Kelly O. Marshall
Slice-100K: A Multimodal Dataset for Extrusion-based 3D Printing
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:G-code (Geometric code) or RS-274 is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) and 3D printing programming language. G-code provides machine instructions for the movement of the 3D printer, especially for the nozzle, stage, and extrusion of material for extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Currently there does not exist a large repository of curated CAD models along with their corresponding G-code files for additive manufacturing. To address this issue, we present SLICE-100K, a first-of-its-kind dataset of over 100,000 G-code files, along with their tessellated CAD model, LVIS (Large Vocabulary Instance Segmentation) categories, geometric properties, and renderings. We build our dataset from triangulated meshes derived from Objaverse-XL and Thingi10K datasets. We demonstrate the utility of this dataset by finetuning GPT-2 on a subset of the dataset for G-code translation from a legacy G-code format (Sailfish) to a more modern, widely used format (Marlin). SLICE-100K will be the first step in developing a multimodal foundation model for digital manufacturing.
Robust Concept Erasure Using Task Vectors
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid growth of text-to-image models, a variety of techniques have been suggested to prevent undesirable image generations. Yet, these methods often only protect against specific user prompts and have been shown to allow unsafe generations with other inputs. Here we focus on unconditionally erasing a concept from a text-to-image model rather than conditioning the erasure on the user's prompt. We first show that compared to input-dependent erasure methods, concept erasure that uses Task Vectors (TV) is more robust to unexpected user inputs, not seen during training. However, TV-based erasure can also affect the core performance of the edited model, particularly when the required edit strength is unknown. To this end, we propose a method called Diverse Inversion, which we use to estimate the required strength of the TV edit. Diverse Inversion finds within the model input space a large set of word embeddings, each of which induces the generation of the target concept. We find that encouraging diversity in the set makes our estimation more robust to unexpected prompts. Finally, we show that Diverse Inversion enables us to apply a TV edit only to a subset of the model weights, enhancing the erasure capabilities while better maintaining the core functionality of the model.
AI-assisted Tagging of Deepfake Audio Calls using Challenge-Response
Feb 28, 2024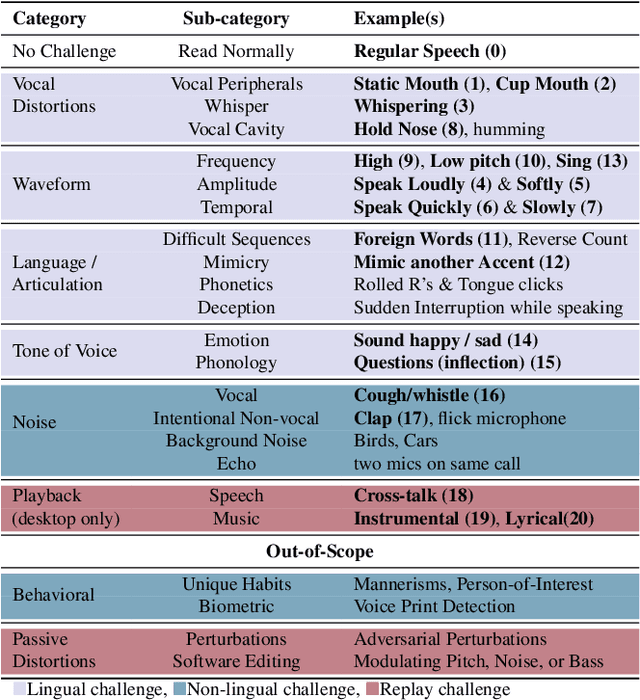
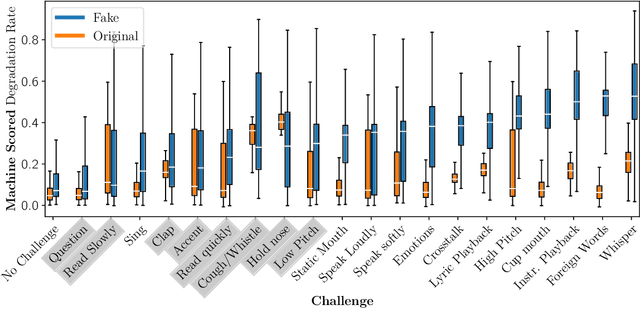
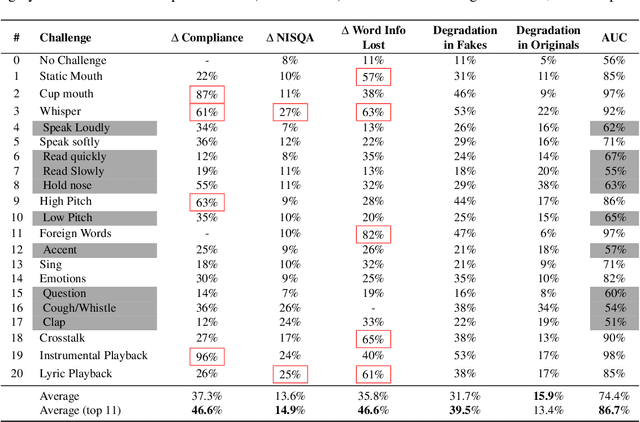
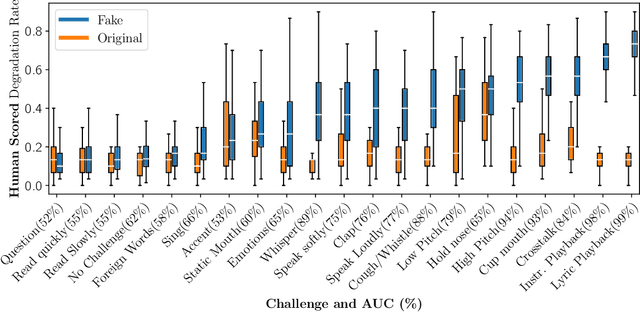
Abstract:Scammers are aggressively leveraging AI voice-cloning technology for social engineering attacks, a situation significantly worsened by the advent of audio Real-time Deepfakes (RTDFs). RTDFs can clone a target's voice in real-time over phone calls, making these interactions highly interactive and thus far more convincing. Our research confidently addresses the gap in the existing literature on deepfake detection, which has largely been ineffective against RTDF threats. We introduce a robust challenge-response-based method to detect deepfake audio calls, pioneering a comprehensive taxonomy of audio challenges. Our evaluation pitches 20 prospective challenges against a leading voice-cloning system. We have compiled a novel open-source challenge dataset with contributions from 100 smartphone and desktop users, yielding 18,600 original and 1.6 million deepfake samples. Through rigorous machine and human evaluations of this dataset, we achieved a deepfake detection rate of 86% and an 80% AUC score, respectively. Notably, utilizing a set of 11 challenges significantly enhances detection capabilities. Our findings reveal that combining human intuition with machine precision offers complementary advantages. Consequently, we have developed an innovative human-AI collaborative system that melds human discernment with algorithmic accuracy, boosting final joint accuracy to 82.9%. This system highlights the significant advantage of AI-assisted pre-screening in call verification processes. Samples can be heard at https://mittalgovind.github.io/autch-samples/
Circumventing Concept Erasure Methods For Text-to-Image Generative Models
Aug 03, 2023Abstract:Text-to-image generative models can produce photo-realistic images for an extremely broad range of concepts, and their usage has proliferated widely among the general public. On the flip side, these models have numerous drawbacks, including their potential to generate images featuring sexually explicit content, mirror artistic styles without permission, or even hallucinate (or deepfake) the likenesses of celebrities. Consequently, various methods have been proposed in order to "erase" sensitive concepts from text-to-image models. In this work, we examine five recently proposed concept erasure methods, and show that targeted concepts are not fully excised from any of these methods. Specifically, we leverage the existence of special learned word embeddings that can retrieve "erased" concepts from the sanitized models with no alterations to their weights. Our results highlight the brittleness of post hoc concept erasure methods, and call into question their use in the algorithmic toolkit for AI safety.
ZeroForge: Feedforward Text-to-Shape Without 3D Supervision
Jun 16, 2023
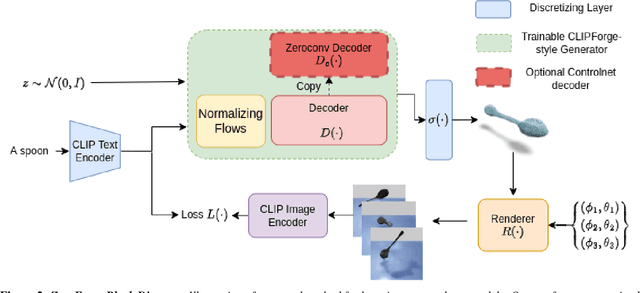
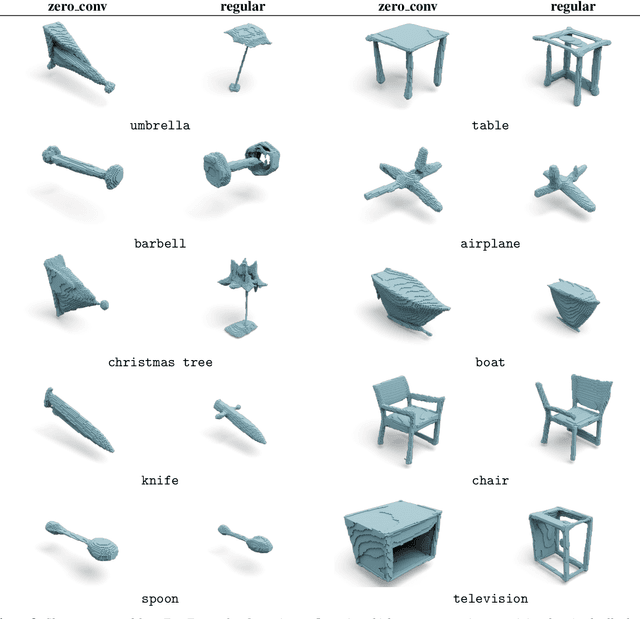
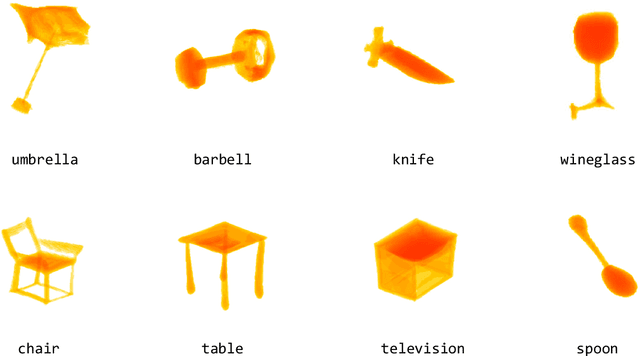
Abstract:Current state-of-the-art methods for text-to-shape generation either require supervised training using a labeled dataset of pre-defined 3D shapes, or perform expensive inference-time optimization of implicit neural representations. In this work, we present ZeroForge, an approach for zero-shot text-to-shape generation that avoids both pitfalls. To achieve open-vocabulary shape generation, we require careful architectural adaptation of existing feed-forward approaches, as well as a combination of data-free CLIP-loss and contrastive losses to avoid mode collapse. Using these techniques, we are able to considerably expand the generative ability of existing feed-forward text-to-shape models such as CLIP-Forge. We support our method via extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge