Jun Kwan
Tabletop Object Rearrangement: Team ACRV's Entry to OCRTOC
Apr 15, 2021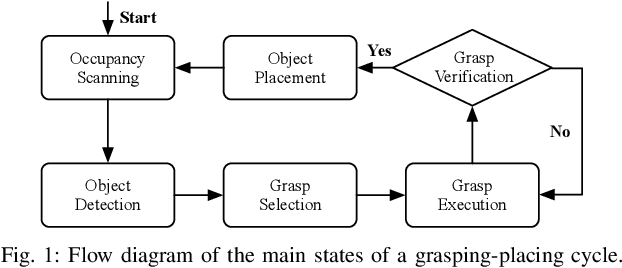
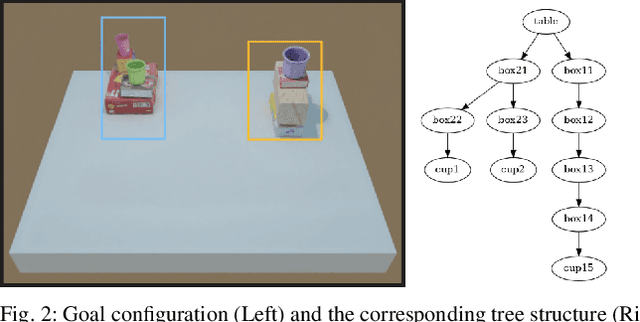
Abstract:Open Cloud Robot Table Organization Challenge (OCRTOC) is one of the most comprehensive cloud-based robotic manipulation competitions. It focuses on rearranging tabletop objects using vision as its primary sensing modality. In this extended abstract, we present our entry to the OCRTOC2020 and the key challenges the team has experienced.
Gesture Recognition for Initiating Human-to-Robot Handovers
Jul 20, 2020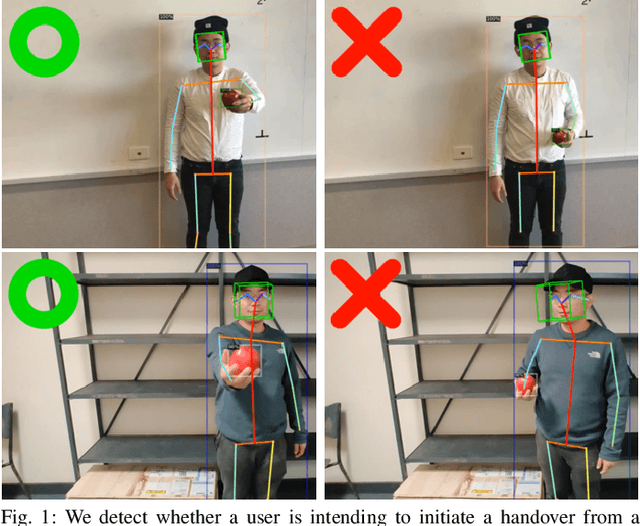
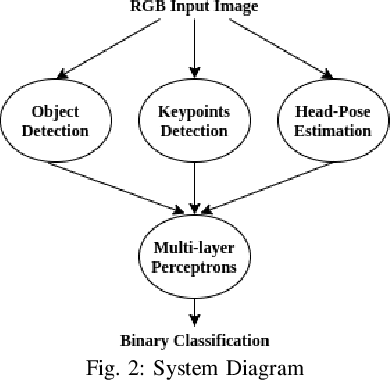
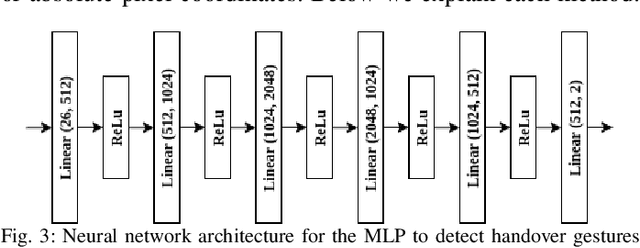

Abstract:Human-to-Robot handovers are useful for many Human-Robot Interaction scenarios. It is important to recognize when a human intends to initiate handovers, so that the robot does not try to take objects from humans when a handover is not intended. We pose the handover gesture recognition as a binary classification problem in a single RGB image. Three separate neural network modules for detecting the object, human body key points and head orientation, are implemented to extract relevant features from the RGB images, and then the feature vectors are passed into a deep neural net to perform binary classification. Our results show that the handover gestures are correctly identified with an accuracy of over 90%. The abstraction of the features makes our approach modular and generalizable to different objects and human body types.
Object-Independent Human-to-Robot Handovers using Real Time Robotic Vision
Jun 02, 2020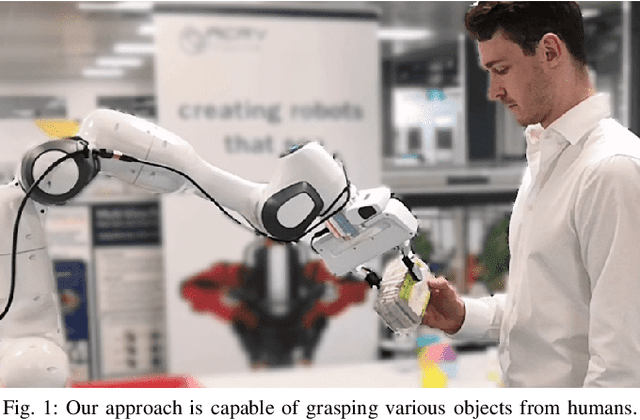
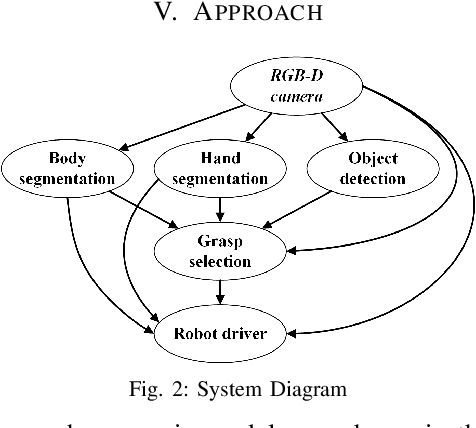
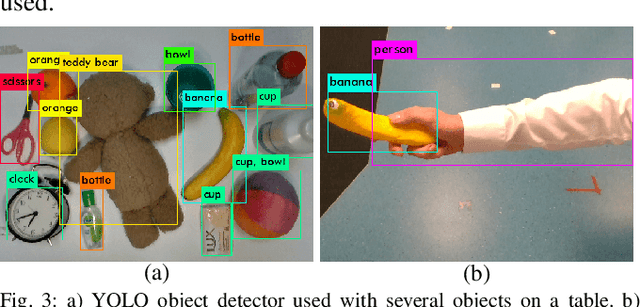

Abstract:We present an approach for safe and object-independent human-to-robot handovers using real time robotic vision and manipulation. We aim for general applicability with a generic object detector, a fast grasp selection algorithm and by using a single gripper-mounted RGB-D camera, hence not relying on external sensors. The robot is controlled via visual servoing towards the object of interest. Putting a high emphasis on safety, we use two perception modules: human body part segmentation and hand/finger segmentation. Pixels that are deemed to belong to the human are filtered out from candidate grasp poses, hence ensuring that the robot safely picks the object without colliding with the human partner. The grasp selection and perception modules run concurrently in real-time, which allows monitoring of the progress. In experiments with 13 objects, the robot was able to successfully take the object from the human in 81.9% of the trials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge