Guodong Cao
CSPM: A Contrastive Spatiotemporal Preference Model for CTR Prediction in On-Demand Food Delivery Services
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is a crucial task in the context of an online on-demand food delivery (OFD) platform for precisely estimating the probability of a user clicking on food items. Unlike universal e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and Amazon, user behaviors and interests on the OFD platform are more location and time-sensitive due to limited delivery ranges and regional commodity supplies. However, existing CTR prediction algorithms in OFD scenarios concentrate on capturing interest from historical behavior sequences, which fails to effectively model the complex spatiotemporal information within features, leading to poor performance. To address this challenge, this paper introduces the Contrastive Sres under different search states using three modules: contrastive spatiotemporal representation learning (CSRL), spatiotemporal preference extractor (StPE), and spatiotemporal information filter (StIF). CSRL utilizes a contrastive learning framework to generate a spatiotemporal activation representation (SAR) for the search action. StPE employs SAR to activate users' diverse preferences related to location and time from the historical behavior sequence field, using a multi-head attention mechanism. StIF incorporates SAR into a gating network to automatically capture important features with latent spatiotemporal effects. Extensive experiments conducted on two large-scale industrial datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of CSPM. Notably, CSPM has been successfully deployed in Alibaba's online OFD platform Ele.me, resulting in a significant 0.88% lift in CTR, which has substantial business implications.
Spatiotemporal-Enhanced Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction in Location-based Services
Sep 20, 2022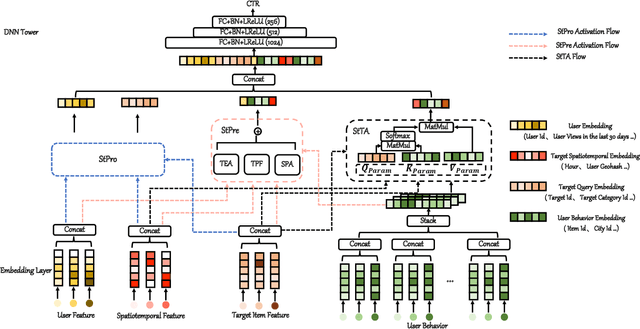
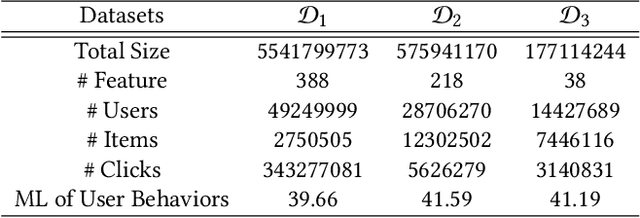
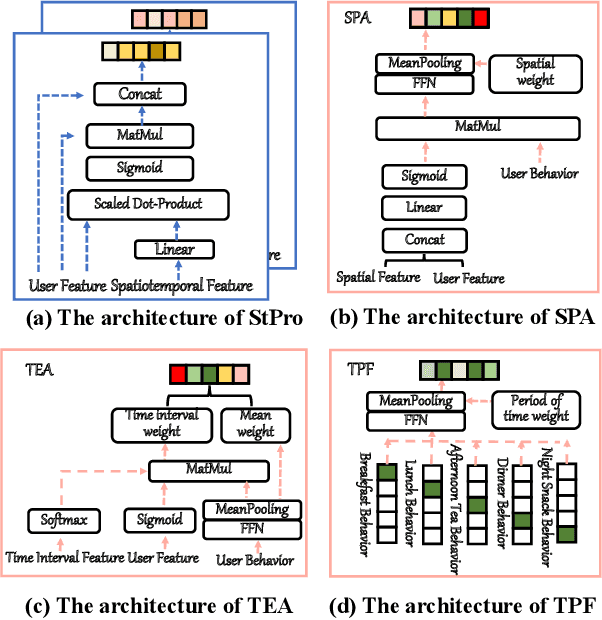
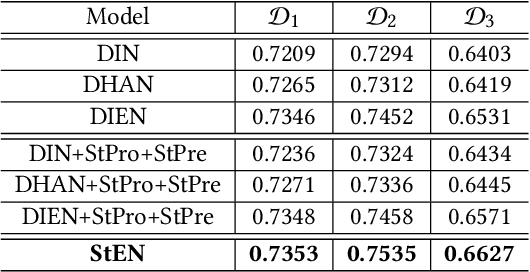
Abstract:In Location-Based Services(LBS), user behavior naturally has a strong dependence on the spatiotemporal information, i.e., in different geographical locations and at different times, user click behavior will change significantly. Appropriate spatiotemporal enhancement modeling of user click behavior and large-scale sparse attributes is key to building an LBS model. Although most of existing methods have been proved to be effective, they are difficult to apply to takeaway scenarios due to insufficient modeling of spatiotemporal information. In this paper, we address this challenge by seeking to explicitly model the timing and locations of interactions and proposing a Spatiotemporal-Enhanced Network, namely StEN. In particular, StEN applies a Spatiotemporal Profile Activation module to capture common spatiotemporal preference through attribute features. A Spatiotemporal Preference Activation is further applied to model the personalized spatiotemporal preference embodied by behaviors in detail. Moreover, a Spatiotemporal-aware Target Attention mechanism is adopted to generate different parameters for target attention at different locations and times, thereby improving the personalized spatiotemporal awareness of the model.Comprehensive experiments are conducted on three large-scale industrial datasets, and the results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our methods. In addition, we have also released an industrial dataset for takeaway industry to make up for the lack of public datasets in this community.
Vanilla Feature Distillation for Improving the Accuracy-Robustness Trade-Off in Adversarial Training
Jun 05, 2022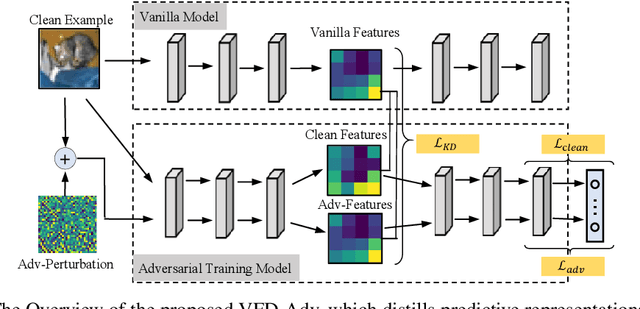
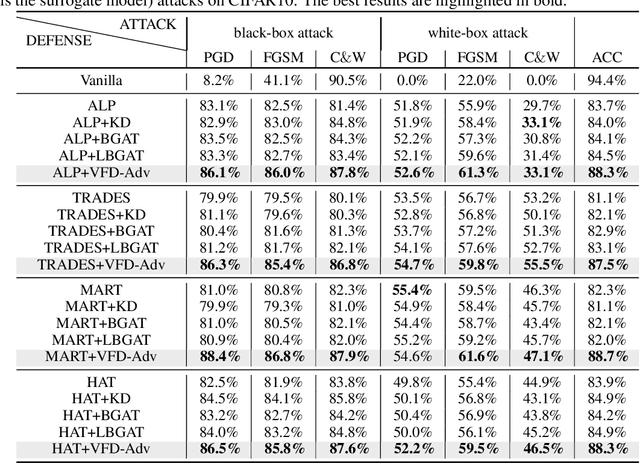
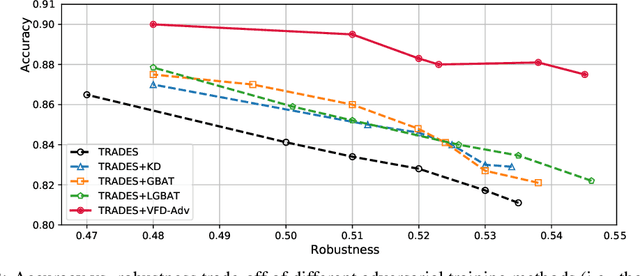
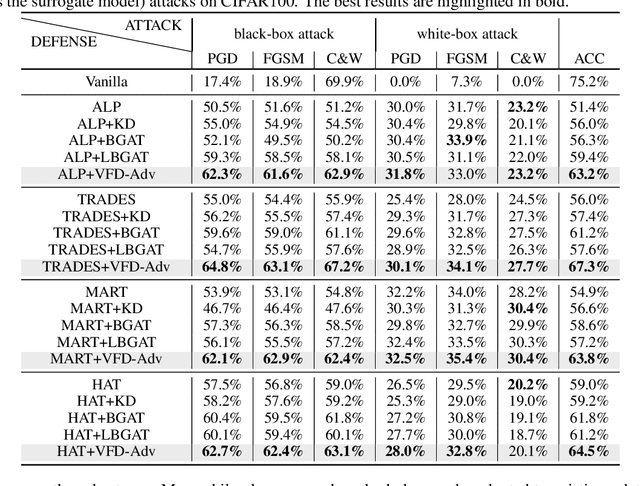
Abstract:Adversarial training has been widely explored for mitigating attacks against deep models. However, most existing works are still trapped in the dilemma between higher accuracy and stronger robustness since they tend to fit a model towards robust features (not easily tampered with by adversaries) while ignoring those non-robust but highly predictive features. To achieve a better robustness-accuracy trade-off, we propose the Vanilla Feature Distillation Adversarial Training (VFD-Adv), which conducts knowledge distillation from a pre-trained model (optimized towards high accuracy) to guide adversarial training towards higher accuracy, i.e., preserving those non-robust but predictive features. More specifically, both adversarial examples and their clean counterparts are forced to be aligned in the feature space by distilling predictive representations from the pre-trained/clean model, while previous works barely utilize predictive features from clean models. Therefore, the adversarial training model is updated towards maximally preserving the accuracy as gaining robustness. A key advantage of our method is that it can be universally adapted to and boost existing works. Exhaustive experiments on various datasets, classification models, and adversarial training algorithms demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Context-aware Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network for User Behavior Prediction in Local Consumer Service Platform
Jun 29, 2021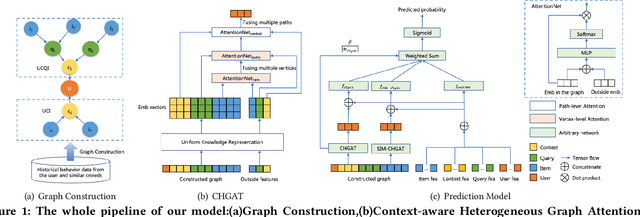
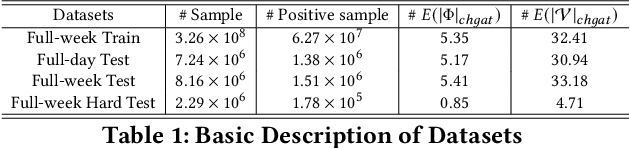
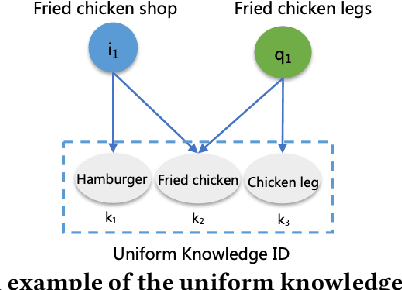
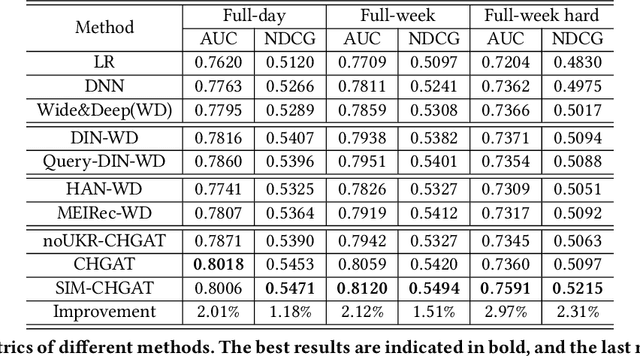
Abstract:As a new type of e-commerce platform developed in recent years, local consumer service platform provides users with software to consume service to the nearby store or to the home, such as Groupon and Koubei. Different from other common e-commerce platforms, the behavior of users on the local consumer service platform is closely related to their real-time local context information. Therefore, building a context-aware user behavior prediction system is able to provide both merchants and users better service in local consumer service platforms. However, most of the previous work just treats the contextual information as an ordinary feature into the prediction model to obtain the prediction list under a specific context, which ignores the fact that the interest of a user in different contexts is often significantly different. Hence, in this paper, we propose a context-aware heterogeneous graph attention network (CHGAT) to dynamically generate the representation of the user and to estimate the probability for future behavior. Specifically, we first construct the meta-path based heterogeneous graphs with the historical behaviors from multiple sources and comprehend heterogeneous vertices in the graph with a novel unified knowledge representing approach. Next, a multi-level attention mechanism is introduced for context-aware aggregation with graph vertices, which contains the vertex-level attention network and the path-level attention network. Both of them aim to capture the semantic correlation between information contained in the graph and the outside real-time contextual information in the search system. Then the model proposed in this paper aggregates specific graphs with their corresponding context features and obtains the representation of user interest under a specific context and input it into the prediction network to finally obtain the predicted probability of user behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge