Tanise Ceron
What Is The Political Content in LLMs' Pre- and Post-Training Data?
Sep 26, 2025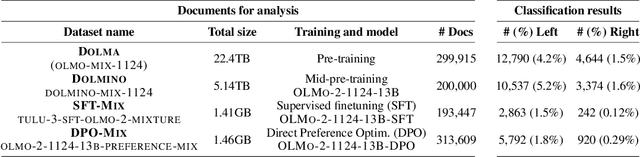
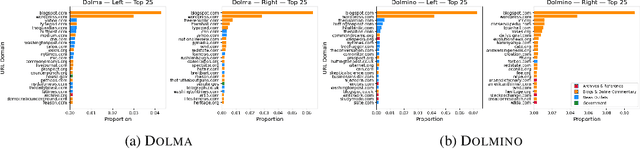
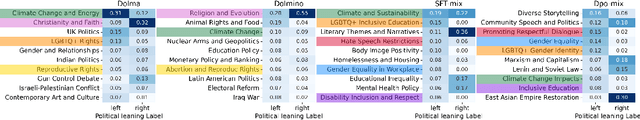
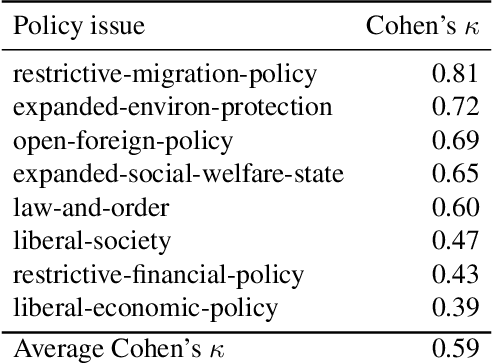
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are known to generate politically biased text, yet how such biases arise remains unclear. A crucial step toward answering this question is the analysis of training data, whose political content remains largely underexplored in current LLM research. To address this gap, we present in this paper an analysis of the pre- and post-training corpora of OLMO2, the largest fully open-source model released together with its complete dataset. From these corpora, we draw large random samples, automatically annotate documents for political orientation, and analyze their source domains and content. We then assess how political content in the training data correlates with models' stance on specific policy issues. Our analysis shows that left-leaning documents predominate across datasets, with pre-training corpora containing significantly more politically engaged content than post-training data. We also find that left- and right-leaning documents frame similar topics through distinct values and sources of legitimacy. Finally, the predominant stance in the training data strongly correlates with models' political biases when evaluated on policy issues. These findings underscore the need to integrate political content analysis into future data curation pipelines as well as in-depth documentation of filtering strategies for transparency.
Do Political Opinions Transfer Between Western Languages? An Analysis of Unaligned and Aligned Multilingual LLMs
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Public opinion surveys show cross-cultural differences in political opinions between socio-cultural contexts. However, there is no clear evidence whether these differences translate to cross-lingual differences in multilingual large language models (MLLMs). We analyze whether opinions transfer between languages or whether there are separate opinions for each language in MLLMs of various sizes across five Western languages. We evaluate MLLMs' opinions by prompting them to report their (dis)agreement with political statements from voting advice applications. To better understand the interaction between languages in the models, we evaluate them both before and after aligning them with more left or right views using direct preference optimization and English alignment data only. Our findings reveal that unaligned models show only very few significant cross-lingual differences in the political opinions they reflect. The political alignment shifts opinions almost uniformly across all five languages. We conclude that in Western language contexts, political opinions transfer between languages, demonstrating the challenges in achieving explicit socio-linguistic, cultural, and political alignment of MLLMs.
Toeing the Party Line: Election Manifestos as a Key to Understand Political Discourse on Twitter
Oct 21, 2024
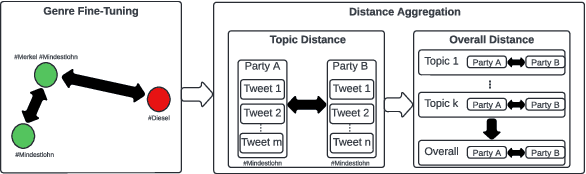
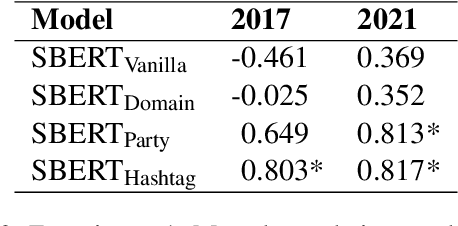
Abstract:Political discourse on Twitter is a moving target: politicians continuously make statements about their positions. It is therefore crucial to track their discourse on social media to understand their ideological positions and goals. However, Twitter data is also challenging to work with since it is ambiguous and often dependent on social context, and consequently, recent work on political positioning has tended to focus strongly on manifestos (parties' electoral programs) rather than social media. In this paper, we extend recently proposed methods to predict pairwise positional similarities between parties from the manifesto case to the Twitter case, using hashtags as a signal to fine-tune text representations, without the need for manual annotation. We verify the efficacy of fine-tuning and conduct a series of experiments that assess the robustness of our method for low-resource scenarios. We find that our method yields stable positioning reflective of manifesto positioning, both in scenarios with all tweets of candidates across years available and when only smaller subsets from shorter time periods are available. This indicates that it is possible to reliably analyze the relative positioning of actors forgoing manual annotation, even in the noisier context of social media.
Beyond prompt brittleness: Evaluating the reliability and consistency of political worldviews in LLMs
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Due to the widespread use of large language models (LLMs) in ubiquitous systems, we need to understand whether they embed a specific worldview and what these views reflect. Recent studies report that, prompted with political questionnaires, LLMs show left-liberal leanings. However, it is as yet unclear whether these leanings are reliable (robust to prompt variations) and whether the leaning is consistent across policies and political leaning. We propose a series of tests which assess the reliability and consistency of LLMs' stances on political statements based on a dataset of voting-advice questionnaires collected from seven EU countries and annotated for policy domains. We study LLMs ranging in size from 7B to 70B parameters and find that their reliability increases with parameter count. Larger models show overall stronger alignment with left-leaning parties but differ among policy programs: They evince a (left-wing) positive stance towards environment protection, social welfare but also (right-wing) law and order, with no consistent preferences in foreign policy, migration, and economy.
Multilingual estimation of political-party positioning: From label aggregation to long-input Transformers
Oct 19, 2023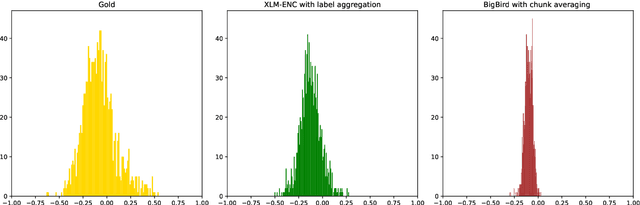
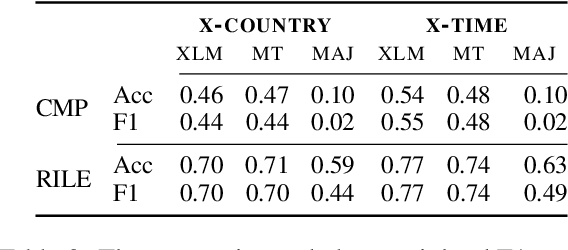
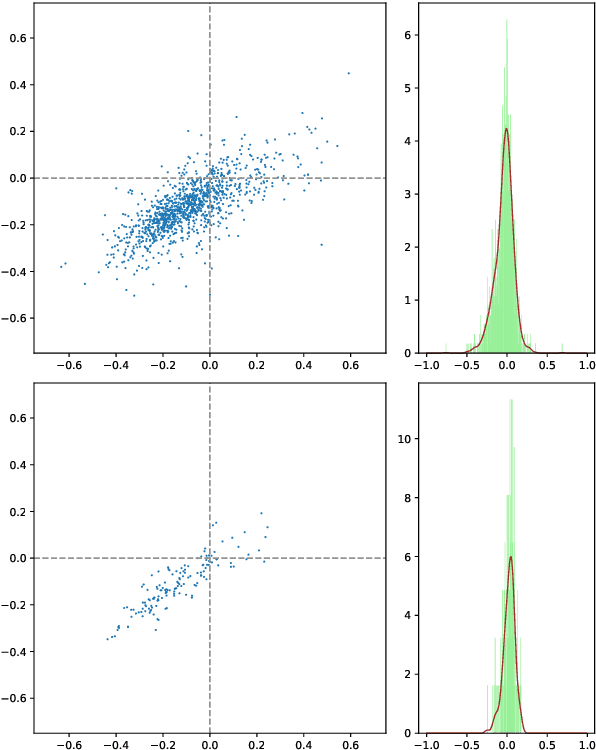
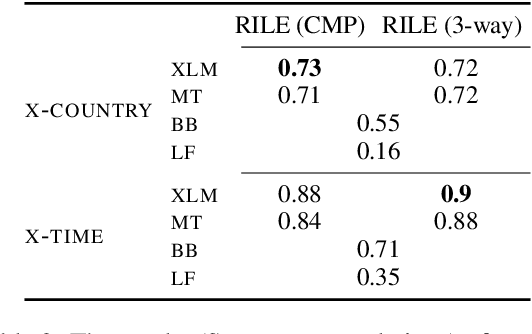
Abstract:Scaling analysis is a technique in computational political science that assigns a political actor (e.g. politician or party) a score on a predefined scale based on a (typically long) body of text (e.g. a parliamentary speech or an election manifesto). For example, political scientists have often used the left--right scale to systematically analyse political landscapes of different countries. NLP methods for automatic scaling analysis can find broad application provided they (i) are able to deal with long texts and (ii) work robustly across domains and languages. In this work, we implement and compare two approaches to automatic scaling analysis of political-party manifestos: label aggregation, a pipeline strategy relying on annotations of individual statements from the manifestos, and long-input-Transformer-based models, which compute scaling values directly from raw text. We carry out the analysis of the Comparative Manifestos Project dataset across 41 countries and 27 languages and find that the task can be efficiently solved by state-of-the-art models, with label aggregation producing the best results.
Additive manifesto decomposition: A policy domain aware method for understanding party positioning
May 17, 2023Abstract:Automatic extraction of party (dis)similarities from texts such as party election manifestos or parliamentary speeches plays an increasing role in computational political science. However, existing approaches are fundamentally limited to targeting only global party (dis)-similarity: they condense the relationship between a pair of parties into a single figure, their similarity. In aggregating over all policy domains (e.g., health or foreign policy), they do not provide any qualitative insights into which domains parties agree or disagree on. This paper proposes a workflow for estimating policy domain aware party similarity that overcomes this limitation. The workflow covers (a) definition of suitable policy domains; (b) automatic labeling of domains, if no manual labels are available; (c) computation of domain-level similarities and aggregation at a global level; (d) extraction of interpretable party positions on major policy axes via multidimensional scaling. We evaluate our workflow on manifestos from the German federal elections. We find that our method (a) yields high correlation when predicting party similarity at a global level and (b) provides accurate party-specific positions, even with automatically labelled policy domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge