Gorka Labaka
Conditioning LLMs to Generate Code-Switched Text: A Methodology Grounded in Naturally Occurring Data
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Code-switching (CS) is still a critical challenge in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Current Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to interpret and generate code-switched text, primarily due to the scarcity of large-scale CS datasets for training. This paper presents a novel methodology to generate CS data using LLMs, and test it on the English-Spanish language pair. We propose back-translating natural CS sentences into monolingual English, and using the resulting parallel corpus to fine-tune LLMs to turn monolingual sentences into CS. Unlike previous approaches to CS generation, our methodology uses natural CS data as a starting point, allowing models to learn its natural distribution beyond grammatical patterns. We thoroughly analyse the models' performance through a study on human preferences, a qualitative error analysis and an evaluation with popular automatic metrics. Results show that our methodology generates fluent code-switched text, expanding research opportunities in CS communication, and that traditional metrics do not correlate with human judgement when assessing the quality of the generated CS data. We release our code and generated dataset under a CC-BY-NC-SA license.
Principled Paraphrase Generation with Parallel Corpora
May 24, 2022



Abstract:Round-trip Machine Translation (MT) is a popular choice for paraphrase generation, which leverages readily available parallel corpora for supervision. In this paper, we formalize the implicit similarity function induced by this approach, and show that it is susceptible to non-paraphrase pairs sharing a single ambiguous translation. Based on these insights, we design an alternative similarity metric that mitigates this issue by requiring the entire translation distribution to match, and implement a relaxation of it through the Information Bottleneck method. Our approach incorporates an adversarial term into MT training in order to learn representations that encode as much information about the reference translation as possible, while keeping as little information about the input as possible. Paraphrases can be generated by decoding back to the source from this representation, without having to generate pivot translations. In addition to being more principled and efficient than round-trip MT, our approach offers an adjustable parameter to control the fidelity-diversity trade-off, and obtains better results in our experiments.
Label Verbalization and Entailment for Effective Zero- and Few-Shot Relation Extraction
Sep 08, 2021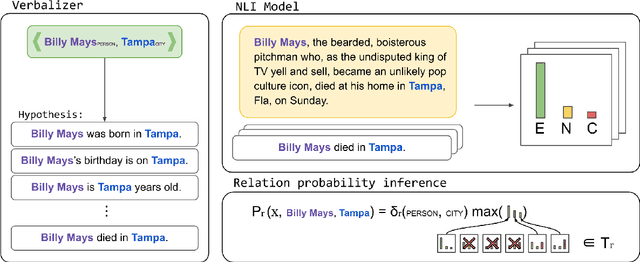
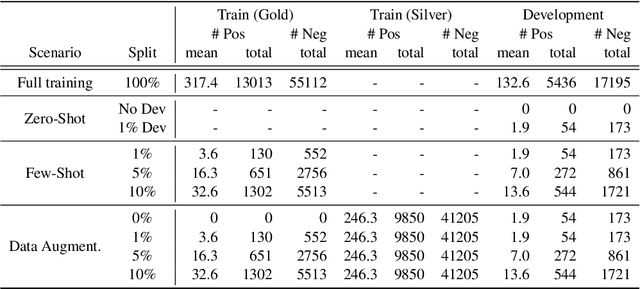
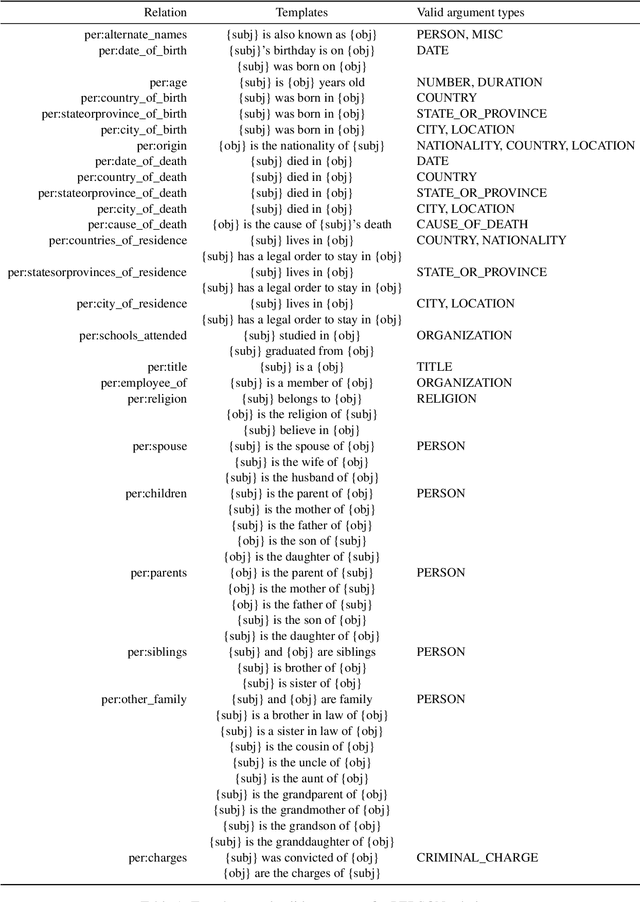
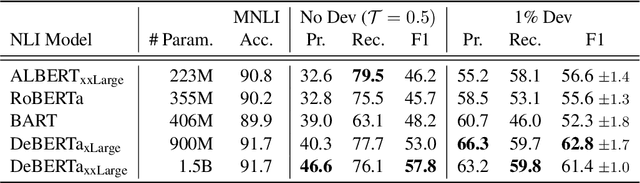
Abstract:Relation extraction systems require large amounts of labeled examples which are costly to annotate. In this work we reformulate relation extraction as an entailment task, with simple, hand-made, verbalizations of relations produced in less than 15 min per relation. The system relies on a pretrained textual entailment engine which is run as-is (no training examples, zero-shot) or further fine-tuned on labeled examples (few-shot or fully trained). In our experiments on TACRED we attain 63% F1 zero-shot, 69% with 16 examples per relation (17% points better than the best supervised system on the same conditions), and only 4 points short to the state-of-the-art (which uses 20 times more training data). We also show that the performance can be improved significantly with larger entailment models, up to 12 points in zero-shot, allowing to report the best results to date on TACRED when fully trained. The analysis shows that our few-shot systems are specially effective when discriminating between relations, and that the performance difference in low data regimes comes mainly from identifying no-relation cases.
Unsupervised Multilingual Sentence Embeddings for Parallel Corpus Mining
May 21, 2021



Abstract:Existing models of multilingual sentence embeddings require large parallel data resources which are not available for low-resource languages. We propose a novel unsupervised method to derive multilingual sentence embeddings relying only on monolingual data. We first produce a synthetic parallel corpus using unsupervised machine translation, and use it to fine-tune a pretrained cross-lingual masked language model (XLM) to derive the multilingual sentence representations. The quality of the representations is evaluated on two parallel corpus mining tasks with improvements of up to 22 F1 points over vanilla XLM. In addition, we observe that a single synthetic bilingual corpus is able to improve results for other language pairs.
* ACL SRW 2020
Beyond Offline Mapping: Learning Cross Lingual Word Embeddings through Context Anchoring
Dec 31, 2020



Abstract:Recent research on cross-lingual word embeddings has been dominated by unsupervised mapping approaches that align monolingual embeddings. Such methods critically rely on those embeddings having a similar structure, but it was recently shown that the separate training in different languages causes departures from this assumption. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach that does not have this limitation, while requiring a weak seed dictionary (e.g., a list of identical words) as the only form of supervision. Rather than aligning two fixed embedding spaces, our method works by fixing the target language embeddings, and learning a new set of embeddings for the source language that are aligned with them. To that end, we use an extension of skip-gram that leverages translated context words as anchor points, and incorporates self-learning and iterative restarts to reduce the dependency on the initial dictionary. Our approach outperforms conventional mapping methods on bilingual lexicon induction, and obtains competitive results in the downstream XNLI task.
A Call for More Rigor in Unsupervised Cross-lingual Learning
Apr 30, 2020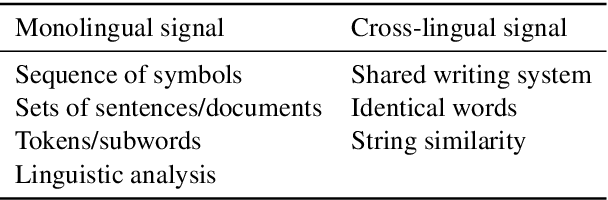
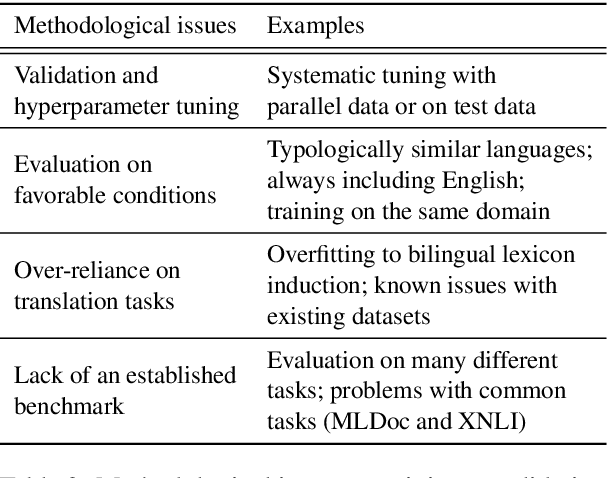
Abstract:We review motivations, definition, approaches, and methodology for unsupervised cross-lingual learning and call for a more rigorous position in each of them. An existing rationale for such research is based on the lack of parallel data for many of the world's languages. However, we argue that a scenario without any parallel data and abundant monolingual data is unrealistic in practice. We also discuss different training signals that have been used in previous work, which depart from the pure unsupervised setting. We then describe common methodological issues in tuning and evaluation of unsupervised cross-lingual models and present best practices. Finally, we provide a unified outlook for different types of research in this area (i.e., cross-lingual word embeddings, deep multilingual pretraining, and unsupervised machine translation) and argue for comparable evaluation of these models.
Translation Artifacts in Cross-lingual Transfer Learning
Apr 14, 2020



Abstract:Both human and machine translation play a central role in cross-lingual transfer learning: many multilingual datasets have been created through professional translation services, and using machine translation to translate either the test set or the training set is a widely used transfer technique. In this paper, we show that such translation process can introduce subtle artifacts that have a notable impact in existing cross-lingual models. For instance, in natural language inference, translating the premise and the hypothesis independently can reduce the lexical overlap between them, which current models are highly sensitive to. We show that some previous findings in cross-lingual transfer learning need to be reconsidered in the light of this phenomenon. Based on the gained insights, we also improve the state-of-the-art in XNLI for the translate-test and zero-shot approaches by 4.3 and 2.8 points, respectively.
Do all Roads Lead to Rome? Understanding the Role of Initialization in Iterative Back-Translation
Feb 28, 2020

Abstract:Back-translation provides a simple yet effective approach to exploit monolingual corpora in Neural Machine Translation (NMT). Its iterative variant, where two opposite NMT models are jointly trained by alternately using a synthetic parallel corpus generated by the reverse model, plays a central role in unsupervised machine translation. In order to start producing sound translations and provide a meaningful training signal to each other, existing approaches rely on either a separate machine translation system to warm up the iterative procedure, or some form of pre-training to initialize the weights of the model. In this paper, we analyze the role that such initialization plays in iterative back-translation. Is the behavior of the final system heavily dependent on it? Or does iterative back-translation converge to a similar solution given any reasonable initialization? Through a series of empirical experiments over a diverse set of warmup systems, we show that, although the quality of the initial system does affect final performance, its effect is relatively small, as iterative back-translation has a strong tendency to convergence to a similar solution. As such, the margin of improvement left for the initialization method is narrow, suggesting that future research should focus more on improving the iterative mechanism itself.
Bilingual Lexicon Induction through Unsupervised Machine Translation
Jul 24, 2019

Abstract:A recent research line has obtained strong results on bilingual lexicon induction by aligning independently trained word embeddings in two languages and using the resulting cross-lingual embeddings to induce word translation pairs through nearest neighbor or related retrieval methods. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach to this problem that builds on the recent work on unsupervised machine translation. This way, instead of directly inducing a bilingual lexicon from cross-lingual embeddings, we use them to build a phrase-table, combine it with a language model, and use the resulting machine translation system to generate a synthetic parallel corpus, from which we extract the bilingual lexicon using statistical word alignment techniques. As such, our method can work with any word embedding and cross-lingual mapping technique, and it does not require any additional resource besides the monolingual corpus used to train the embeddings. When evaluated on the exact same cross-lingual embeddings, our proposed method obtains an average improvement of 6 accuracy points over nearest neighbor and 4 points over CSLS retrieval, establishing a new state-of-the-art in the standard MUSE dataset.
Analyzing the Limitations of Cross-lingual Word Embedding Mappings
Jun 12, 2019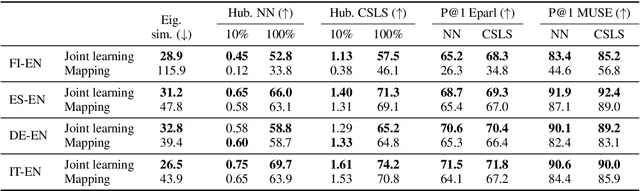
Abstract:Recent research in cross-lingual word embeddings has almost exclusively focused on offline methods, which independently train word embeddings in different languages and map them to a shared space through linear transformations. While several authors have questioned the underlying isomorphism assumption, which states that word embeddings in different languages have approximately the same structure, it is not clear whether this is an inherent limitation of mapping approaches or a more general issue when learning cross-lingual embeddings. So as to answer this question, we experiment with parallel corpora, which allows us to compare offline mapping to an extension of skip-gram that jointly learns both embedding spaces. We observe that, under these ideal conditions, joint learning yields to more isomorphic embeddings, is less sensitive to hubness, and obtains stronger results in bilingual lexicon induction. We thus conclude that current mapping methods do have strong limitations, calling for further research to jointly learn cross-lingual embeddings with a weaker cross-lingual signal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge