Xiyu Ji
BASM: A Bottom-up Adaptive Spatiotemporal Model for Online Food Ordering Service
Nov 22, 2022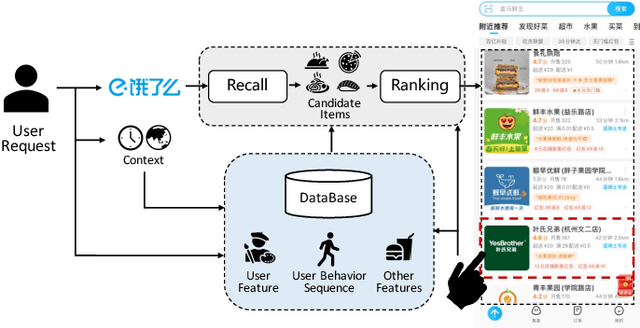
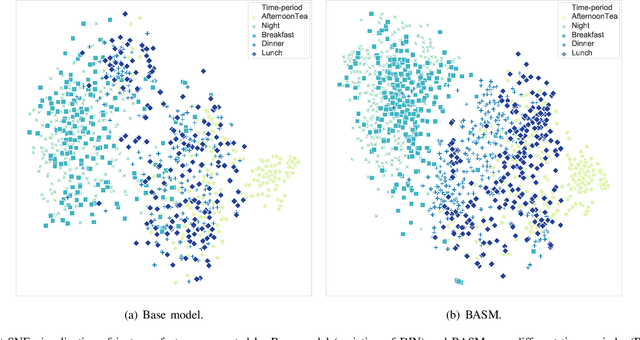
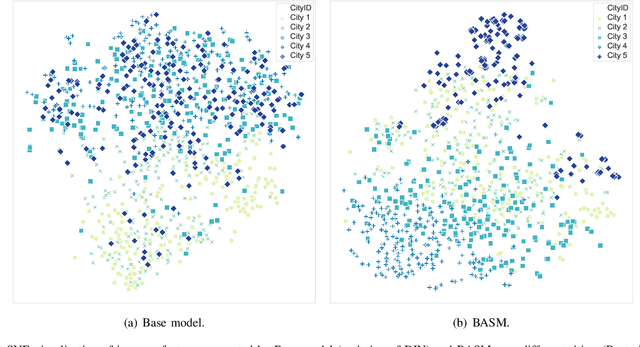
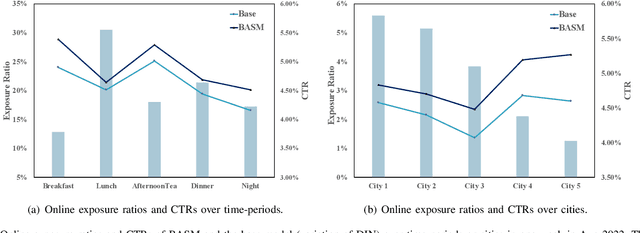
Abstract:Online Food Ordering Service (OFOS) is a popular location-based service that helps people to order what you want. Compared with traditional e-commerce recommendation systems, users' interests may be diverse under different spatiotemporal contexts, leading to various spatiotemporal data distribution, which limits the fitting capacity of the model. However, numerous current works simply mix all samples to train a set of model parameters, which makes it difficult to capture the diversity in different spatiotemporal contexts. Therefore, we address this challenge by proposing a Bottom-up Adaptive Spatiotemporal Model(BASM) to adaptively fit the spatiotemporal data distribution, which further improve the fitting capability of the model. Specifically, a spatiotemporal-aware embedding layer performs weight adaptation on field granularity in feature embedding, to achieve the purpose of dynamically perceiving spatiotemporal contexts. Meanwhile, we propose a spatiotemporal semantic transformation layer to explicitly convert the concatenated input of the raw semantic to spatiotemporal semantic, which can further enhance the semantic representation under different spatiotemporal contexts. Furthermore, we introduce a novel spatiotemporal adaptive bias tower to capture diverse spatiotemporal bias, reducing the difficulty to model spatiotemporal distinction. To further verify the effectiveness of BASM, we also novelly propose two new metrics, Time-period-wise AUC (TAUC) and City-wise AUC (CAUC). Extensive offline evaluations on public and industrial datasets are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed modle. The online A/B experiment also further illustrates the practicability of the model online service. This proposed method has now been implemented on the Ele.me, a major online food ordering platform in China, serving more than 100 million online users.
Spatiotemporal-Enhanced Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction in Location-based Services
Sep 20, 2022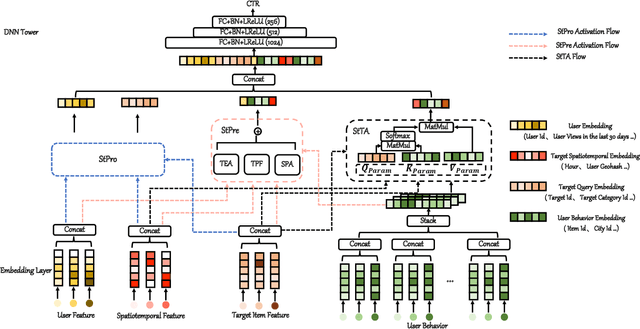
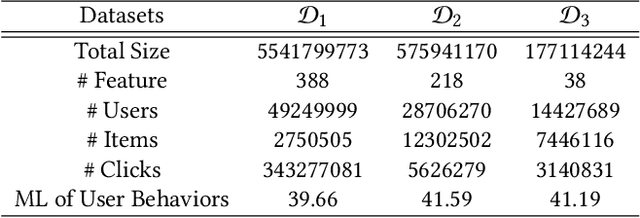
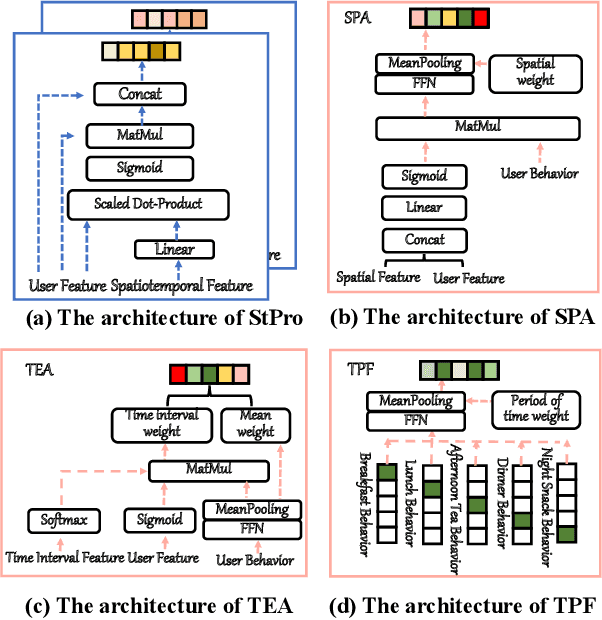
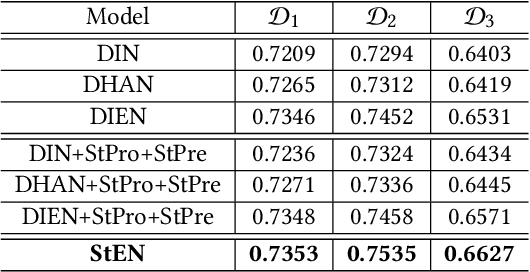
Abstract:In Location-Based Services(LBS), user behavior naturally has a strong dependence on the spatiotemporal information, i.e., in different geographical locations and at different times, user click behavior will change significantly. Appropriate spatiotemporal enhancement modeling of user click behavior and large-scale sparse attributes is key to building an LBS model. Although most of existing methods have been proved to be effective, they are difficult to apply to takeaway scenarios due to insufficient modeling of spatiotemporal information. In this paper, we address this challenge by seeking to explicitly model the timing and locations of interactions and proposing a Spatiotemporal-Enhanced Network, namely StEN. In particular, StEN applies a Spatiotemporal Profile Activation module to capture common spatiotemporal preference through attribute features. A Spatiotemporal Preference Activation is further applied to model the personalized spatiotemporal preference embodied by behaviors in detail. Moreover, a Spatiotemporal-aware Target Attention mechanism is adopted to generate different parameters for target attention at different locations and times, thereby improving the personalized spatiotemporal awareness of the model.Comprehensive experiments are conducted on three large-scale industrial datasets, and the results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our methods. In addition, we have also released an industrial dataset for takeaway industry to make up for the lack of public datasets in this community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge