Geon Yeong Park
Inference-Time Diffusion Model Distillation
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Diffusion distillation models effectively accelerate reverse sampling by compressing the process into fewer steps. However, these models still exhibit a performance gap compared to their pre-trained diffusion model counterparts, exacerbated by distribution shifts and accumulated errors during multi-step sampling. To address this, we introduce Distillation++, a novel inference-time distillation framework that reduces this gap by incorporating teacher-guided refinement during sampling. Inspired by recent advances in conditional sampling, our approach recasts student model sampling as a proximal optimization problem with a score distillation sampling loss (SDS). To this end, we integrate distillation optimization during reverse sampling, which can be viewed as teacher guidance that drives student sampling trajectory towards the clean manifold using pre-trained diffusion models. Thus, Distillation++ improves the denoising process in real-time without additional source data or fine-tuning. Distillation++ demonstrates substantial improvements over state-of-the-art distillation baselines, particularly in early sampling stages, positioning itself as a robust guided sampling process crafted for diffusion distillation models. Code: https://github.com/geonyeong-park/inference_distillation.
VideoGuide: Improving Video Diffusion Models without Training Through a Teacher's Guide
Oct 06, 2024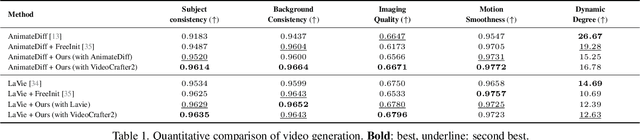
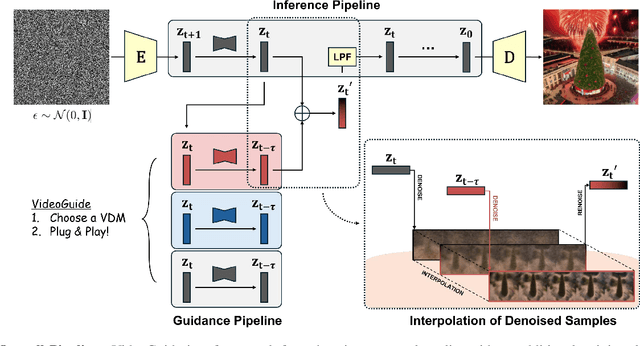


Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have revolutionized visual content creation, but extending these capabilities to text-to-video (T2V) generation remains a challenge, particularly in preserving temporal consistency. Existing methods that aim to improve consistency often cause trade-offs such as reduced imaging quality and impractical computational time. To address these issues we introduce VideoGuide, a novel framework that enhances the temporal consistency of pretrained T2V models without the need for additional training or fine-tuning. Instead, VideoGuide leverages any pretrained video diffusion model (VDM) or itself as a guide during the early stages of inference, improving temporal quality by interpolating the guiding model's denoised samples into the sampling model's denoising process. The proposed method brings about significant improvement in temporal consistency and image fidelity, providing a cost-effective and practical solution that synergizes the strengths of various video diffusion models. Furthermore, we demonstrate prior distillation, revealing that base models can achieve enhanced text coherence by utilizing the superior data prior of the guiding model through the proposed method. Project Page: http://videoguide2025.github.io/
CFG++: Manifold-constrained Classifier Free Guidance for Diffusion Models
Jun 12, 2024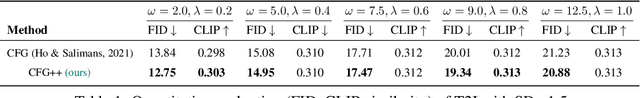
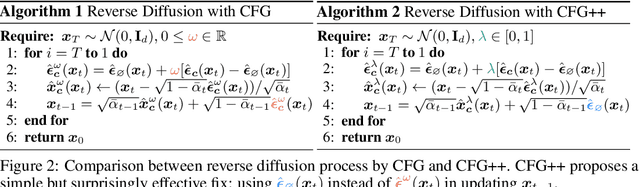
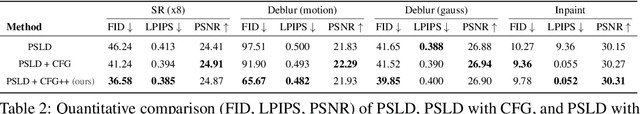
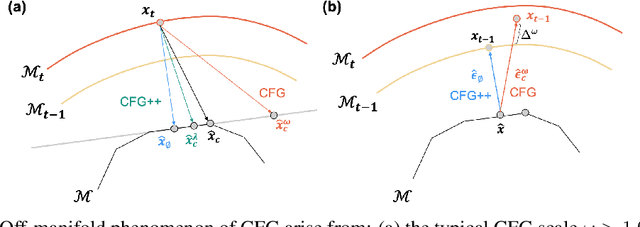
Abstract:Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is a fundamental tool in modern diffusion models for text-guided generation. Although effective, CFG has notable drawbacks. For instance, DDIM with CFG lacks invertibility, complicating image editing; furthermore, high guidance scales, essential for high-quality outputs, frequently result in issues like mode collapse. Contrary to the widespread belief that these are inherent limitations of diffusion models, this paper reveals that the problems actually stem from the off-manifold phenomenon associated with CFG, rather than the diffusion models themselves. More specifically, inspired by the recent advancements of diffusion model-based inverse problem solvers (DIS), we reformulate text-guidance as an inverse problem with a text-conditioned score matching loss, and develop CFG++, a novel approach that tackles the off-manifold challenges inherent in traditional CFG. CFG++ features a surprisingly simple fix to CFG, yet it offers significant improvements, including better sample quality for text-to-image generation, invertibility, smaller guidance scales, reduced mode collapse, etc. Furthermore, CFG++ enables seamless interpolation between unconditional and conditional sampling at lower guidance scales, consistently outperforming traditional CFG at all scales. Experimental results confirm that our method significantly enhances performance in text-to-image generation, DDIM inversion, editing, and solving inverse problems, suggesting a wide-ranging impact and potential applications in various fields that utilize text guidance. Project Page: https://cfgpp-diffusion.github.io/.
Spectral Motion Alignment for Video Motion Transfer using Diffusion Models
Mar 22, 2024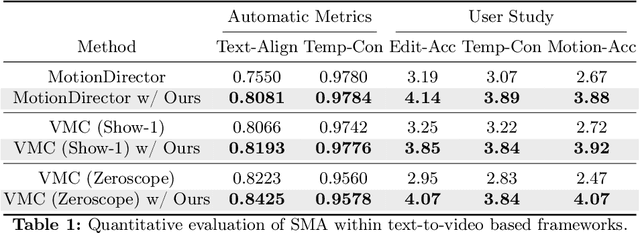
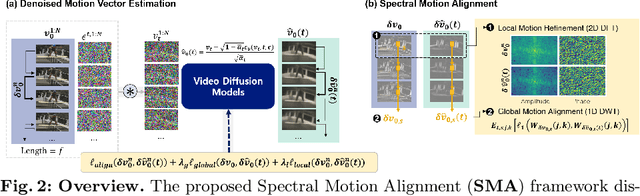
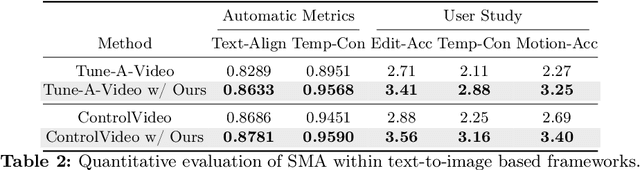

Abstract:The evolution of diffusion models has greatly impacted video generation and understanding. Particularly, text-to-video diffusion models (VDMs) have significantly facilitated the customization of input video with target appearance, motion, etc. Despite these advances, challenges persist in accurately distilling motion information from video frames. While existing works leverage the consecutive frame residual as the target motion vector, they inherently lack global motion context and are vulnerable to frame-wise distortions. To address this, we present Spectral Motion Alignment (SMA), a novel framework that refines and aligns motion vectors using Fourier and wavelet transforms. SMA learns motion patterns by incorporating frequency-domain regularization, facilitating the learning of whole-frame global motion dynamics, and mitigating spatial artifacts. Extensive experiments demonstrate SMA's efficacy in improving motion transfer while maintaining computational efficiency and compatibility across various video customization frameworks.
DreamMotion: Space-Time Self-Similarity Score Distillation for Zero-Shot Video Editing
Mar 18, 2024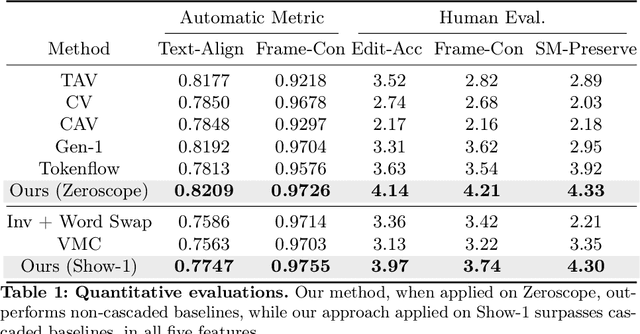


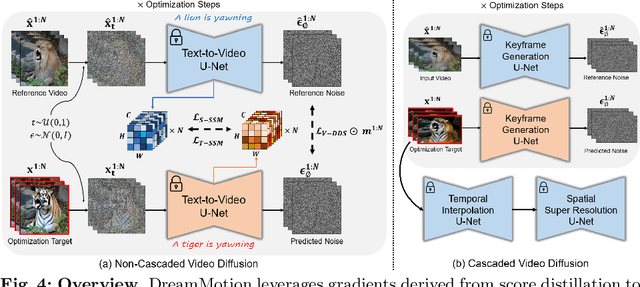
Abstract:Text-driven diffusion-based video editing presents a unique challenge not encountered in image editing literature: establishing real-world motion. Unlike existing video editing approaches, here we focus on score distillation sampling to circumvent the standard reverse diffusion process and initiate optimization from videos that already exhibit natural motion. Our analysis reveals that while video score distillation can effectively introduce new content indicated by target text, it can also cause significant structure and motion deviation. To counteract this, we propose to match space-time self-similarities of the original video and the edited video during the score distillation. Thanks to the use of score distillation, our approach is model-agnostic, which can be applied for both cascaded and non-cascaded video diffusion frameworks. Through extensive comparisons with leading methods, our approach demonstrates its superiority in altering appearances while accurately preserving the original structure and motion.
DreamSampler: Unifying Diffusion Sampling and Score Distillation for Image Manipulation
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Reverse sampling and score-distillation have emerged as main workhorses in recent years for image manipulation using latent diffusion models (LDMs). While reverse diffusion sampling often requires adjustments of LDM architecture or feature engineering, score distillation offers a simple yet powerful model-agnostic approach, but it is often prone to mode-collapsing. To address these limitations and leverage the strengths of both approaches, here we introduce a novel framework called {\em DreamSampler}, which seamlessly integrates these two distinct approaches through the lens of regularized latent optimization. Similar to score-distillation, DreamSampler is a model-agnostic approach applicable to any LDM architecture, but it allows both distillation and reverse sampling with additional guidance for image editing and reconstruction. Through experiments involving image editing, SVG reconstruction and etc, we demonstrate the competitive performance of DreamSampler compared to existing approaches, while providing new applications.
VMC: Video Motion Customization using Temporal Attention Adaption for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Text-to-video diffusion models have advanced video generation significantly. However, customizing these models to generate videos with tailored motions presents a substantial challenge. In specific, they encounter hurdles in (a) accurately reproducing motion from a target video, and (b) creating diverse visual variations. For example, straightforward extensions of static image customization methods to video often lead to intricate entanglements of appearance and motion data. To tackle this, here we present the Video Motion Customization (VMC) framework, a novel one-shot tuning approach crafted to adapt temporal attention layers within video diffusion models. Our approach introduces a novel motion distillation objective using residual vectors between consecutive frames as a motion reference. The diffusion process then preserves low-frequency motion trajectories while mitigating high-frequency motion-unrelated noise in image space. We validate our method against state-of-the-art video generative models across diverse real-world motions and contexts. Our codes, data and the project demo can be found at https://video-motion-customization.github.io
Contrastive Denoising Score for Text-guided Latent Diffusion Image Editing
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:With the remarkable advent of text-to-image diffusion models, image editing methods have become more diverse and continue to evolve. A promising recent approach in this realm is Delta Denoising Score (DDS) - an image editing technique based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) framework that leverages the rich generative prior of text-to-image diffusion models. However, relying solely on the difference between scoring functions is insufficient for preserving specific structural elements from the original image, a crucial aspect of image editing. Inspired by the similarity and importance differences between DDS and the contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation (CUT), here we present an embarrassingly simple yet very powerful modification of DDS, called Contrastive Denoising Score (CDS), for latent diffusion models (LDM). Specifically, to enforce structural correspondence between the input and output while maintaining the controllability of contents, we introduce a straightforward approach to regulate structural consistency using CUT loss within the DDS framework. To calculate this loss, instead of employing auxiliary networks, we utilize the intermediate features of LDM, in particular, those from the self-attention layers, which possesses rich spatial information. Our approach enables zero-shot image-to-image translation and neural radiance field (NeRF) editing, achieving a well-balanced interplay between maintaining the structural details and transforming content. Qualitative results and comparisons demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed method. Project page with code is available at https://hyelinnam.github.io/CDS/.
Regularization by Texts for Latent Diffusion Inverse Solvers
Nov 27, 2023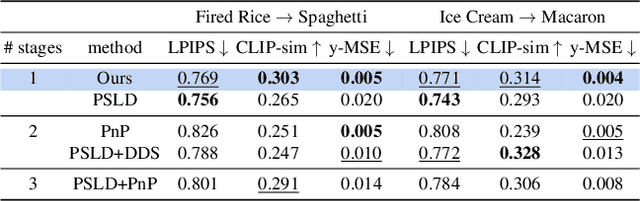
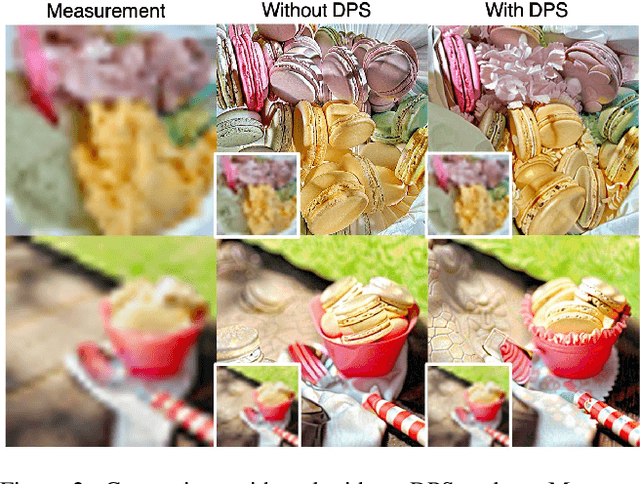
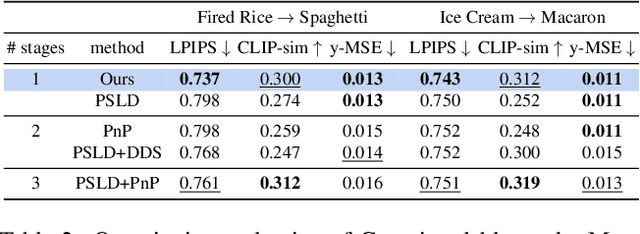
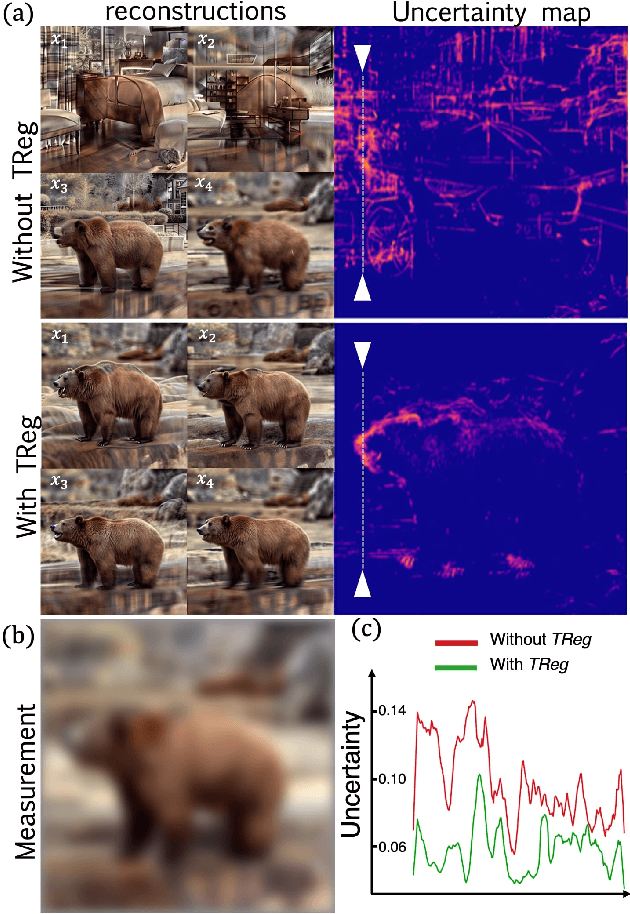
Abstract:The recent advent of diffusion models has led to significant progress in solving inverse problems, leveraging these models as effective generative priors. Nonetheless, challenges related to the ill-posed nature of such problems remain, often due to inherent ambiguities in measurements. Drawing inspiration from the human ability to resolve visual ambiguities through perceptual biases, here we introduce a novel latent diffusion inverse solver by incorporating regularization by texts (TReg). Specifically, TReg applies the textual description of the preconception of the solution during the reverse sampling phase, of which description isndynamically reinforced through null-text optimization for adaptive negation. Our comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that TReg successfully mitigates ambiguity in latent diffusion inverse solvers, enhancing their effectiveness and accuracy.
Energy-Based Cross Attention for Bayesian Context Update in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Jun 26, 2023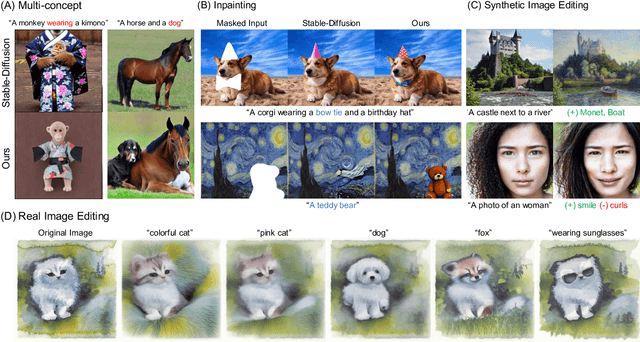
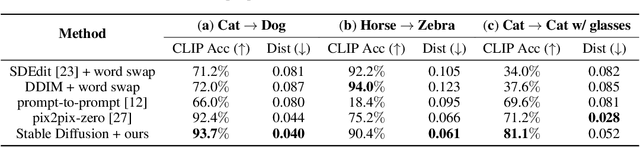
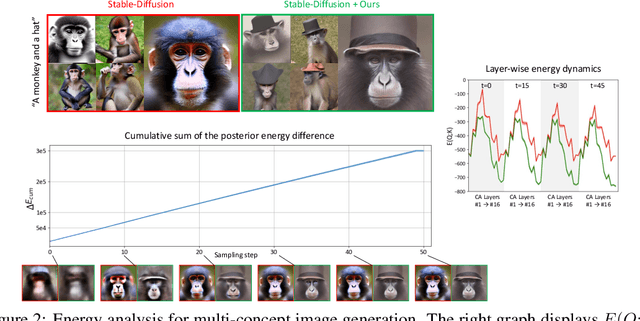

Abstract:Despite the remarkable performance of text-to-image diffusion models in image generation tasks, recent studies have raised the issue that generated images sometimes cannot capture the intended semantic contents of the text prompts, which phenomenon is often called semantic misalignment. To address this, here we present a novel energy-based model (EBM) framework. Specifically, we first formulate EBMs of latent image representations and text embeddings in each cross-attention layer of the denoising autoencoder. Then, we obtain the gradient of the log posterior of context vectors, which can be updated and transferred to the subsequent cross-attention layer, thereby implicitly minimizing a nested hierarchy of energy functions. Our latent EBMs further allow zero-shot compositional generation as a linear combination of cross-attention outputs from different contexts. Using extensive experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed method is highly effective in handling various image generation tasks, including multi-concept generation, text-guided image inpainting, and real and synthetic image editing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge