Guangyuan Weng
Action Recognition based on Cross-Situational Action-object Statistics
Aug 15, 2022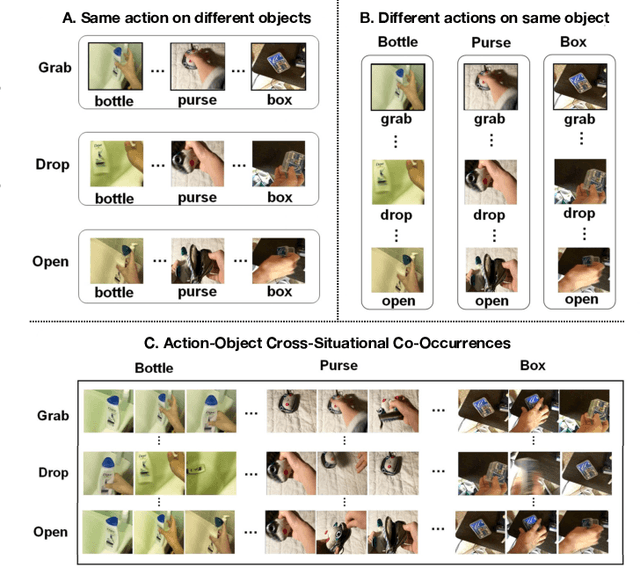
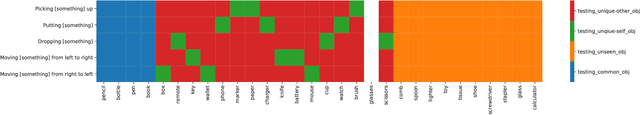
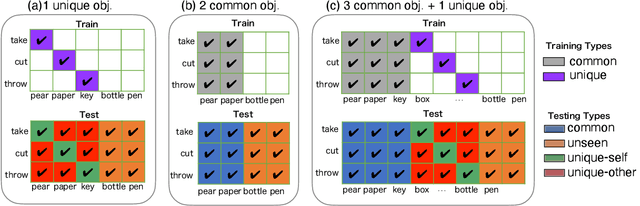
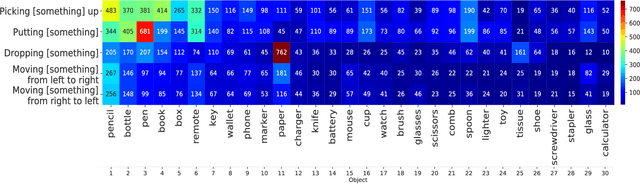
Abstract:Machine learning models of visual action recognition are typically trained and tested on data from specific situations where actions are associated with certain objects. It is an open question how action-object associations in the training set influence a model's ability to generalize beyond trained situations. We set out to identify properties of training data that lead to action recognition models with greater generalization ability. To do this, we take inspiration from a cognitive mechanism called cross-situational learning, which states that human learners extract the meaning of concepts by observing instances of the same concept across different situations. We perform controlled experiments with various types of action-object associations, and identify key properties of action-object co-occurrence in training data that lead to better classifiers. Given that these properties are missing in the datasets that are typically used to train action classifiers in the computer vision literature, our work provides useful insights on how we should best construct datasets for efficiently training for better generalization.
Advanced Mapping Robot and High-Resolution Dataset
Jul 23, 2020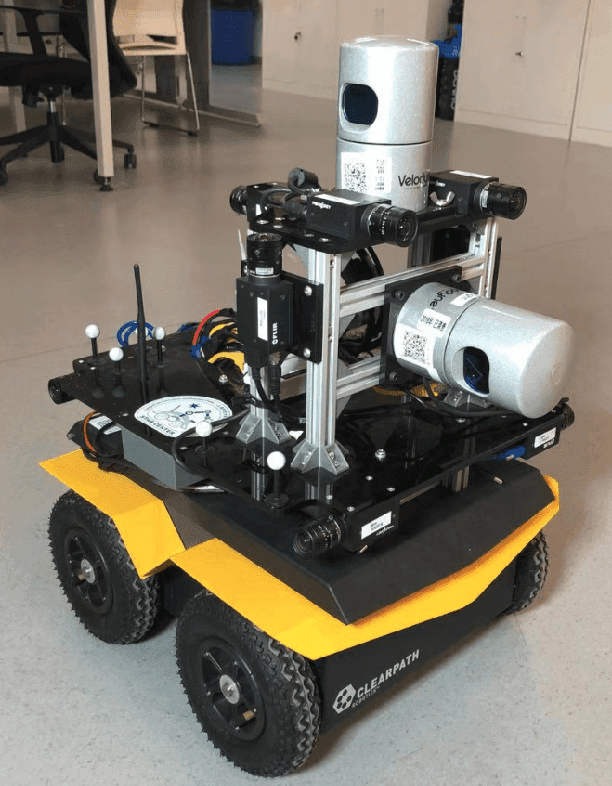
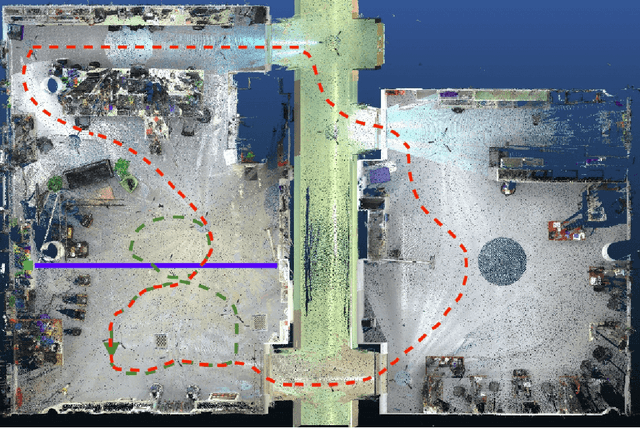
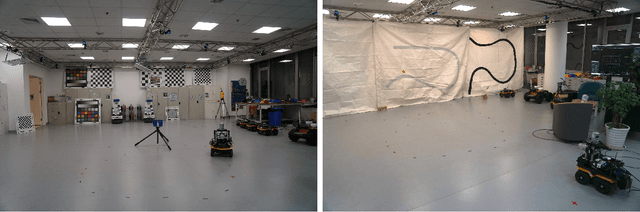
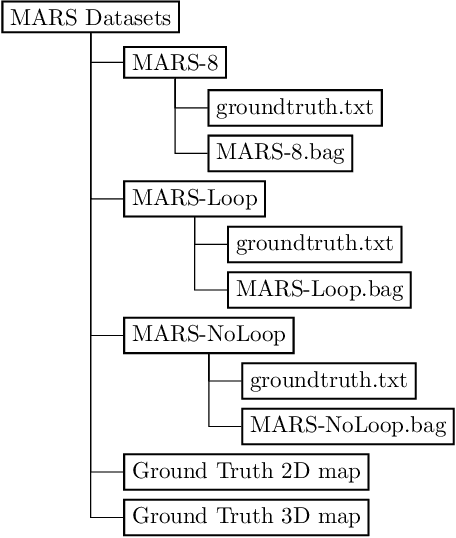
Abstract:This paper presents a fully hardware synchronized mapping robot with support for a hardware synchronized external tracking system, for super-precise timing and localization. Nine high-resolution cameras and two 32-beam 3D Lidars were used along with a professional, static 3D scanner for ground truth map collection. With all the sensors calibrated on the mapping robot, three datasets are collected to evaluate the performance of mapping algorithms within a room and between rooms. Based on these datasets we generate maps and trajectory data, which is then fed into evaluation algorithms. We provide the datasets for download and the mapping and evaluation procedures are made in a very easily reproducible manner for maximum comparability. We have also conducted a survey on available robotics-related datasets and compiled a big table with those datasets and a number of properties of them.
Towards Generation and Evaluation of Comprehensive Mapping Robot Datasets
May 23, 2019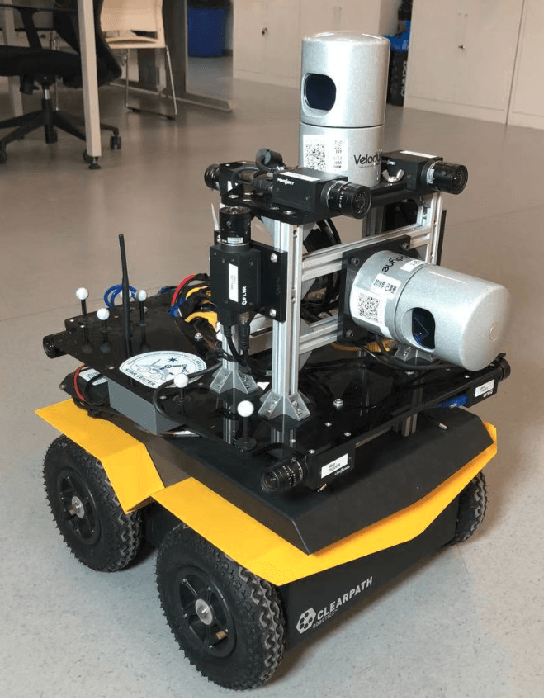
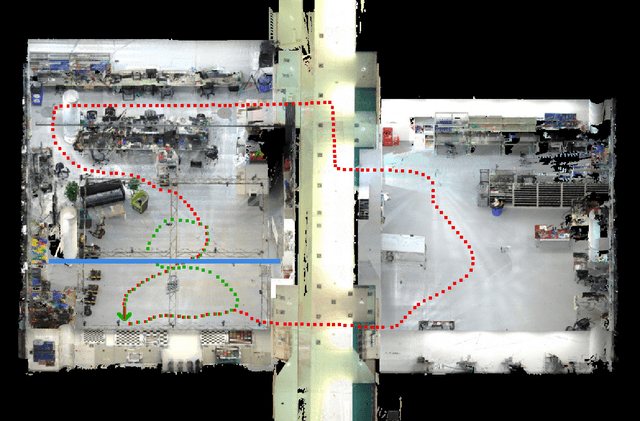
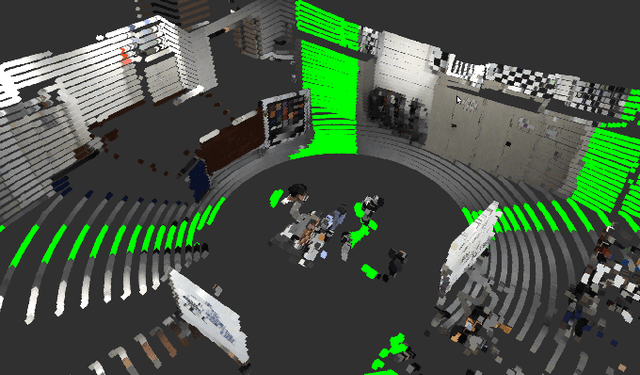
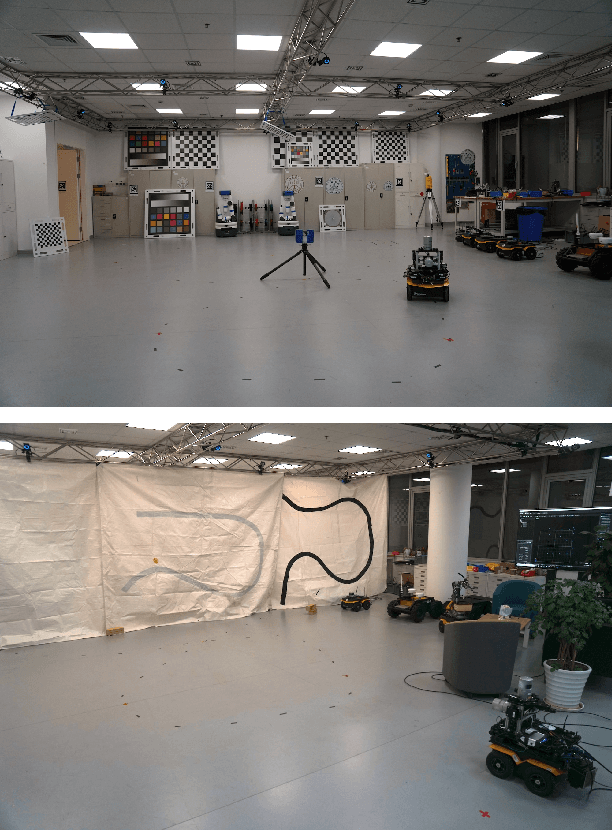
Abstract:This paper presents a fully hardware synchronized mapping robot with support for a hardware synchronized external tracking system, for super-precise timing and localization. We also employ a professional, static 3D scanner for ground truth map collection. Three datasets are generated to evaluate the performance of mapping algorithms within a room and between rooms. Based on these datasets we generate maps and trajectory data, which is then fed into evaluation algorithms. The mapping and evaluation procedures are made in a very easily reproducible manner for maximum comparability. In the end we can draw a couple of conclusions about the tested SLAM algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge