Jinho Chang
Contrastive CFG: Improving CFG in Diffusion Models by Contrasting Positive and Negative Concepts
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:As Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) has proven effective in conditional diffusion model sampling for improved condition alignment, many applications use a negated CFG term to filter out unwanted features from samples. However, simply negating CFG guidance creates an inverted probability distribution, often distorting samples away from the marginal distribution. Inspired by recent advances in conditional diffusion models for inverse problems, here we present a novel method to enhance negative CFG guidance using contrastive loss. Specifically, our guidance term aligns or repels the denoising direction based on the given condition through contrastive loss, achieving a nearly identical guiding direction to traditional CFG for positive guidance while overcoming the limitations of existing negative guidance methods. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach effectively removes undesirable concepts while maintaining sample quality across diverse scenarios, from simple class conditions to complex and overlapping text prompts.
LDMol: Text-Conditioned Molecule Diffusion Model Leveraging Chemically Informative Latent Space
May 28, 2024Abstract:With the emergence of diffusion models as the frontline of generative models, many researchers have proposed molecule generation techniques using conditional diffusion models. However, due to the fundamental nature of a molecule, which carries highly entangled correlations within a small number of atoms and bonds, it becomes difficult for a model to connect raw data with the conditions when the conditions become more complex as natural language. To address this, here we present a novel latent diffusion model dubbed LDMol, which enables a natural text-conditioned molecule generation. Specifically, LDMol is composed of three building blocks: a molecule encoder that produces a chemically informative feature space, a natural language-conditioned latent diffusion model using a Diffusion Transformer (DiT), and an autoregressive decoder for molecule re. In particular, recognizing that multiple SMILES notations can represent the same molecule, we employ a contrastive learning strategy to extract the chemical informative feature space. LDMol not only beats the existing baselines on the text-to-molecule generation benchmark but is also capable of zero-shot inference with unseen scenarios. Furthermore, we show that LDMol can be applied to downstream tasks such as molecule-to-text retrieval and text-driven molecule editing, demonstrating its versatility as a diffusion model.
Ground-A-Score: Scaling Up the Score Distillation for Multi-Attribute Editing
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:Despite recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models facilitating various image editing techniques, complex text prompts often lead to an oversight of some requests due to a bottleneck in processing text information. To tackle this challenge, we present Ground-A-Score, a simple yet powerful model-agnostic image editing method by incorporating grounding during score distillation. This approach ensures a precise reflection of intricate prompt requirements in the editing outcomes, taking into account the prior knowledge of the object locations within the image. Moreover, the selective application with a new penalty coefficient and contrastive loss helps to precisely target editing areas while preserving the integrity of the objects in the source image. Both qualitative assessments and quantitative analyses confirm that Ground-A-Score successfully adheres to the intricate details of extended and multifaceted prompts, ensuring high-quality outcomes that respect the original image attributes.
DreamMotion: Space-Time Self-Similarity Score Distillation for Zero-Shot Video Editing
Mar 18, 2024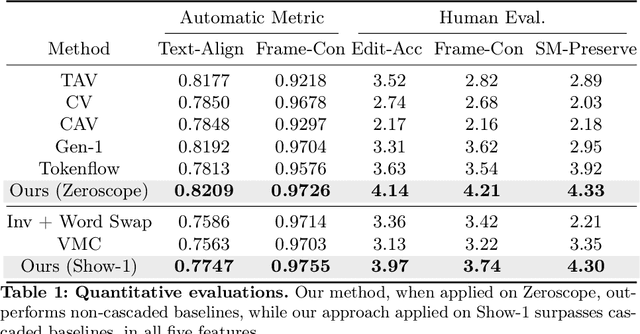


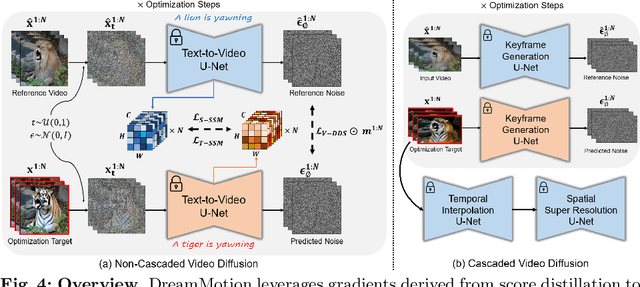
Abstract:Text-driven diffusion-based video editing presents a unique challenge not encountered in image editing literature: establishing real-world motion. Unlike existing video editing approaches, here we focus on score distillation sampling to circumvent the standard reverse diffusion process and initiate optimization from videos that already exhibit natural motion. Our analysis reveals that while video score distillation can effectively introduce new content indicated by target text, it can also cause significant structure and motion deviation. To counteract this, we propose to match space-time self-similarities of the original video and the edited video during the score distillation. Thanks to the use of score distillation, our approach is model-agnostic, which can be applied for both cascaded and non-cascaded video diffusion frameworks. Through extensive comparisons with leading methods, our approach demonstrates its superiority in altering appearances while accurately preserving the original structure and motion.
Molecular Structure-Property Co-Trained Foundation Model for In Silico Chemistry
Nov 19, 2022Abstract:Recently, deep learning approaches have been extensively studied for various problems in chemistry, such as virtual screening, de novo molecule design, etc. Despite the impressive successes, end-to-end training for specific tasks usually requires separately designed networks, so it's often difficult to acquire a unified principle to synergistically combine existing architectures and training datasets for novel tasks. To address this, inspired by recent advances of pre-trained multi-modal foundation models such as Vision-Language Pretrained models (VLP), here we present a novel multimodal foundation model that can be used {\em in silico} for various downstream tasks in chemistry. Specifically, our framework, dubbed as the structure-property multi-modal (SPMM) foundation model, is based on the dual-stream transformer with X-shape attention, so that it can align the molecule structure and the chemical properties in a common embedding space. Accordingly, SPMM can simultaneously perform chemical property prediction from given structure-describing strings and allows the generation of molecular structures for given chemical properties, which was previously not possible with a single architecture. Furthermore, we show that the outstanding unimodal representation of a molecule emerges from multimodal learning, which has the potential to be fine-tuned for many other downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge