of these large models by introducing a transductive approach. By using text-based predictions and affinity relationships among patches, our approach leverages the strong zero-shot capabilities of these new VLMs without any additional labels. Our experiments cover four histopathology datasets and five different VLMs. Operating solely in the embedding space (i.e., in a black-box setting), our approach is highly efficient, processing $10^5$ patches in just a few seconds, and shows significant accuracy improvements over inductive zero-shot classification. Code available at https://github.com/FereshteShakeri/Histo-TransCLIP.
LP++: A Surprisingly Strong Linear Probe for Few-Shot CLIP
Apr 02, 2024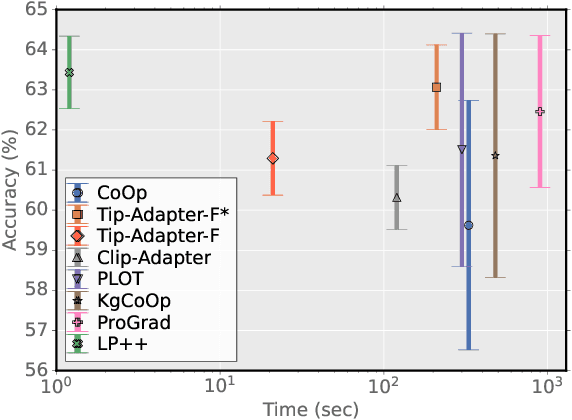
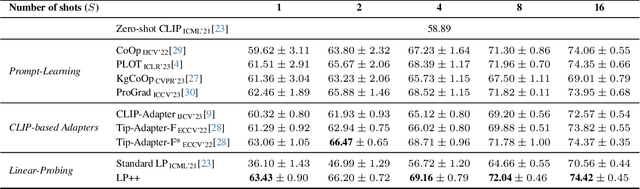
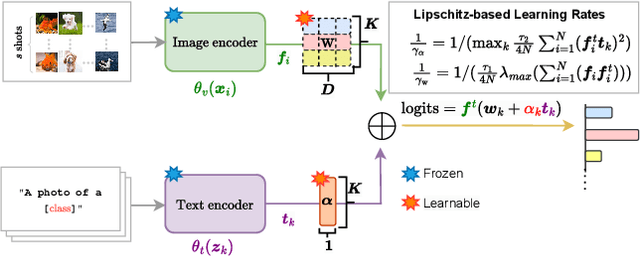
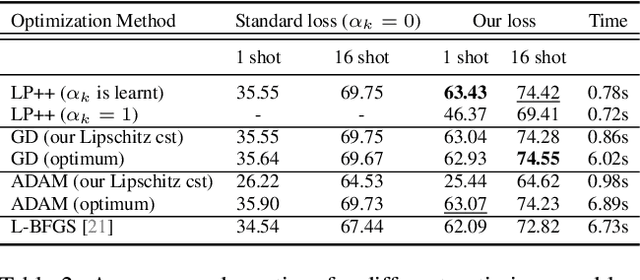
Abstract:In a recent, strongly emergent literature on few-shot CLIP adaptation, Linear Probe (LP) has been often reported as a weak baseline. This has motivated intensive research building convoluted prompt learning or feature adaptation strategies. In this work, we propose and examine from convex-optimization perspectives a generalization of the standard LP baseline, in which the linear classifier weights are learnable functions of the text embedding, with class-wise multipliers blending image and text knowledge. As our objective function depends on two types of variables, i.e., the class visual prototypes and the learnable blending parameters, we propose a computationally efficient block coordinate Majorize-Minimize (MM) descent algorithm. In our full-batch MM optimizer, which we coin LP++, step sizes are implicit, unlike standard gradient descent practices where learning rates are intensively searched over validation sets. By examining the mathematical properties of our loss (e.g., Lipschitz gradient continuity), we build majorizing functions yielding data-driven learning rates and derive approximations of the loss's minima, which provide data-informed initialization of the variables. Our image-language objective function, along with these non-trivial optimization insights and ingredients, yields, surprisingly, highly competitive few-shot CLIP performances. Furthermore, LP++ operates in black-box, relaxes intensive validation searches for the optimization hyper-parameters, and runs orders-of-magnitudes faster than state-of-the-art few-shot CLIP adaptation methods. Our code is available at: \url{https://github.com/FereshteShakeri/FewShot-CLIP-Strong-Baseline.git}.
Comparing 3D deformations between longitudinal daily CBCT acquisitions using CNN for head and neck radiotherapy toxicity prediction
Mar 07, 2023Abstract:Adaptive radiotherapy is a growing field of study in cancer treatment due to it's objective in sparing healthy tissue. The standard of care in several institutions includes longitudinal cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) acquisitions to monitor changes, but have yet to be used to improve tumor control while managing side-effects. The aim of this study is to demonstrate the clinical value of pre-treatment CBCT acquired daily during radiation therapy treatment for head and neck cancers for the downstream task of predicting severe toxicity occurrence: reactive feeding tube (NG), hospitalization and radionecrosis. For this, we propose a deformable 3D classification pipeline that includes a component analyzing the Jacobian matrix of the deformation between planning CT and longitudinal CBCT, as well as clinical data. The model is based on a multi-branch 3D residual convolutional neural network, while the CT to CBCT registration is based on a pair of VoxelMorph architectures. Accuracies of 85.8% and 75.3% was found for radionecrosis and hospitalization, respectively, with similar performance as early as after the first week of treatment. For NG tube risk, performance improves with increasing the timing of the CBCT fraction, reaching 83.1% after the $5_{th}$ week of treatment.
Beyond pixel-wise supervision for segmentation: A few global shape descriptors might be surprisingly good!
May 03, 2021
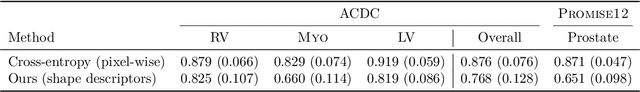
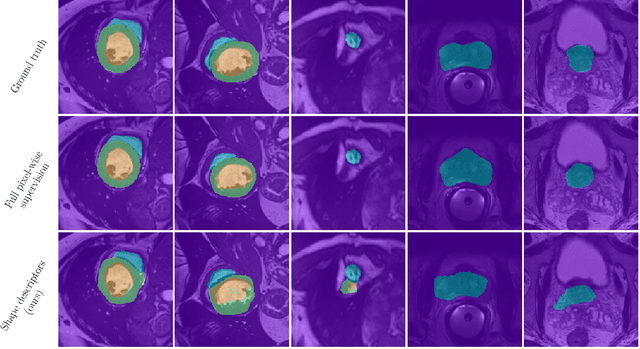

Abstract:Standard losses for training deep segmentation networks could be seen as individual classifications of pixels, instead of supervising the global shape of the predicted segmentations. While effective, they require exact knowledge of the label of each pixel in an image. This study investigates how effective global geometric shape descriptors could be, when used on their own as segmentation losses for training deep networks. Not only interesting theoretically, there exist deeper motivations to posing segmentation problems as a reconstruction of shape descriptors: Annotations to obtain approximations of low-order shape moments could be much less cumbersome than their full-mask counterparts, and anatomical priors could be readily encoded into invariant shape descriptions, which might alleviate the annotation burden. Also, and most importantly, we hypothesize that, given a task, certain shape descriptions might be invariant across image acquisition protocols/modalities and subject populations, which might open interesting research avenues for generalization in medical image segmentation. We introduce and formulate a few shape descriptors in the context of deep segmentation, and evaluate their potential as standalone losses on two different challenging tasks. Inspired by recent works in constrained optimization for deep networks, we propose a way to use those descriptors to supervise segmentation, without any pixel-level label. Very surprisingly, as little as 4 descriptors values per class can approach the performance of a segmentation mask with 65k individual discrete labels. We also found that shape descriptors can be a valid way to encode anatomical priors about the task, enabling to leverage expert knowledge without additional annotations. Our implementation is publicly available and can be easily extended to other tasks and descriptors: https://github.com/hkervadec/shape_descriptors
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge