Hongya Tuo
Self-Adaptive Partial Domain Adaptation
Sep 18, 2021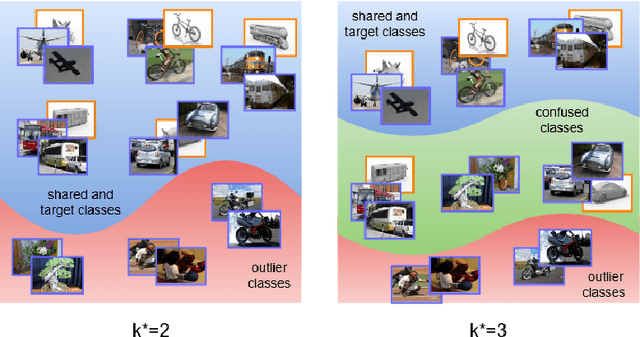
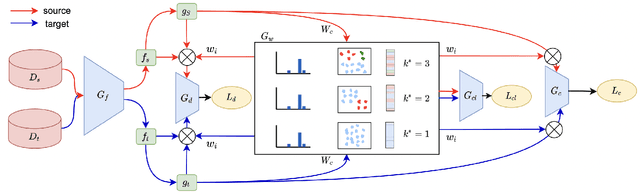
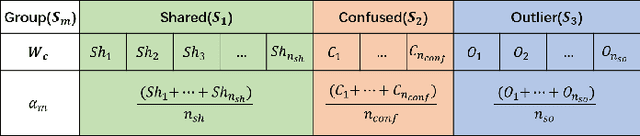
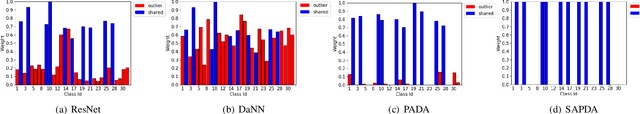
Abstract:Partial Domain adaptation (PDA) aims to solve a more practical cross-domain learning problem that assumes target label space is a subset of source label space. However, the mismatched label space causes significant negative transfer. A traditional solution is using soft weights to increase weights of source shared domain and reduce those of source outlier domain. But it still learns features of outliers and leads to negative immigration. The other mainstream idea is to distinguish source domain into shared and outlier parts by hard binary weights, while it is unavailable to correct the tangled shared and outlier classes. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end Self-Adaptive Partial Domain Adaptation(SAPDA) Network. Class weights evaluation mechanism is introduced to dynamically self-rectify the weights of shared, outlier and confused classes, thus the higher confidence samples have the more sufficient weights. Meanwhile it can eliminate the negative transfer caused by the mismatching of label space greatly. Moreover, our strategy can efficiently measure the transferability of samples in a broader sense, so that our method can achieve competitive results on unsupervised DA task likewise. A large number of experiments on multiple benchmarks have demonstrated the effectiveness of our SAPDA.
Domain Adaptive YOLO for One-Stage Cross-Domain Detection
Jul 04, 2021



Abstract:Domain shift is a major challenge for object detectors to generalize well to real world applications. Emerging techniques of domain adaptation for two-stage detectors help to tackle this problem. However, two-stage detectors are not the first choice for industrial applications due to its long time consumption. In this paper, a novel Domain Adaptive YOLO (DA-YOLO) is proposed to improve cross-domain performance for one-stage detectors. Image level features alignment is used to strictly match for local features like texture, and loosely match for global features like illumination. Multi-scale instance level features alignment is presented to reduce instance domain shift effectively , such as variations in object appearance and viewpoint. A consensus regularization to these domain classifiers is employed to help the network generate domain-invariant detections. We evaluate our proposed method on popular datasets like Cityscapes, KITTI, SIM10K and etc.. The results demonstrate significant improvement when tested under different cross-domain scenarios.
Efficient Image Categorization with Sparse Fisher Vector
Oct 15, 2014



Abstract:In object recognition, Fisher vector (FV) representation is one of the state-of-art image representations ways at the expense of dense, high dimensional features and increased computation time. A simplification of FV is attractive, so we propose Sparse Fisher vector (SFV). By incorporating locality strategy, we can accelerate the Fisher coding step in image categorization which is implemented from a collective of local descriptors. Combining with pooling step, we explore the relationship between coding step and pooling step to give a theoretical explanation about SFV. Experiments on benchmark datasets have shown that SFV leads to a speedup of several-fold of magnitude compares with FV, while maintaining the categorization performance. In addition, we demonstrate how SFV preserves the consistence in representation of similar local features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge