Govind Mittal
WavePulse: Real-time Content Analytics of Radio Livestreams
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Radio remains a pervasive medium for mass information dissemination, with AM/FM stations reaching more Americans than either smartphone-based social networking or live television. Increasingly, radio broadcasts are also streamed online and accessed over the Internet. We present WavePulse, a framework that records, documents, and analyzes radio content in real-time. While our framework is generally applicable, we showcase the efficacy of WavePulse in a collaborative project with a team of political scientists focusing on the 2024 Presidential Elections. We use WavePulse to monitor livestreams of 396 news radio stations over a period of three months, processing close to 500,000 hours of audio streams. These streams were converted into time-stamped, diarized transcripts and analyzed to track answer key political science questions at both the national and state levels. Our analysis revealed how local issues interacted with national trends, providing insights into information flow. Our results demonstrate WavePulse's efficacy in capturing and analyzing content from radio livestreams sourced from the Web. Code and dataset can be accessed at \url{https://wave-pulse.io}.
SELECT: A Large-Scale Benchmark of Data Curation Strategies for Image Classification
Oct 07, 2024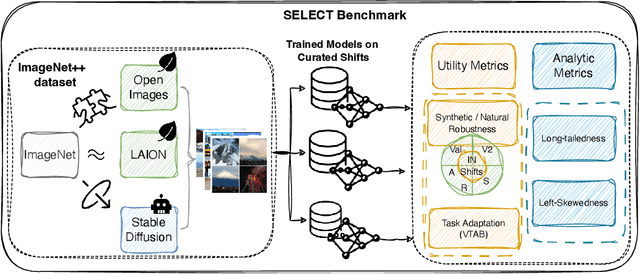
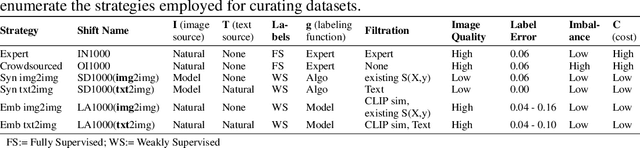

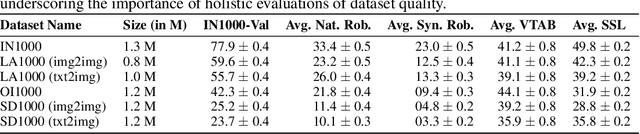
Abstract:Data curation is the problem of how to collect and organize samples into a dataset that supports efficient learning. Despite the centrality of the task, little work has been devoted towards a large-scale, systematic comparison of various curation methods. In this work, we take steps towards a formal evaluation of data curation strategies and introduce SELECT, the first large-scale benchmark of curation strategies for image classification. In order to generate baseline methods for the SELECT benchmark, we create a new dataset, ImageNet++, which constitutes the largest superset of ImageNet-1K to date. Our dataset extends ImageNet with 5 new training-data shifts, each approximately the size of ImageNet-1K itself, and each assembled using a distinct curation strategy. We evaluate our data curation baselines in two ways: (i) using each training-data shift to train identical image classification models from scratch (ii) using the data itself to fit a pretrained self-supervised representation. Our findings show interesting trends, particularly pertaining to recent methods for data curation such as synthetic data generation and lookup based on CLIP embeddings. We show that although these strategies are highly competitive for certain tasks, the curation strategy used to assemble the original ImageNet-1K dataset remains the gold standard. We anticipate that our benchmark can illuminate the path for new methods to further reduce the gap. We release our checkpoints, code, documentation, and a link to our dataset at https://github.com/jimmyxu123/SELECT.
AI-assisted Tagging of Deepfake Audio Calls using Challenge-Response
Feb 28, 2024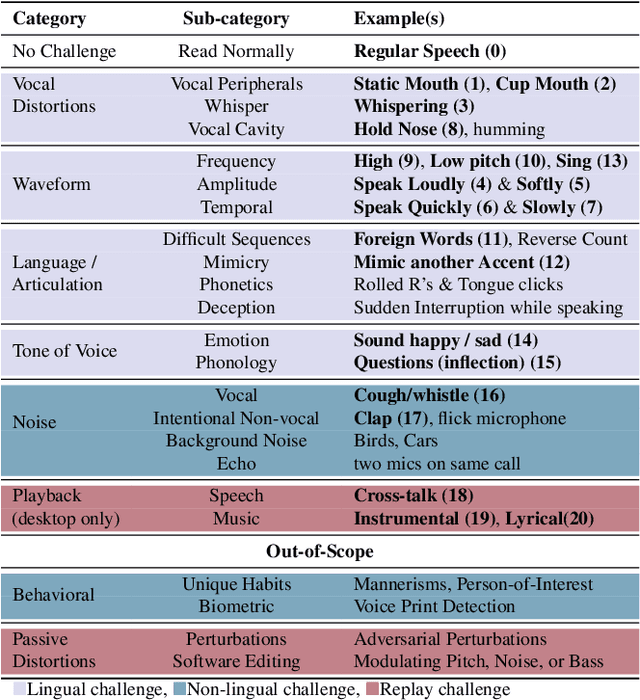
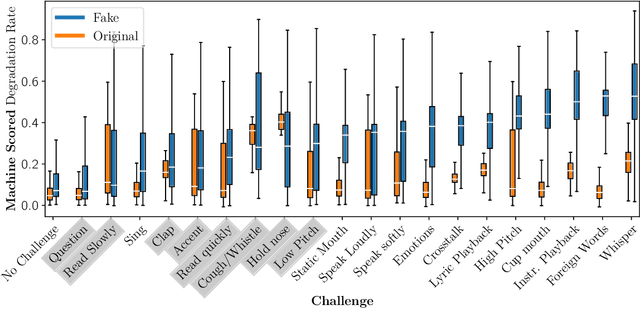
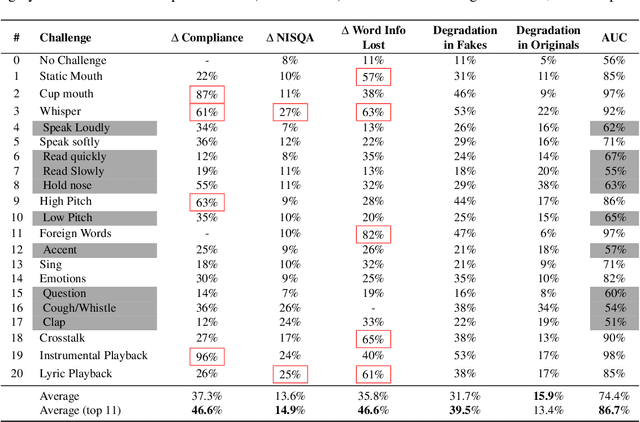
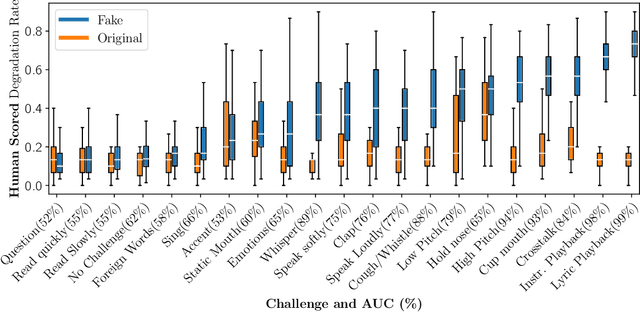
Abstract:Scammers are aggressively leveraging AI voice-cloning technology for social engineering attacks, a situation significantly worsened by the advent of audio Real-time Deepfakes (RTDFs). RTDFs can clone a target's voice in real-time over phone calls, making these interactions highly interactive and thus far more convincing. Our research confidently addresses the gap in the existing literature on deepfake detection, which has largely been ineffective against RTDF threats. We introduce a robust challenge-response-based method to detect deepfake audio calls, pioneering a comprehensive taxonomy of audio challenges. Our evaluation pitches 20 prospective challenges against a leading voice-cloning system. We have compiled a novel open-source challenge dataset with contributions from 100 smartphone and desktop users, yielding 18,600 original and 1.6 million deepfake samples. Through rigorous machine and human evaluations of this dataset, we achieved a deepfake detection rate of 86% and an 80% AUC score, respectively. Notably, utilizing a set of 11 challenges significantly enhances detection capabilities. Our findings reveal that combining human intuition with machine precision offers complementary advantages. Consequently, we have developed an innovative human-AI collaborative system that melds human discernment with algorithmic accuracy, boosting final joint accuracy to 82.9%. This system highlights the significant advantage of AI-assisted pre-screening in call verification processes. Samples can be heard at https://mittalgovind.github.io/autch-samples/
Identity-Preserving Aging of Face Images via Latent Diffusion Models
Jul 17, 2023
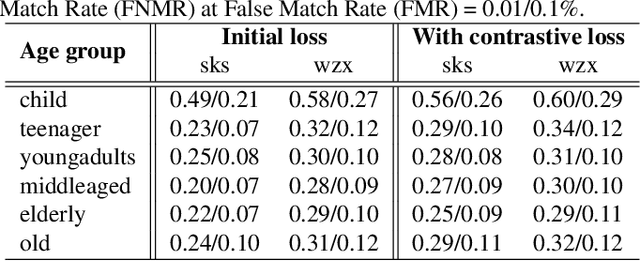


Abstract:The performance of automated face recognition systems is inevitably impacted by the facial aging process. However, high quality datasets of individuals collected over several years are typically small in scale. In this work, we propose, train, and validate the use of latent text-to-image diffusion models for synthetically aging and de-aging face images. Our models succeed with few-shot training, and have the added benefit of being controllable via intuitive textual prompting. We observe high degrees of visual realism in the generated images while maintaining biometric fidelity measured by commonly used metrics. We evaluate our method on two benchmark datasets (CelebA and AgeDB) and observe significant reduction (~44%) in the False Non-Match Rate compared to existing state-of the-art baselines.
Gotcha: A Challenge-Response System for Real-Time Deepfake Detection
Oct 12, 2022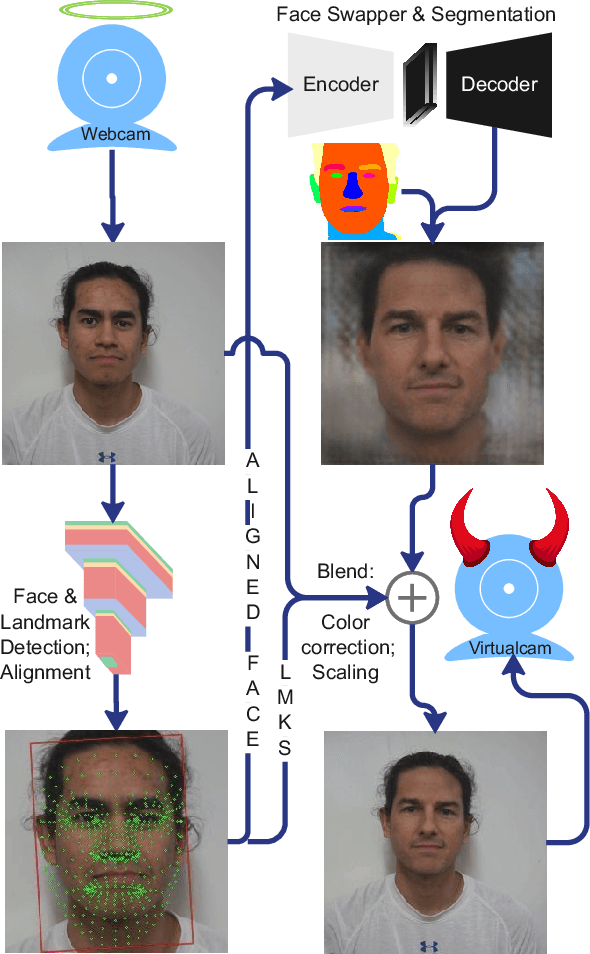
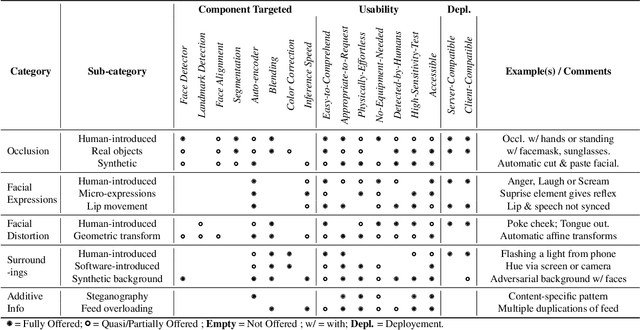
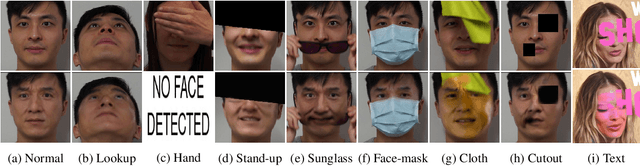
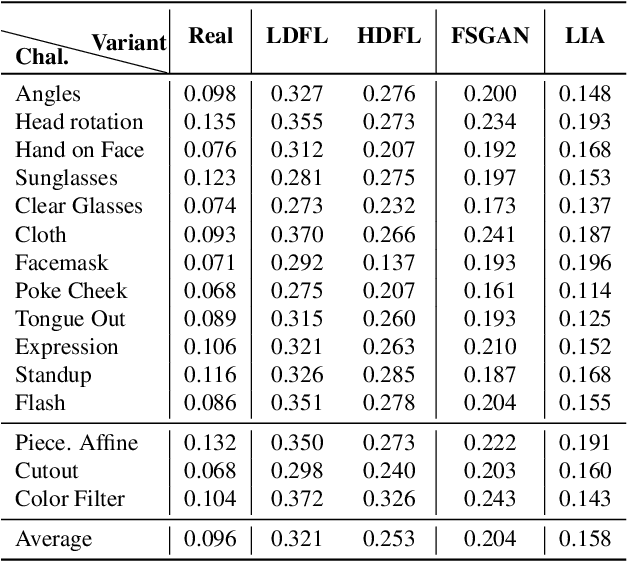
Abstract:The integrity of online video interactions is threatened by the widespread rise of AI-enabled high-quality deepfakes that are now deployable in real-time. This paper presents Gotcha, a real-time deepfake detection system for live video interactions. The core principle underlying Gotcha is the presentation of a specially chosen cascade of both active and passive challenges to video conference participants. Active challenges include inducing changes in face occlusion, face expression, view angle, and ambiance; passive challenges include digital manipulation of the webcam feed. The challenges are designed to target vulnerabilities in the structure of modern deepfake generators and create perceptible artifacts for the human eye while inducing robust signals for ML-based automatic deepfake detectors. We present a comprehensive taxonomy of a large set of challenge tasks, which reveals a natural hierarchy among different challenges. Our system leverages this hierarchy by cascading progressively more demanding challenges to a suspected deepfake. We evaluate our system on a novel dataset of live users emulating deepfakes and show that our system provides consistent, measurable degradation of deepfake quality, showcasing its promise for robust real-time deepfake detection when deployed in the wild.
Detecting Hostile Posts using Relational Graph Convolutional Network
Jan 10, 2021



Abstract:This work is based on the submission to the competition Hindi Constraint conducted by AAAI@2021 for detection of hostile posts in Hindi on social media platforms. Here, a model is presented for detection and classification of hostile posts and further classify into fake, offensive, hate and defamation using Relational Graph Convolutional Networks. Unlike other existing work, our approach is focused on using semantic meaning along with contextutal information for better classification. The results from AAAI@2021 indicates that the proposed model is performing at par with Google's XLM-RoBERTa on the given dataset. Our best submission with RGCN achieves an F1 score of 0.97 (7th Rank) on coarse-grained evaluation and achieved best performance on identifying fake posts. Among all submissions to the challenge, our classification system with XLM-Roberta secured 2nd rank on fine-grained classification.
Spoken Language Identification using ConvNets
Oct 09, 2019



Abstract:Language Identification (LI) is an important first step in several speech processing systems. With a growing number of voice-based assistants, speech LI has emerged as a widely researched field. To approach the problem of identifying languages, we can either adopt an implicit approach where only the speech for a language is present or an explicit one where text is available with its corresponding transcript. This paper focuses on an implicit approach due to the absence of transcriptive data. This paper benchmarks existing models and proposes a new attention based model for language identification which uses log-Mel spectrogram images as input. We also present the effectiveness of raw waveforms as features to neural network models for LI tasks. For training and evaluation of models, we classified six languages (English, French, German, Spanish, Russian and Italian) with an accuracy of 95.4% and four languages (English, French, German, Spanish) with an accuracy of 96.3% obtained from the VoxForge dataset. This approach can further be scaled to incorporate more languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge