Hiroshi Kanayama
Bias Analysis and Mitigation through Protected Attribute Detection and Regard Classification
Apr 19, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) acquire general linguistic knowledge from massive-scale pretraining. However, pretraining data mainly comprised of web-crawled texts contain undesirable social biases which can be perpetuated or even amplified by LLMs. In this study, we propose an efficient yet effective annotation pipeline to investigate social biases in the pretraining corpora. Our pipeline consists of protected attribute detection to identify diverse demographics, followed by regard classification to analyze the language polarity towards each attribute. Through our experiments, we demonstrate the effect of our bias analysis and mitigation measures, focusing on Common Crawl as the most representative pretraining corpus.
Sentence Identification with BOS and EOS Label Combinations
Jan 31, 2023Abstract:The sentence is a fundamental unit in many NLP applications. Sentence segmentation is widely used as the first preprocessing task, where an input text is split into consecutive sentences considering the end of the sentence (EOS) as their boundaries. This task formulation relies on a strong assumption that the input text consists only of sentences, or what we call the sentential units (SUs). However, real-world texts often contain non-sentential units (NSUs) such as metadata, sentence fragments, nonlinguistic markers, etc. which are unreasonable or undesirable to be treated as a part of an SU. To tackle this issue, we formulate a novel task of sentence identification, where the goal is to identify SUs while excluding NSUs in a given text. To conduct sentence identification, we propose a simple yet effective method which combines the beginning of the sentence (BOS) and EOS labels to determine the most probable SUs and NSUs based on dynamic programming. To evaluate this task, we design an automatic, language-independent procedure to convert the Universal Dependencies corpora into sentence identification benchmarks. Finally, our experiments on the sentence identification task demonstrate that our proposed method generally outperforms sentence segmentation baselines which only utilize EOS labels.
PriMeSRL-Eval: A Practical Quality Metric for Semantic Role Labeling Systems Evaluation
Oct 12, 2022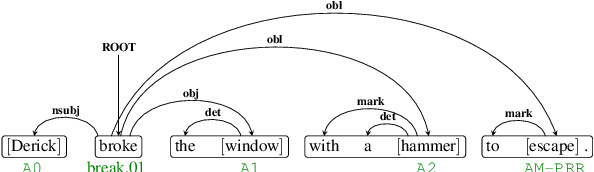

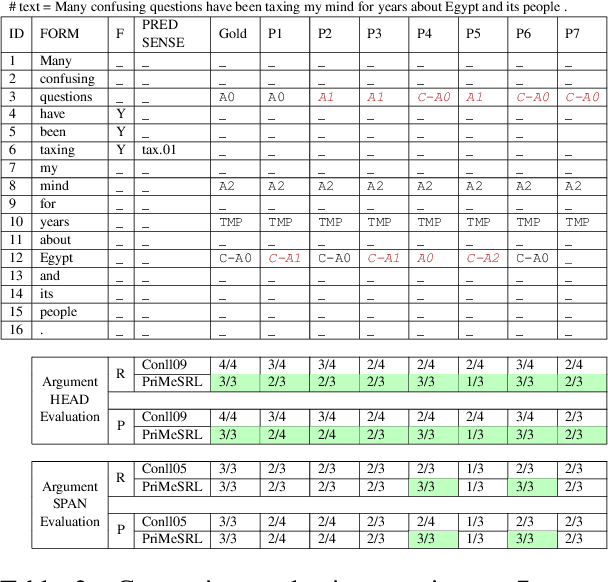
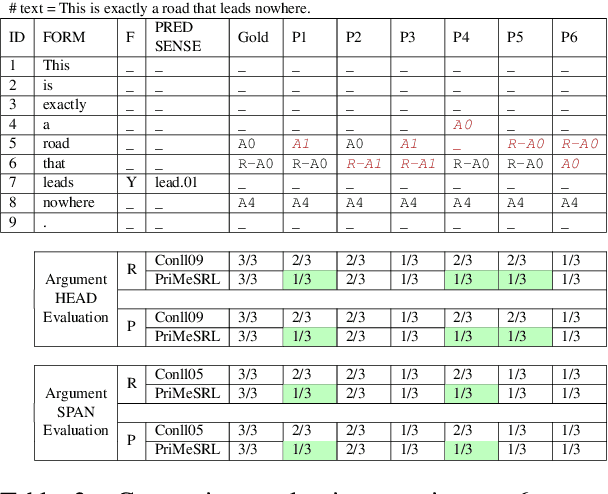
Abstract:Semantic role labeling (SRL) identifies the predicate-argument structure in a sentence. This task is usually accomplished in four steps: predicate identification, predicate sense disambiguation, argument identification, and argument classification. Errors introduced at one step propagate to later steps. Unfortunately, the existing SRL evaluation scripts do not consider the full effect of this error propagation aspect. They either evaluate arguments independent of predicate sense (CoNLL09) or do not evaluate predicate sense at all (CoNLL05), yielding an inaccurate SRL model performance on the argument classification task. In this paper, we address key practical issues with existing evaluation scripts and propose a more strict SRL evaluation metric PriMeSRL. We observe that by employing PriMeSRL, the quality evaluation of all SoTA SRL models drops significantly, and their relative rankings also change. We also show that PriMeSRLsuccessfully penalizes actual failures in SoTA SRL models.
Learning Crosslingual Word Embeddings without Bilingual Corpora
Jun 30, 2016



Abstract:Crosslingual word embeddings represent lexical items from different languages in the same vector space, enabling transfer of NLP tools. However, previous attempts had expensive resource requirements, difficulty incorporating monolingual data or were unable to handle polysemy. We address these drawbacks in our method which takes advantage of a high coverage dictionary in an EM style training algorithm over monolingual corpora in two languages. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on bilingual lexicon induction task exceeding models using large bilingual corpora, and competitive results on the monolingual word similarity and cross-lingual document classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge