Haowen Zhong
PromptV: Leveraging LLM-powered Multi-Agent Prompting for High-quality Verilog Generation
Dec 15, 2024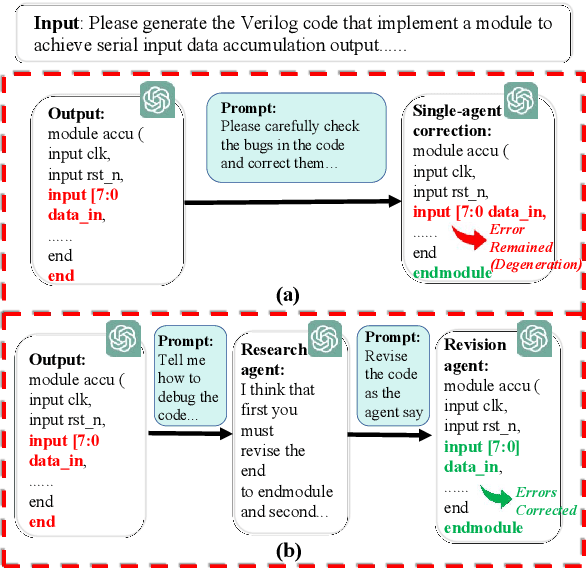
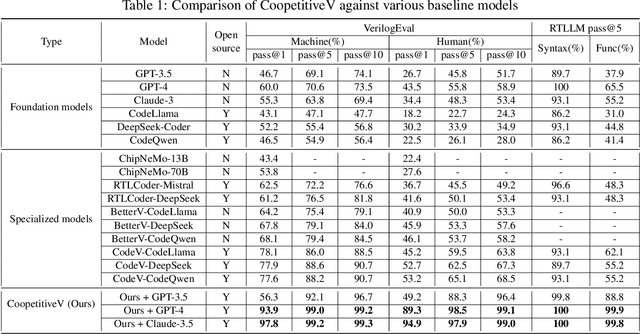
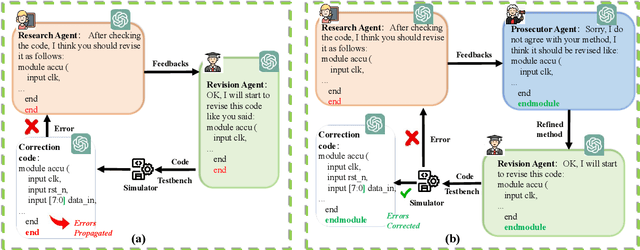
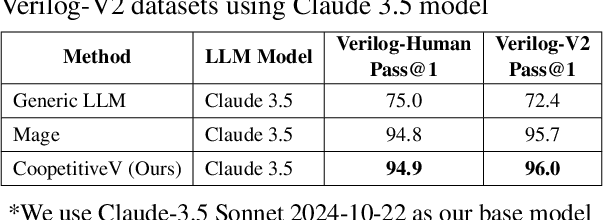
Abstract:Recent advances in agentic LLMs have demonstrated remarkable automated Verilog code generation capabilities. However, existing approaches either demand substantial computational resources or rely on LLM-assisted single-agent prompt learning techniques, which we observe for the first time has a degeneration issue - characterized by deteriorating generative performance and diminished error detection and correction capabilities. This paper proposes a novel multi-agent prompt learning framework to address these limitations and enhance code generation quality. We show for the first time that multi-agent architectures can effectively mitigate the degeneration risk while improving code error correction capabilities, resulting in higher-quality Verilog code generation. Experimental results show that the proposed method could achieve 96.4% and 96.5% pass@10 scores on VerilogEval Machine and Human benchmarks, respectively while attaining 100% Syntax and 99.9% Functionality pass@5 metrics on the RTLLM benchmark.
Learning Unbiased Transferability for Domain Adaptation by Uncertainty Modeling
Jun 02, 2022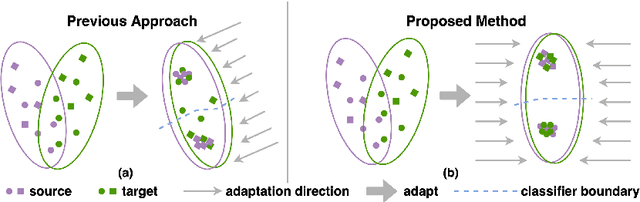
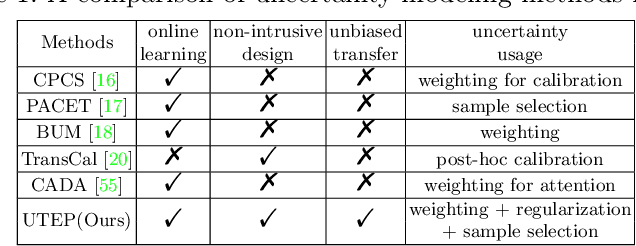
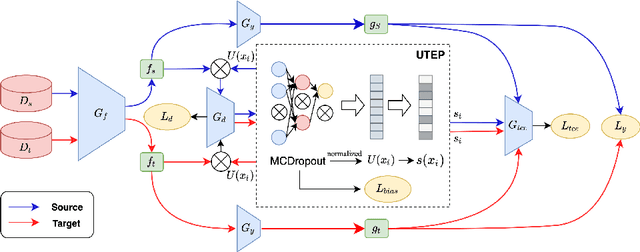
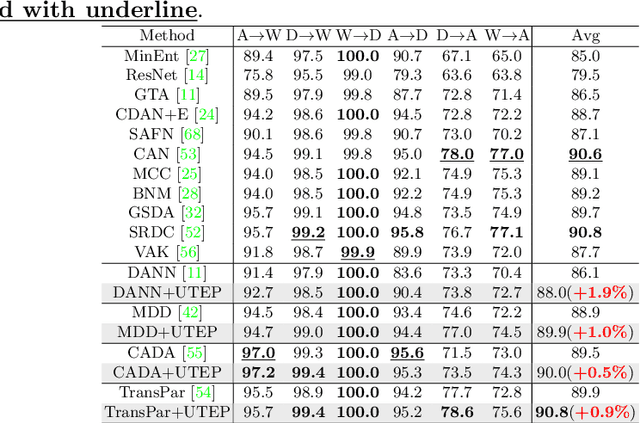
Abstract:Domain adaptation (DA) aims to transfer knowledge learned from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled or a less labeled but related target domain. Ideally, the source and target distributions should be aligned to each other equally to achieve unbiased knowledge transfer. However, due to the significant imbalance between the amount of annotated data in the source and target domains, usually only the target distribution is aligned to the source domain, leading to adapting unnecessary source specific knowledge to the target domain, i.e., biased domain adaptation. To resolve this problem, in this work, we delve into the transferability estimation problem in domain adaptation and propose a non-intrusive Unbiased Transferability Estimation Plug-in (UTEP) by modeling the uncertainty of a discriminator in adversarial-based DA methods to optimize unbiased transfer. We theoretically analyze the effectiveness of the proposed approach to unbiased transferability learning in DA. Furthermore, to alleviate the impact of imbalanced annotated data, we utilize the estimated uncertainty for pseudo label selection of unlabeled samples in the target domain, which helps achieve better marginal and conditional distribution alignments between domains. Extensive experimental results on a high variety of DA benchmark datasets show that the proposed approach can be readily incorporated into various adversarial-based DA methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Self-Adaptive Partial Domain Adaptation
Sep 18, 2021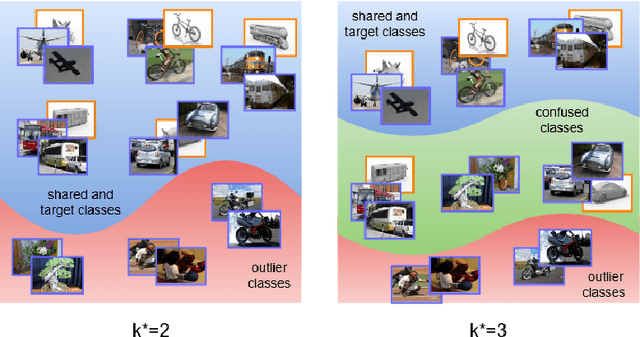
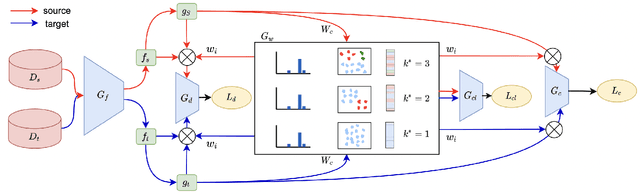
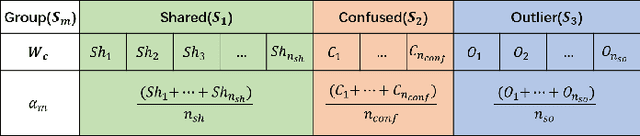
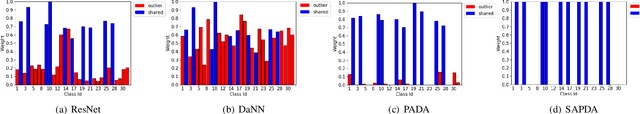
Abstract:Partial Domain adaptation (PDA) aims to solve a more practical cross-domain learning problem that assumes target label space is a subset of source label space. However, the mismatched label space causes significant negative transfer. A traditional solution is using soft weights to increase weights of source shared domain and reduce those of source outlier domain. But it still learns features of outliers and leads to negative immigration. The other mainstream idea is to distinguish source domain into shared and outlier parts by hard binary weights, while it is unavailable to correct the tangled shared and outlier classes. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end Self-Adaptive Partial Domain Adaptation(SAPDA) Network. Class weights evaluation mechanism is introduced to dynamically self-rectify the weights of shared, outlier and confused classes, thus the higher confidence samples have the more sufficient weights. Meanwhile it can eliminate the negative transfer caused by the mismatching of label space greatly. Moreover, our strategy can efficiently measure the transferability of samples in a broader sense, so that our method can achieve competitive results on unsupervised DA task likewise. A large number of experiments on multiple benchmarks have demonstrated the effectiveness of our SAPDA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge