Homa Esfahanizadeh
Shitz
MultiTok: Variable-Length Tokenization for Efficient LLMs Adapted from LZW Compression
Oct 28, 2024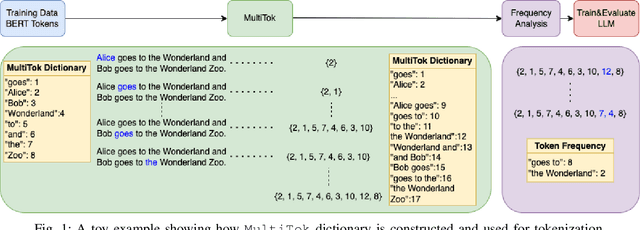
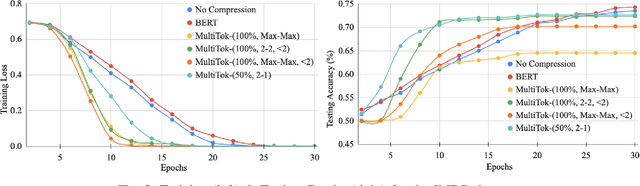
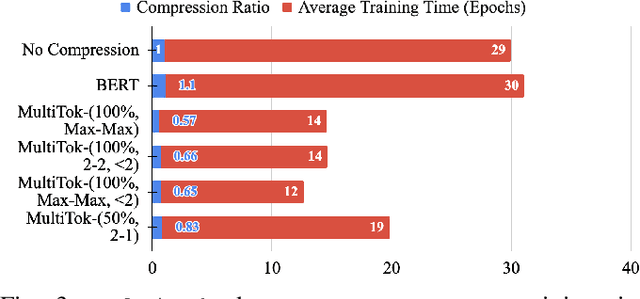

Abstract:Large language models have drastically changed the prospects of AI by introducing technologies for more complex natural language processing. However, current methodologies to train such LLMs require extensive resources including but not limited to large amounts of data, expensive machinery, and lengthy training. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a new tokenization method inspired by universal Lempel-Ziv-Welch data compression that compresses repetitive phrases into multi-word tokens. With MultiTok as a new tokenizing tool, we show that language models are able to be trained notably more efficiently while offering a similar accuracy on more succinct and compressed training data. In fact, our results demonstrate that MultiTok achieves a comparable performance to the BERT standard as a tokenizer while also providing close to 2.5x faster training with more than 30% less training data.
Multi-level Reliability Interface for Semantic Communications over Wireless Networks
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:Semantic communication, when examined through the lens of joint source-channel coding (JSCC), maps source messages directly into channel input symbols, where the measure of success is defined by end-to-end distortion rather than traditional metrics such as block error rate. Previous studies have shown significant improvements achieved through deep learning (DL)-driven JSCC compared to traditional separate source and channel coding. However, JSCC is impractical in existing communication networks, where application and network providers are typically different entities connected over general-purpose TCP/IP links. In this paper, we propose designing the source and channel mappings separately and sequentially via a novel multi-level reliability interface. This conceptual interface enables semi-JSCC at both the learned source and channel mappers and achieves many of the gains observed in existing DL-based JSCC work (which would require a fully joint design between the application and the network), such as lower end-to-end distortion and graceful degradation of distortion with channel quality. We believe this work represents an important step towards realizing semantic communications in wireless networks.
Successive Refinement in Large-Scale Computation: Advancing Model Inference Applications
Feb 11, 2024Abstract:Modern computationally-intensive applications often operate under time constraints, necessitating acceleration methods and distribution of computational workloads across multiple entities. However, the outcome is either achieved within the desired timeline or not, and in the latter case, valuable resources are wasted. In this paper, we introduce solutions for layered-resolution computation. These solutions allow lower-resolution results to be obtained at an earlier stage than the final result. This innovation notably enhances the deadline-based systems, as if a computational job is terminated due to time constraints, an approximate version of the final result can still be generated. Moreover, in certain operational regimes, a high-resolution result might be unnecessary, because the low-resolution result may already deviate significantly from the decision threshold, for example in AI-based decision-making systems. Therefore, operators can decide whether higher resolution is needed or not based on intermediate results, enabling computations with adaptive resolution. We present our framework for two critical and computationally demanding jobs: distributed matrix multiplication (linear) and model inference in machine learning (nonlinear). Our theoretical and empirical results demonstrate that the execution delay for the first resolution is significantly shorter than that for the final resolution, while maintaining overall complexity comparable to the conventional one-shot approach. Our experiments further illustrate how the layering feature increases the likelihood of meeting deadlines and enables adaptability and transparency in massive, large-scale computations.
TexShape: Information Theoretic Sentence Embedding for Language Models
Feb 05, 2024



Abstract:With the exponential growth in data volume and the emergence of data-intensive applications, particularly in the field of machine learning, concerns related to resource utilization, privacy, and fairness have become paramount. This paper focuses on the textual domain of data and addresses challenges regarding encoding sentences to their optimized representations through the lens of information-theory. In particular, we use empirical estimates of mutual information, using the Donsker-Varadhan definition of Kullback-Leibler divergence. Our approach leverages this estimation to train an information-theoretic sentence embedding, called TexShape, for (task-based) data compression or for filtering out sensitive information, enhancing privacy and fairness. In this study, we employ a benchmark language model for initial text representation, complemented by neural networks for information-theoretic compression and mutual information estimations. Our experiments demonstrate significant advancements in preserving maximal targeted information and minimal sensitive information over adverse compression ratios, in terms of predictive accuracy of downstream models that are trained using the compressed data.
PEOPL: Characterizing Privately Encoded Open Datasets with Public Labels
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Allowing organizations to share their data for training of machine learning (ML) models without unintended information leakage is an open problem in practice. A promising technique for this still-open problem is to train models on the encoded data. Our approach, called Privately Encoded Open Datasets with Public Labels (PEOPL), uses a certain class of randomly constructed transforms to encode sensitive data. Organizations publish their randomly encoded data and associated raw labels for ML training, where training is done without knowledge of the encoding realization. We investigate several important aspects of this problem: We introduce information-theoretic scores for privacy and utility, which quantify the average performance of an unfaithful user (e.g., adversary) and a faithful user (e.g., model developer) that have access to the published encoded data. We then theoretically characterize primitives in building families of encoding schemes that motivate the use of random deep neural networks. Empirically, we compare the performance of our randomized encoding scheme and a linear scheme to a suite of computational attacks, and we also show that our scheme achieves competitive prediction accuracy to raw-sample baselines. Moreover, we demonstrate that multiple institutions, using independent random encoders, can collaborate to train improved ML models.
Syfer: Neural Obfuscation for Private Data Release
Jan 28, 2022Abstract:Balancing privacy and predictive utility remains a central challenge for machine learning in healthcare. In this paper, we develop Syfer, a neural obfuscation method to protect against re-identification attacks. Syfer composes trained layers with random neural networks to encode the original data (e.g. X-rays) while maintaining the ability to predict diagnoses from the encoded data. The randomness in the encoder acts as the private key for the data owner. We quantify privacy as the number of attacker guesses required to re-identify a single image (guesswork). We propose a contrastive learning algorithm to estimate guesswork. We show empirically that differentially private methods, such as DP-Image, obtain privacy at a significant loss of utility. In contrast, Syfer achieves strong privacy while preserving utility. For example, X-ray classifiers built with DP-image, Syfer, and original data achieve average AUCs of 0.53, 0.78, and 0.86, respectively.
NeuraCrypt: Hiding Private Health Data via Random Neural Networks for Public Training
Jun 04, 2021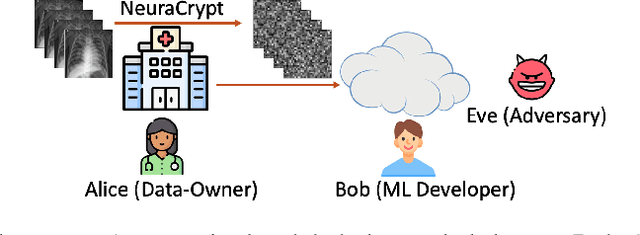
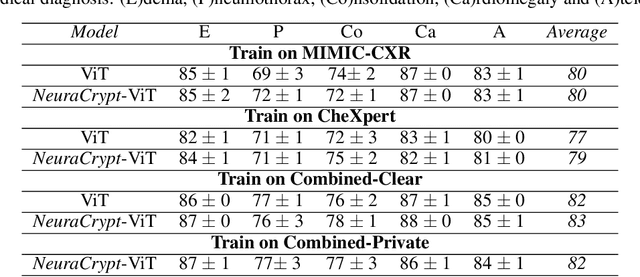
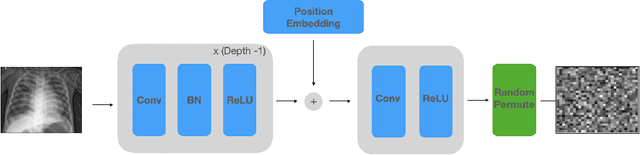
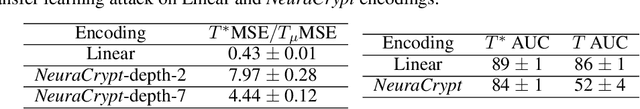
Abstract:Balancing the needs of data privacy and predictive utility is a central challenge for machine learning in healthcare. In particular, privacy concerns have led to a dearth of public datasets, complicated the construction of multi-hospital cohorts and limited the utilization of external machine learning resources. To remedy this, new methods are required to enable data owners, such as hospitals, to share their datasets publicly, while preserving both patient privacy and modeling utility. We propose NeuraCrypt, a private encoding scheme based on random deep neural networks. NeuraCrypt encodes raw patient data using a randomly constructed neural network known only to the data-owner, and publishes both the encoded data and associated labels publicly. From a theoretical perspective, we demonstrate that sampling from a sufficiently rich family of encoding functions offers a well-defined and meaningful notion of privacy against a computationally unbounded adversary with full knowledge of the underlying data-distribution. We propose to approximate this family of encoding functions through random deep neural networks. Empirically, we demonstrate the robustness of our encoding to a suite of adversarial attacks and show that NeuraCrypt achieves competitive accuracy to non-private baselines on a variety of x-ray tasks. Moreover, we demonstrate that multiple hospitals, using independent private encoders, can collaborate to train improved x-ray models. Finally, we release a challenge dataset to encourage the development of new attacks on NeuraCrypt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge