Gavin Suddrey
A Brief Wellbeing Training Session Delivered by a Humanoid Social Robot: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Aug 12, 2023
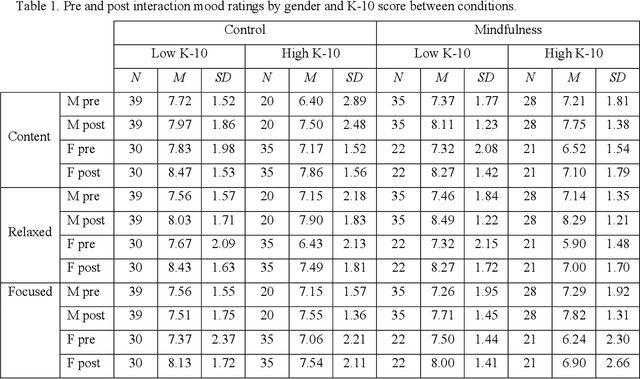
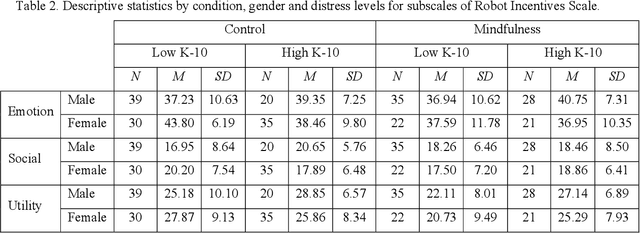
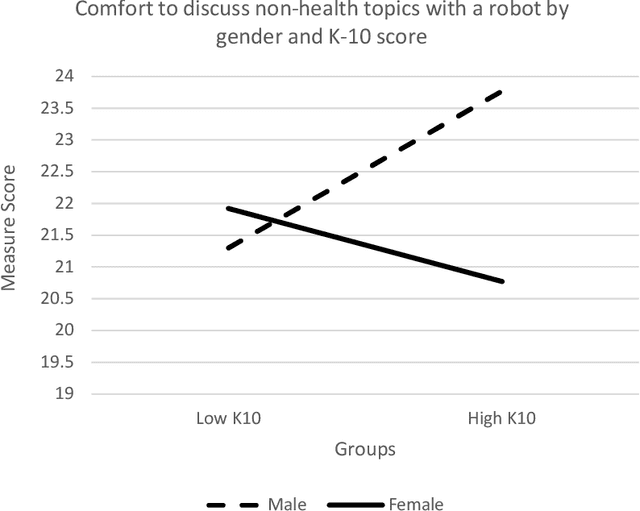
Abstract:Mental health and psychological distress are rising in adults, showing the importance of wellbeing promotion, support, and technique practice that is effective and accessible. Interactive social robots have been tested to deliver health programs but have not been explored to deliver wellbeing technique training in detail. A pilot randomised controlled trial was conducted to explore the feasibility of an autonomous humanoid social robot to deliver a brief mindful breathing technique to promote information around wellbeing. It contained two conditions: brief technique training (Technique) and control designed to represent a simple wait-list activity to represent a relationship-building discussion (Simple Rapport). This trial also explored willingness to discuss health-related topics with a robot. Recruitment uptake rate through convenience sampling was high (53%). A total of 230 participants took part (mean age = 29 years) with 71% being higher education students. There were moderate ratings of technique enjoyment, perceived usefulness, and likelihood to repeat the technique again. Interaction effects were found across measures with scores varying across gender and distress levels. Males with high distress and females with low distress who received the simple rapport activity reported greater comfort to discuss non-health topics than males with low distress and females with high distress. This trial marks a notable step towards the design and deployment of an autonomous wellbeing intervention to investigate the impact of a brief robot-delivered mindfulness training program for a sub-clinical population.
Learning and Executing Re-usable Behaviour Trees from Natural Language Instruction
Jun 03, 2021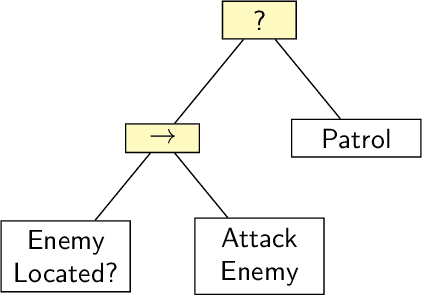
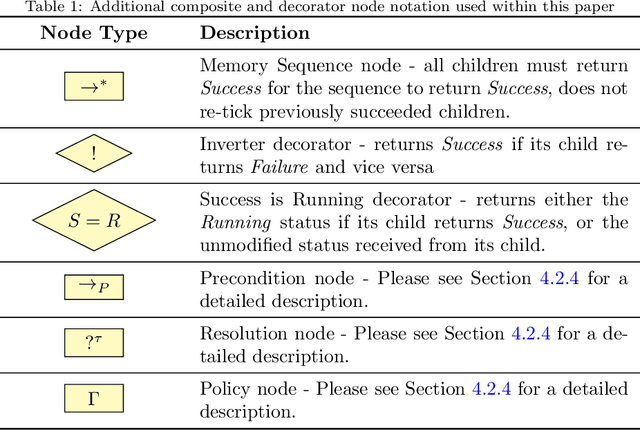

Abstract:Domestic and service robots have the potential to transform industries such as health care and small-scale manufacturing, as well as the homes in which we live. However, due to the overwhelming variety of tasks these robots will be expected to complete, providing generic out-of-the-box solutions that meet the needs of every possible user is clearly intractable. To address this problem, robots must therefore not only be capable of learning how to complete novel tasks at run-time, but the solutions to these tasks must also be informed by the needs of the user. In this paper we demonstrate how behaviour trees, a well established control architecture in the fields of gaming and robotics, can be used in conjunction with natural language instruction to provide a robust and modular control architecture for instructing autonomous agents to learn and perform novel complex tasks. We also show how behaviour trees generated using our approach can be generalised to novel scenarios, and can be re-used in future learning episodes to create increasingly complex behaviours. We validate this work against an existing corpus of natural language instructions, demonstrate the application of our approach on both a simulated robot solving a toy problem, as well as two distinct real-world robot platforms which, respectively, complete a block sorting scenario, and a patrol scenario.
Tabletop Object Rearrangement: Team ACRV's Entry to OCRTOC
Apr 15, 2021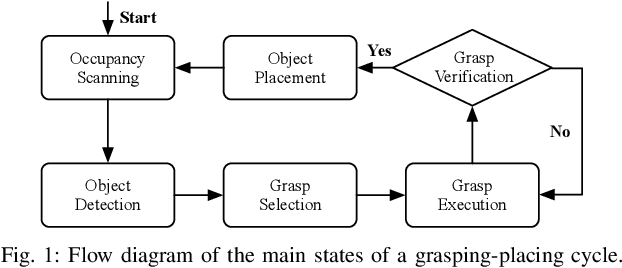
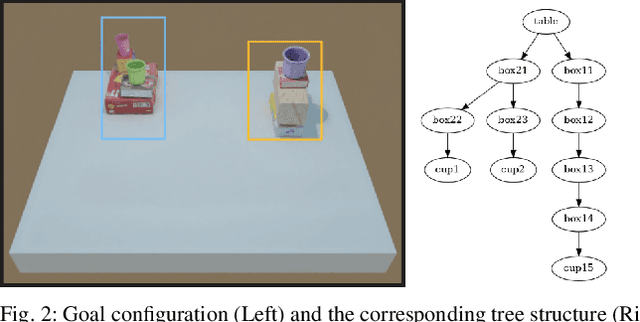
Abstract:Open Cloud Robot Table Organization Challenge (OCRTOC) is one of the most comprehensive cloud-based robotic manipulation competitions. It focuses on rearranging tabletop objects using vision as its primary sensing modality. In this extended abstract, we present our entry to the OCRTOC2020 and the key challenges the team has experienced.
Enabling a Pepper Robot to provide Automated and Interactive Tours of a Robotics Laboratory
Apr 10, 2018
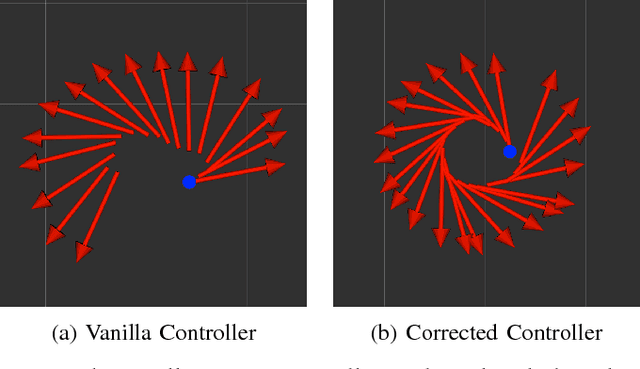
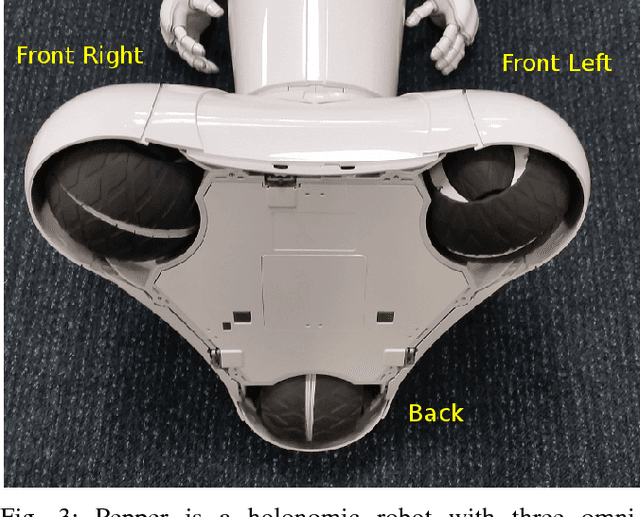

Abstract:The Pepper robot has become a widely recognised face for the perceived potential of social robots to enter our homes and businesses. However, to date, commercial and research applications of the Pepper have been largely restricted to roles in which the robot is able to remain stationary. This restriction is the result of a number of technical limitations, including limited sensing capabilities, and have as a result, reduced the number of roles in which use of the robot can be explored. In this paper, we present our approach to solving these problems, with the intention of opening up new research applications for the robot. To demonstrate the applicability of our approach, we have framed this work within the context of providing interactive tours of an open-plan robotics laboratory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge