Gabriella Lapesa
From Emotion to Expression: Theoretical Foundations and Resources for Fear Speech
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Few forces rival fear in their ability to mobilize societies, distort communication, and reshape collective behavior. In computational linguistics, fear is primarily studied as an emotion, but not as a distinct form of speech. Fear speech content is widespread and growing, and often outperforms hate-speech content in reach and engagement because it appears "civiler" and evades moderation. Yet the computational study of fear speech remains fragmented and under-resourced. This can be understood by recognizing that fear speech is a phenomenon shaped by contributions from multiple disciplines. In this paper, we bridge cross-disciplinary perspectives by comparing theories of fear from Psychology, Political science, Communication science, and Linguistics. Building on this, we review existing definitions. We follow up with a survey of datasets from related research areas and propose a taxonomy that consolidates different dimensions of fear for studying fear speech. By reviewing current datasets and defining core concepts, our work offers both theoretical and practical guidance for creating datasets and advancing fear speech research.
Investigating Subjective Factors of Argument Strength: Storytelling, Emotions, and Hedging
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:In assessing argument strength, the notions of what makes a good argument are manifold. With the broader trend towards treating subjectivity as an asset and not a problem in NLP, new dimensions of argument quality are studied. Although studies on individual subjective features like personal stories exist, there is a lack of large-scale analyses of the relation between these features and argument strength. To address this gap, we conduct regression analysis to quantify the impact of subjective factors $-$ emotions, storytelling, and hedging $-$ on two standard datasets annotated for objective argument quality and subjective persuasion. As such, our contribution is twofold: at the level of contributed resources, as there are no datasets annotated with all studied dimensions, this work compares and evaluates automated annotation methods for each subjective feature. At the level of novel insights, our regression analysis uncovers different patterns of impact of subjective features on the two facets of argument strength encoded in the datasets. Our results show that storytelling and hedging have contrasting effects on objective and subjective argument quality, while the influence of emotions depends on their rhetoric utilization rather than the domain.
Tell Me What You Know About Sexism: Expert-LLM Interaction Strategies and Co-Created Definitions for Zero-Shot Sexism Detection
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates hybrid intelligence and collaboration between researchers of sexism and Large Language Models (LLMs), with a four-component pipeline. First, nine sexism researchers answer questions about their knowledge of sexism and of LLMs. They then participate in two interactive experiments involving an LLM (GPT3.5). The first experiment has experts assessing the model's knowledge about sexism and suitability for use in research. The second experiment tasks them with creating three different definitions of sexism: an expert-written definition, an LLM-written one, and a co-created definition. Lastly, zero-shot classification experiments use the three definitions from each expert in a prompt template for sexism detection, evaluating GPT4o on 2.500 texts sampled from five sexism benchmarks. We then analyze the resulting 67.500 classification decisions. The LLM interactions lead to longer and more complex definitions of sexism. Expert-written definitions on average perform poorly compared to LLM-generated definitions. However, some experts do improve classification performance with their co-created definitions of sexism, also experts who are inexperienced in using LLMs.
Towards a Perspectivist Turn in Argument Quality Assessment
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:The assessment of argument quality depends on well-established logical, rhetorical, and dialectical properties that are unavoidably subjective: multiple valid assessments may exist, there is no unequivocal ground truth. This aligns with recent paths in machine learning, which embrace the co-existence of different perspectives. However, this potential remains largely unexplored in NLP research on argument quality. One crucial reason seems to be the yet unexplored availability of suitable datasets. We fill this gap by conducting a systematic review of argument quality datasets. We assign them to a multi-layered categorization targeting two aspects: (a) What has been annotated: we collect the quality dimensions covered in datasets and consolidate them in an overarching taxonomy, increasing dataset comparability and interoperability. (b) Who annotated: we survey what information is given about annotators, enabling perspectivist research and grounding our recommendations for future actions. To this end, we discuss datasets suitable for developing perspectivist models (i.e., those containing individual, non-aggregated annotations), and we showcase the importance of a controlled selection of annotators in a pilot study.
Toeing the Party Line: Election Manifestos as a Key to Understand Political Discourse on Twitter
Oct 21, 2024
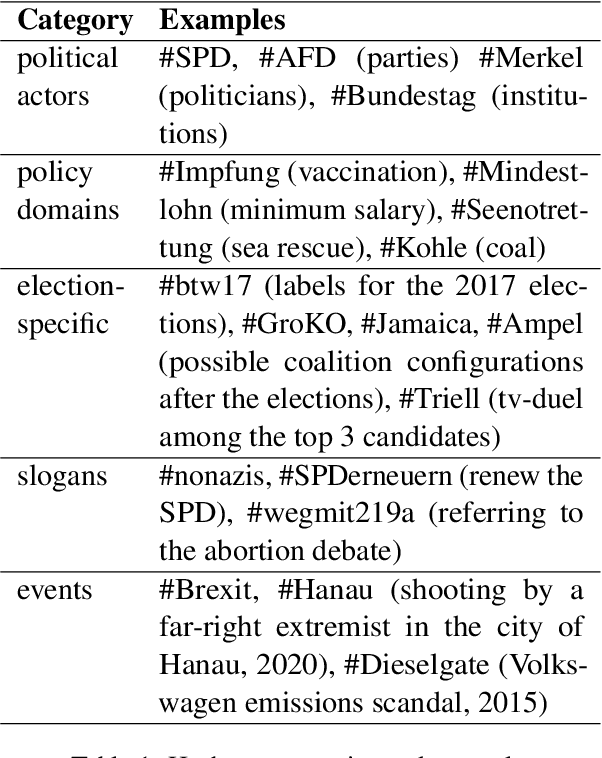
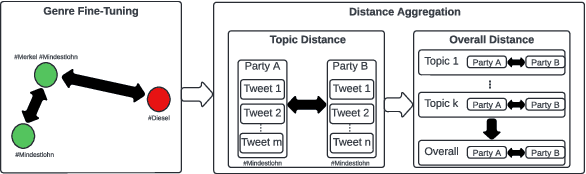
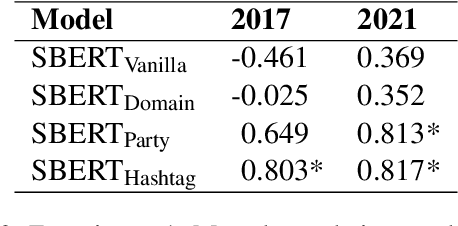
Abstract:Political discourse on Twitter is a moving target: politicians continuously make statements about their positions. It is therefore crucial to track their discourse on social media to understand their ideological positions and goals. However, Twitter data is also challenging to work with since it is ambiguous and often dependent on social context, and consequently, recent work on political positioning has tended to focus strongly on manifestos (parties' electoral programs) rather than social media. In this paper, we extend recently proposed methods to predict pairwise positional similarities between parties from the manifesto case to the Twitter case, using hashtags as a signal to fine-tune text representations, without the need for manual annotation. We verify the efficacy of fine-tuning and conduct a series of experiments that assess the robustness of our method for low-resource scenarios. We find that our method yields stable positioning reflective of manifesto positioning, both in scenarios with all tweets of candidates across years available and when only smaller subsets from shorter time periods are available. This indicates that it is possible to reliably analyze the relative positioning of actors forgoing manual annotation, even in the noisier context of social media.
Argument Quality Assessment in the Age of Instruction-Following Large Language Models
Mar 24, 2024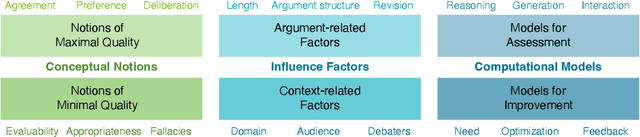
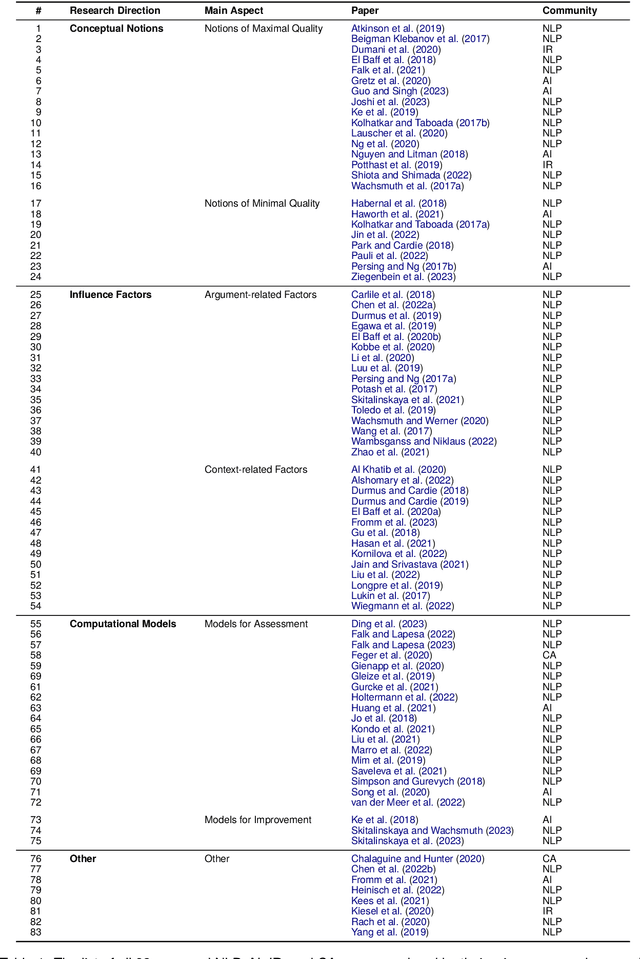
Abstract:The computational treatment of arguments on controversial issues has been subject to extensive NLP research, due to its envisioned impact on opinion formation, decision making, writing education, and the like. A critical task in any such application is the assessment of an argument's quality - but it is also particularly challenging. In this position paper, we start from a brief survey of argument quality research, where we identify the diversity of quality notions and the subjectiveness of their perception as the main hurdles towards substantial progress on argument quality assessment. We argue that the capabilities of instruction-following large language models (LLMs) to leverage knowledge across contexts enable a much more reliable assessment. Rather than just fine-tuning LLMs towards leaderboard chasing on assessment tasks, they need to be instructed systematically with argumentation theories and scenarios as well as with ways to solve argument-related problems. We discuss the real-world opportunities and ethical issues emerging thereby.
Political claim identification and categorization in a multilingual setting: First experiments
Oct 13, 2023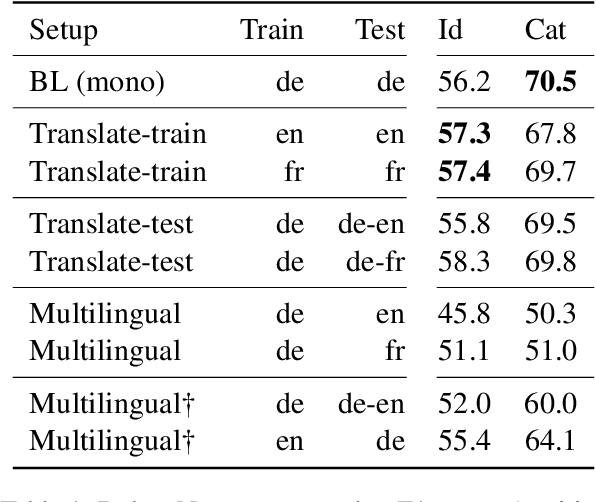



Abstract:The identification and classification of political claims is an important step in the analysis of political newspaper reports; however, resources for this task are few and far between. This paper explores different strategies for the cross-lingual projection of political claims analysis. We conduct experiments on a German dataset, DebateNet2.0, covering the policy debate sparked by the 2015 refugee crisis. Our evaluation involves two tasks (claim identification and categorization), three languages (German, English, and French) and two methods (machine translation -- the best method in our experiments -- and multilingual embeddings).
Between welcome culture and border fence. A dataset on the European refugee crisis in German newspaper reports
Nov 19, 2021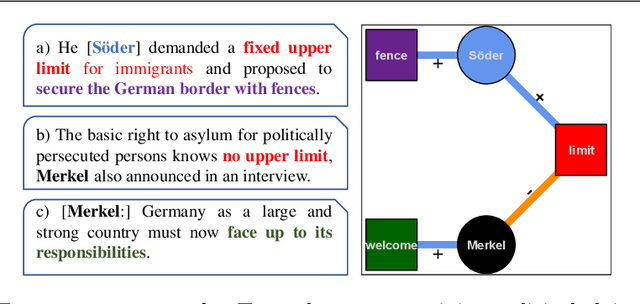
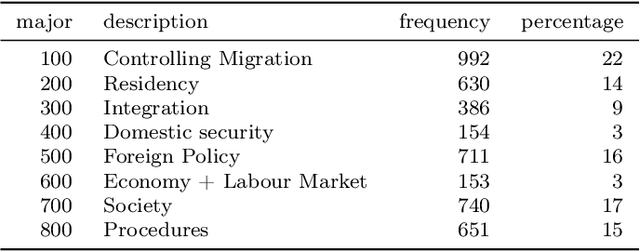
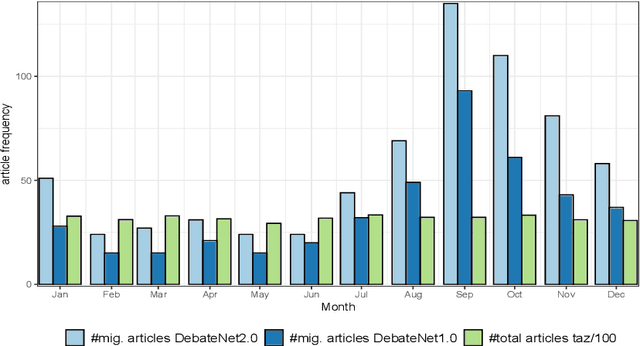
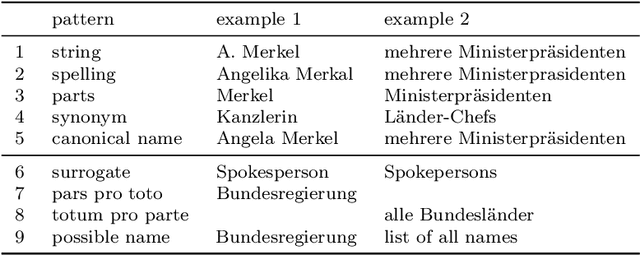
Abstract:Newspaper reports provide a rich source of information on the unfolding of public debate on specific policy fields that can serve as basis for inquiry in political science. Such debates are often triggered by critical events, which attract public attention and incite the reactions of political actors: crisis sparks the debate. However, due to the challenges of reliable annotation and modeling, few large-scale datasets with high-quality annotation are available. This paper introduces DebateNet2.0, which traces the political discourse on the European refugee crisis in the German quality newspaper taz during the year 2015. The core units of our annotation are political claims (requests for specific actions to be taken within the policy field) and the actors who make them (politicians, parties, etc.). The contribution of this paper is twofold. First, we document and release DebateNet2.0 along with its companion R package, mardyR, guiding the reader through the practical and conceptual issues related to the annotation of policy debates in newspapers. Second, we outline and apply a Discourse Network Analysis (DNA) to DebateNet2.0, comparing two crucial moments of the policy debate on the 'refugee crisis': the migration flux through the Mediterranean in April/May and the one along the Balkan route in September/October. Besides the released resources and the case-study, our contribution is also methodological: we talk the reader through the steps from a newspaper article to a discourse network, demonstrating that there is not just one discourse network for the German migration debate, but multiple ones, depending on the topic of interest (political actors, policy fields, time spans).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge