Guodun Li
Exploring Global Diversity and Local Context for Video Summarization
Jan 27, 2022



Abstract:Video summarization aims to automatically generate a diverse and concise summary which is useful in large-scale video processing. Most of methods tend to adopt self attention mechanism across video frames, which fails to model the diversity of video frames. To alleviate this problem, we revisit the pairwise similarity measurement in self attention mechanism and find that the existing inner-product affinity leads to discriminative features rather than diversified features. In light of this phenomenon, we propose global diverse attention by using the squared Euclidean distance instead to compute the affinities. Moreover, we model the local contextual information by proposing local contextual attention to remove the redundancy in the video. By combining these two attention mechanism, a video \textbf{SUM}marization model with Diversified Contextual Attention scheme is developed and named as SUM-DCA. Extensive experiments are conducted on benchmark data sets to verify the effectiveness and the superiority of SUM-DCA in terms of F-score and rank-based evaluation without any bells and whistles.
Similar Scenes arouse Similar Emotions: Parallel Data Augmentation for Stylized Image Captioning
Aug 26, 2021



Abstract:Stylized image captioning systems aim to generate a caption not only semantically related to a given image but also consistent with a given style description. One of the biggest challenges with this task is the lack of sufficient paired stylized data. Many studies focus on unsupervised approaches, without considering from the perspective of data augmentation. We begin with the observation that people may recall similar emotions when they are in similar scenes, and often express similar emotions with similar style phrases, which underpins our data augmentation idea. In this paper, we propose a novel Extract-Retrieve-Generate data augmentation framework to extract style phrases from small-scale stylized sentences and graft them to large-scale factual captions. First, we design the emotional signal extractor to extract style phrases from small-scale stylized sentences. Second, we construct the plugable multi-modal scene retriever to retrieve scenes represented with pairs of an image and its stylized caption, which are similar to the query image or caption in the large-scale factual data. In the end, based on the style phrases of similar scenes and the factual description of the current scene, we build the emotion-aware caption generator to generate fluent and diversified stylized captions for the current scene. Extensive experimental results show that our framework can alleviate the data scarcity problem effectively. It also significantly boosts the performance of several existing image captioning models in both supervised and unsupervised settings, which outperforms the state-of-the-art stylized image captioning methods in terms of both sentence relevance and stylishness by a substantial margin.
Dialogue State Tracking with Multi-Level Fusion of Predicted Dialogue States and Conversations
Jul 12, 2021
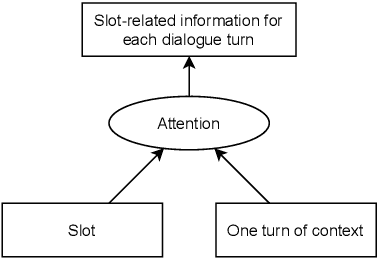
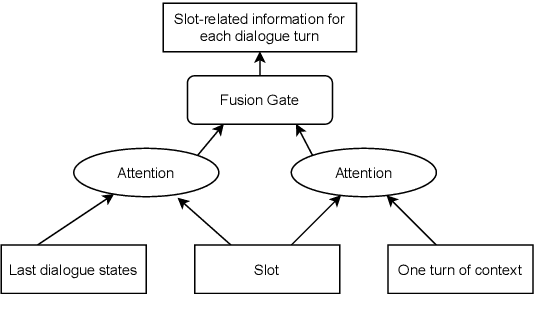
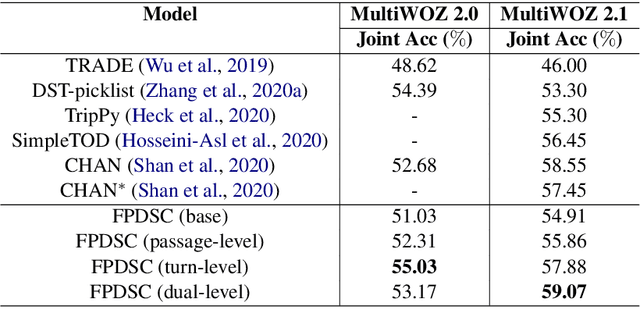
Abstract:Most recently proposed approaches in dialogue state tracking (DST) leverage the context and the last dialogue states to track current dialogue states, which are often slot-value pairs. Although the context contains the complete dialogue information, the information is usually indirect and even requires reasoning to obtain. The information in the lastly predicted dialogue states is direct, but when there is a prediction error, the dialogue information from this source will be incomplete or erroneous. In this paper, we propose the Dialogue State Tracking with Multi-Level Fusion of Predicted Dialogue States and Conversations network (FPDSC). This model extracts information of each dialogue turn by modeling interactions among each turn utterance, the corresponding last dialogue states, and dialogue slots. Then the representation of each dialogue turn is aggregated by a hierarchical structure to form the passage information, which is utilized in the current turn of DST. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the fusion network with 55.03% and 59.07% joint accuracy on MultiWOZ 2.0 and MultiWOZ 2.1 datasets, which reaches the state-of-the-art performance. Furthermore, we conduct the deleted-value and related-slot experiments on MultiWOZ 2.1 to evaluate our model.
Should Answer Immediately or Wait for Further Information? A Novel Wait-or-Answer Task and Its Predictive Approach
May 27, 2020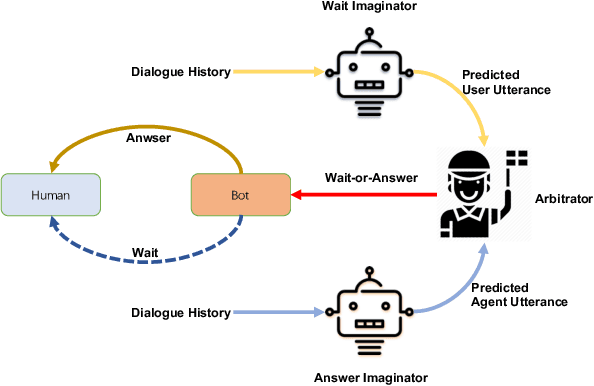
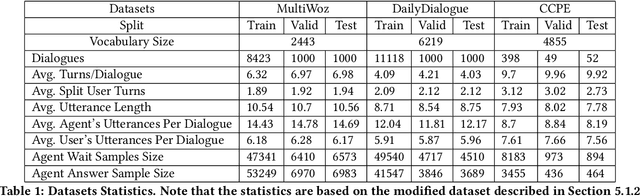
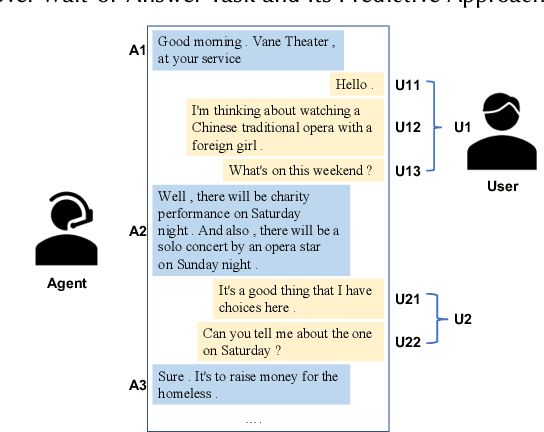
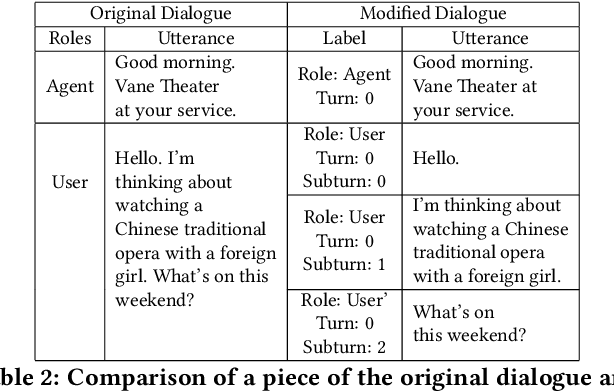
Abstract:Different people have different habits of describing their intents in conversations. Some people may tend to deliberate their full intents in several successive utterances, i.e., they use several consistent messages for readability instead of a long sentence to express their question. This creates a predicament faced by dialogue systems' application, especially in real-world industrial scenarios, in which the dialogue system is unsure that whether it should answer the user's query immediately or wait for users' further supplementary input. Motivated by such interesting quandary, we define a novel task: Wait-or-Answer to better tackle this dilemma faced by dialogue systems. We shed light on a new research topic about how the dialogue system can be more competent to behave in this Wait-or-Answer quandary. Further, we propose a predictive approach dubbed Imagine-then-Arbitrate (ITA) to resolve this Wait-or-Answer task. More specifically, we take advantage of an arbitrator model to help the dialogue system decide to wait or answer. The arbitrator's decision is made with the assistance of two ancillary imaginator models: a wait imaginator and an answer imaginator. The wait imaginator tries to predict what the user would supplement and use its prediction to persuade the arbitrator that the user has some information to add, so the dialogue system should wait. The answer imaginator, nevertheless, struggles to predict the answer of the dialogue system and convince the arbitrator that it's a superior choice to answer the users' query immediately. To our best knowledge, our paper is the first work to explicitly define the Wait-or-Answer task in the dialogue system. Additionally, our proposed ITA approach significantly outperforms the existing models in solving this Wait-or-Answer problem.
"Wait, I'm Still Talking!" Predicting the Dialogue Interaction Behavior Using Imagine-Then-Arbitrate Model
Feb 22, 2020



Abstract:Producing natural and accurate responses like human beings is the ultimate goal of intelligent dialogue agents. So far, most of the past works concentrate on selecting or generating one pertinent and fluent response according to current query and its context. These models work on a one-to-one environment, making one response to one utterance each round. However, in real human-human conversations, human often sequentially sends several short messages for readability instead of a long message in one turn. Thus messages will not end with an explicit ending signal, which is crucial for agents to decide when to reply. So the first step for an intelligent dialogue agent is not replying but deciding if it should reply at the moment. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose a novel Imagine-then-Arbitrate (ITA) neural dialogue model to help the agent decide whether to wait or to make a response directly. Our method has two imaginator modules and an arbitrator module. The two imaginators will learn the agent's and user's speaking style respectively, generate possible utterances as the input of the arbitrator, combining with dialogue history. And the arbitrator decides whether to wait or to make a response to the user directly. To verify the performance and effectiveness of our method, we prepared two dialogue datasets and compared our approach with several popular models. Experimental results show that our model performs well on addressing ending prediction issue and outperforms baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge