Geetanjali Kale
Long Range Named Entity Recognition for Marathi Documents
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:The demand for sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) methods, particularly Named Entity Recognition (NER), has increased due to the exponential growth of Marathi-language digital content. In particular, NER is essential for recognizing distant entities and for arranging and understanding unstructured Marathi text data. With an emphasis on managing long-range entities, this paper offers a comprehensive analysis of current NER techniques designed for Marathi documents. It dives into current practices and investigates the BERT transformer model's potential for long-range Marathi NER. Along with analyzing the effectiveness of earlier methods, the report draws comparisons between NER in English literature and suggests adaptation strategies for Marathi literature. The paper discusses the difficulties caused by Marathi's particular linguistic traits and contextual subtleties while acknowledging NER's critical role in NLP. To conclude, this project is a major step forward in improving Marathi NER techniques, with potential wider applications across a range of NLP tasks and domains.
On Importance of Pruning and Distillation for Efficient Low Resource NLP
Sep 21, 2024


Abstract:The rise of large transformer models has revolutionized Natural Language Processing, leading to significant advances in tasks like text classification. However, this progress demands substantial computational resources, escalating training duration, and expenses with larger model sizes. Efforts have been made to downsize and accelerate English models (e.g., Distilbert, MobileBert). Yet, research in this area is scarce for low-resource languages. In this study, we explore the case of the low-resource Indic language Marathi. Leveraging the marathi-topic-all-doc-v2 model as our baseline, we implement optimization techniques to reduce computation time and memory usage. Our focus is on enhancing the efficiency of Marathi transformer models while maintaining top-tier accuracy and reducing computational demands. Using the MahaNews document classification dataset and the marathi-topic-all-doc-v2 model from L3Cube, we apply Block Movement Pruning, Knowledge Distillation, and Mixed Precision methods individually and in combination to boost efficiency. We demonstrate the importance of strategic pruning levels in achieving desired efficiency gains. Furthermore, we analyze the balance between efficiency improvements and environmental impact, highlighting how optimized model architectures can contribute to a more sustainable computational ecosystem. Implementing these techniques on a single GPU system, we determine that the optimal configuration is 25\% pruning + knowledge distillation. This approach yielded a 2.56x speedup in computation time while maintaining baseline accuracy levels.
TextGram: Towards a better domain-adaptive pretraining
Apr 28, 2024Abstract:For green AI, it is crucial to measure and reduce the carbon footprint emitted during the training of large language models. In NLP, performing pre-training on Transformer models requires significant computational resources. This pre-training involves using a large amount of text data to gain prior knowledge for performing downstream tasks. Thus, it is important that we select the correct data in the form of domain-specific data from this vast corpus to achieve optimum results aligned with our domain-specific tasks. While training on large unsupervised data is expensive, it can be optimized by performing a data selection step before pretraining. Selecting important data reduces the space overhead and the substantial amount of time required to pre-train the model while maintaining constant accuracy. We investigate the existing selection strategies and propose our own domain-adaptive data selection method - TextGram - that effectively selects essential data from large corpora. We compare and evaluate the results of finetuned models for text classification task with and without data selection. We show that the proposed strategy works better compared to other selection methods.
SenTest: Evaluating Robustness of Sentence Encoders
Nov 29, 2023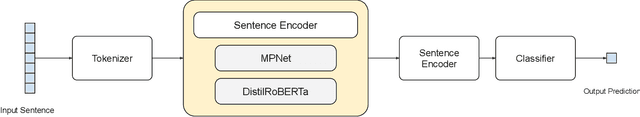
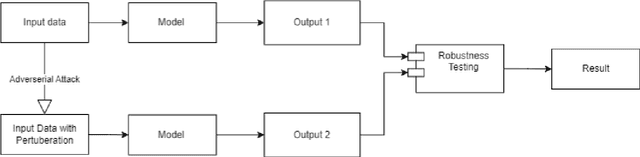

Abstract:Contrastive learning has proven to be an effective method for pre-training models using weakly labeled data in the vision domain. Sentence transformers are the NLP counterparts to this architecture, and have been growing in popularity due to their rich and effective sentence representations. Having effective sentence representations is paramount in multiple tasks, such as information retrieval, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and sentence comparison. Keeping in mind the deployability factor of transformers, evaluating the robustness of sentence transformers is of utmost importance. This work focuses on evaluating the robustness of the sentence encoders. We employ several adversarial attacks to evaluate its robustness. This system uses character-level attacks in the form of random character substitution, word-level attacks in the form of synonym replacement, and sentence-level attacks in the form of intra-sentence word order shuffling. The results of the experiments strongly undermine the robustness of sentence encoders. The models produce significantly different predictions as well as embeddings on perturbed datasets. The accuracy of the models can fall up to 15 percent on perturbed datasets as compared to unperturbed datasets. Furthermore, the experiments demonstrate that these embeddings does capture the semantic and syntactic structure (sentence order) of sentences. However, existing supervised classification strategies fail to leverage this information, and merely function as n-gram detectors.
Robust Sentiment Analysis for Low Resource languages Using Data Augmentation Approaches: A Case Study in Marathi
Oct 01, 2023
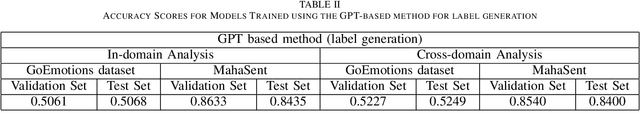
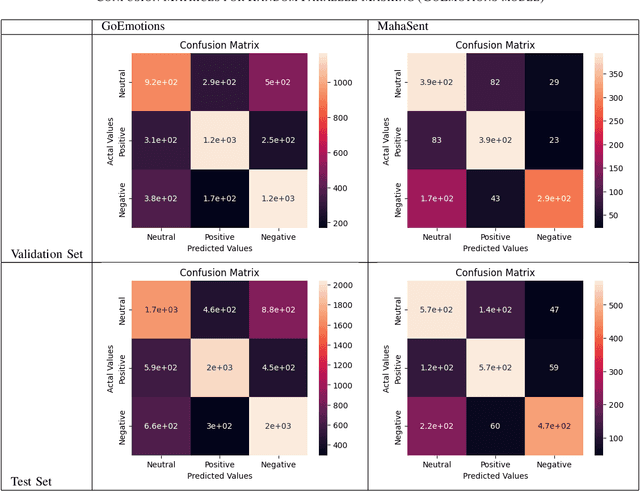
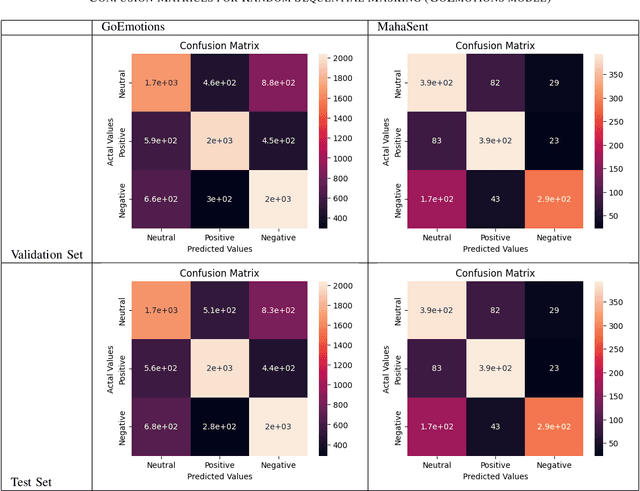
Abstract:Sentiment analysis plays a crucial role in understanding the sentiment expressed in text data. While sentiment analysis research has been extensively conducted in English and other Western languages, there exists a significant gap in research efforts for sentiment analysis in low-resource languages. Limited resources, including datasets and NLP research, hinder the progress in this area. In this work, we present an exhaustive study of data augmentation approaches for the low-resource Indic language Marathi. Although domain-specific datasets for sentiment analysis in Marathi exist, they often fall short when applied to generalized and variable-length inputs. To address this challenge, this research paper proposes four data augmentation techniques for sentiment analysis in Marathi. The paper focuses on augmenting existing datasets to compensate for the lack of sufficient resources. The primary objective is to enhance sentiment analysis model performance in both in-domain and cross-domain scenarios by leveraging data augmentation strategies. The data augmentation approaches proposed showed a significant performance improvement for cross-domain accuracies. The augmentation methods include paraphrasing, back-translation; BERT-based random token replacement, named entity replacement, and pseudo-label generation; GPT-based text and label generation. Furthermore, these techniques can be extended to other low-resource languages and for general text classification tasks.
Comparative Study of Long Document Classification
Nov 01, 2021



Abstract:The amount of information stored in the form of documents on the internet has been increasing rapidly. Thus it has become a necessity to organize and maintain these documents in an optimum manner. Text classification algorithms study the complex relationships between words in a text and try to interpret the semantics of the document. These algorithms have evolved significantly in the past few years. There has been a lot of progress from simple machine learning algorithms to transformer-based architectures. However, existing literature has analyzed different approaches on different data sets thus making it difficult to compare the performance of machine learning algorithms. In this work, we revisit long document classification using standard machine learning approaches. We benchmark approaches ranging from simple Naive Bayes to complex BERT on six standard text classification datasets. We present an exhaustive comparison of different algorithms on a range of long document datasets. We re-iterate that long document classification is a simpler task and even basic algorithms perform competitively with BERT-based approaches on most of the datasets. The BERT-based models perform consistently well on all the datasets and can be blindly used for the document classification task when the computations cost is not a concern. In the shallow model's category, we suggest the usage of raw BiLSTM + Max architecture which performs decently across all the datasets. Even simpler Glove + Attention bag of words model can be utilized for simpler use cases. The importance of using sophisticated models is clearly visible in the IMDB sentiment dataset which is a comparatively harder task.
ShufText: A Simple Black Box Approach to Evaluate the Fragility of Text Classification Models
Jan 30, 2021



Abstract:Text classification is the most basic natural language processing task. It has a wide range of applications ranging from sentiment analysis to topic classification. Recently, deep learning approaches based on CNN, LSTM, and Transformers have been the de facto approach for text classification. In this work, we highlight a common issue associated with these approaches. We show that these systems are over-reliant on the important words present in the text that are useful for classification. With limited training data and discriminative training strategy, these approaches tend to ignore the semantic meaning of the sentence and rather just focus on keywords or important n-grams. We propose a simple black box technique ShutText to present the shortcomings of the model and identify the over-reliance of the model on keywords. This involves randomly shuffling the words in a sentence and evaluating the classification accuracy. We see that on common text classification datasets there is very little effect of shuffling and with high probability these models predict the original class. We also evaluate the effect of language model pretraining on these models and try to answer questions around model robustness to out of domain sentences. We show that simple models based on CNN or LSTM as well as complex models like BERT are questionable in terms of their syntactic and semantic understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge